Abstract
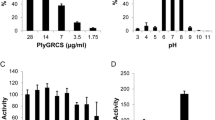
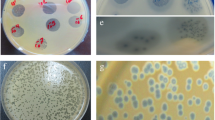
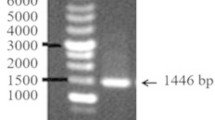
Antibacterial and biofilm removal activity of a new podoviridae Staphylococcus aureus bacteriophage (SAP-2), which belongs to the φ29-like phage genus of the Podoviridae family, and a cell-wall-degrading enzyme (SAL-2), which is derived from bacteriophage SAP-2, have been characterized. The cell-wall-degrading enzyme SAL-2 was expressed in Escherichia coli in a soluble form using a low-temperature culture. The cell-wall-degrading enzyme SAL-2 had specific lytic activity against S. aureus, including methicillin-resistant strains, and showed a minimum inhibitory concentration of about 1 μg/ml. In addition, this enzyme showed a broader spectrum of activity within the Staphylococcus genus compared with bacteriophage SAP-2 in its ability to remove the S. aureus biofilms. Thus, the cell-wall-degrading enzyme SAL-2 can be used to prevent and treat biofilm-associated S. aureus infections either on its own or in combination with other cell-wall-degrading enzymes with anti-S. aureus activity.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ackermann HW (1998) Tailed bacteriophage: the order Caudovirales. Adv Virus Res 51:135–201
Ando E, Monden K, Mitsuhata R, Kariyama R, Kumon H (2004) Biofilm formation among methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolates from patients with urinary tract infection. Acta Med Okayama 58:207–214
Andrews JM (2001) Determination of minimum inhibitory concentrations. J Antimicrob Chemother 48(Suppl 1):5–16
Arciola CR, Montanaro L, Baldassarri L, Borsetti E, Cavedagna D, Donati E (1999) Slime production by Staphylococci isolated from prosthesis-associated infections. New Microbiol 22:337–341
Azeredo J, Sutherland IW (2008) The use of phages for the removal of infectious biofilms. Curr Pharm Biotechnol 9:261–266
Baird-Parker AC (1962) An improved diagnostic and selective medium for isolating coagulase-positive staphylococci. J Appl Bacteriol 25:12–19
Barry AL, García F, Thrupp LD (1970) An improved single-disk method for testing the antibiotic susceptibility of rapidly-growing pathogens. Am J Clin Pathol 53:149–158
Celia LK, Nelson D, Kerr DE (2008) Characterization of a bacteriophage lysin (Ply700) from Streptococcus uberis. Vet Microbiol 130:107–117
Chokr A, Leterme D, Watier D, Jabbouri S (2007) Neither the presence of ica locus, nor in vitro-biofilm formation ability is a crucial parameter for some Staphylococcus epidermidis strains to maintain an infection in a guinea pig tissue cage model. Microb Pathog 42:94–97
Costerton JW, Stewart PS, Greenberg EP (1999) Bacterial biofilms: a common cause of persistent infections. Science 284:1318–1322
Cramton SE, Gerke C, Schnell NF, Nichols WW, Götz F (1999) The intercellular adhesion (ica) locus is present in Staphylococcus aureus and is required for biofilm formation. Infect Immun 67:5427–5433
Davison S, Couture-Tosi E, Candela T, Mock M, Fouet A (2005) Identification of the Bacillus anthracis γ phage receptor. J Bacteriol 187:6742–6749
Donlan RM (2009) Preventing biofilms of clinically relevant organisms using bacteriophage. Trends Microbiol 17:66–72
Götz F (2002) Staphylococcus and biofilms. Mol Microbiol 43:1367–1378
Hanlon GW (2007) Bacteriophages: an appraisal of their role in the treatment of bacterial infections. Int J Antimicrob Agents 30:118–128
Hermoso JA, García JL, García P (2007) Taking aim on bacterial pathogens: from phage therapy to enzybiotics. Curr Opin Microbiol 10:461–472
Johnson AP, Aucken HM, Cavendish S, Ganner M, Wale MC, Warner M, Livermore DM, Cookson BD, the UK EARSS participants (2001) Dominance of EMRSA-15 and -16 among MRSA causing nosocomial bacteraemia in the UK: analysis of isolates from the European Antimicrobial Resistance Surveillance System (EARSS). J Antimicrob Chemother 48:143–144
Le Loir Y, Baron F, Gautier M (2003) Staphylococcus aureus and food poisoning. Genet Mol Res 2:63–76
Loeffler JM, Nelson D, Fischetti VA (2001) Rapid killing of Streptococcus pneumoniae with a bacteriophage cell wall hydrolase. Science 294:2170–2172
Loessner MJ (2005) Bacteriophage endolysins-current state of research and applications. Curr Opin Microbiol 8:480–487
Lu G, Moriyama EN (2004) Vector NTI, a balanced all-in-one sequence analysis suite. Brief Bioinform 5:378–388
Mah TF, Pitts B, Pellock B, Walker GC, Stewart PS, O’Toole GA (2003) A genetic basis for Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm antibiotic resistance. Nature 426:306–310
Melchior MB, Vaarkamp H, Fink-Gremmels J (2006) Biofilms: a role in recurrent mastitis infections? Vet J 171:398–407
Nelson D, Schuch R, Zhu S, Tscherne DM, Fischetti VA (2003) Genomic sequence of C1, the first streptococcal phage. J Bacteriol 185:3325–3332
Novick RP (1963) Analysis by transduction of mutations affecting penicillinase formation in Staphylococcus aureus. J Gen Microbiol 33:121–136
Novick RP (1967) Properties of a cryptic high-frequency transducing phage in Staphylococcus aureus. Virology 33:155–166
O’Flaherty S, Coffey A, Meaney W, Fitzgerald GF, Ross RP (2005) The recombinant phage lysin LysK has a broad spectrum of lytic activity against clinically relevant staphylococci, including methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J Bacteriol 187:7161–7164
O’Gara JP, Humphreys H (2001) Staphylococcus epidermidis biofilms: importance and implications. J Med Microbiol 50:581–587
Sass P, Bierbaum G (2007) Lytic activity of recombinant bacteriophage φ11 and φ12 endolysins on whole cells and biofilms of Staphylococcus aureus. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:347–352
Seidl K, Goerke C, Wolz C, Mack D, Berger-Bächi B, Bischoff M (2008) Staphylococcus aureus CcpA affects biofilm formation. Infect Immun 76:2044–2050
Stewart PS (2002) Mechanisms of antibiotic resistance in bacterial biofilms. Int J Med Microbiol 292:107–113
Takác M, Witte A, Bläsi U (2005) Functional analysis of the lysis genes of Staphylococcus aureus phage P68 in Escherichia coli. Microbiology 151:2331–2342
Tanji Y, Shimada T, Fukudomi H, Miyanaga K, Nakai Y, Unno H (2005) Therapeutic use of phage cocktail for controlling Escherichia coli O157:H7 in gastrointestinal tract of mice. J Biosci Bioeng 100:280–287
Vybiral D, Takáč M, Loessner M, Witte A, von Ahsen U, Bläsi U (2003) Complete nucleotide sequence and molecular characterization of two lytic Staphylococcus aureus phages: 44AHJD and P68. FEMS Microbiol Lett 219:275–283
Wu JA, Kusuma C, Mond JJ, Kokai-Kun JF (2003) Lysostaphin disrupts Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis biofilms on artificial surfaces. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 47:3407–3414
Yoong P, Schuch R, Nelson D, Fischetti VA (2004) Identification of a broadly active phage lytic enzyme with lethal activity against antibiotic-resistant Enterococcus faecalis and Enterococcus faecium. J Bacteriol 186:4808–4812
Acknowledgments
This work was partially supported by a graduate fellowship from the Brain Korea 21 project of the Korean Ministry of Education, Science, and Technology and the Research Institute for Agriculture and Life Sciences, Seoul National University. Electron microscopy was carried out by the National Instrumental Center for Environmental Management (NICEM), Seoul National University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Jee-Soo Son and Se-Jung Lee contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Son, JS., Lee, SJ., Jun, S.Y. et al. Antibacterial and biofilm removal activity of a podoviridae Staphylococcus aureus bacteriophage SAP-2 and a derived recombinant cell-wall-degrading enzyme. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 86, 1439–1449 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-009-2386-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-009-2386-9