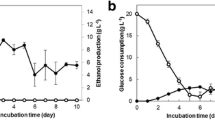
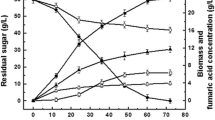
Abstract
Xylose is the second most abundant lignocellulosic component besides glucose, but it cannot be fermented by the widely used ethanol-producing yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. The yeast Scheffersomyces stipitis, however, is well known for its high native capacity to ferment xylose. Here, we applied next-generation sequencing technology for RNA (RNA-Seq) to generate two high-resolution transcriptional maps of the S. stipitis genome when this yeast was grown using glucose or xylose as the sole carbon source. RNA-Seq revealed that 5,176 of 5,816 annotated open reading frames had a uniform transcription and that 214 open reading frames were differentially transcribed. Differential expression analysis showed that, compared with other biological processes, carbohydrate metabolism and oxidation-reduction reactions were highly enhanced in yeast grown on xylose. Measurement of metabolic indicators of fermentation showed that, in yeast grown on xylose, the concentrations of cysteine and ornithine were twofold higher and the concentrations of unsaturated fatty acids were also increased. Analysis of metabolic profiles coincided with analysis of certain differentially expressed genes involved in metabolisms of amino acid and fatty acid. In addition, we predicted protein–protein interactions of S. stipitis through integration of gene orthology and gene expression. Further analysis of metabolic and protein–protein interactions networks through integration of transcriptional and metabolic profiles predicted correlations of genes involved in glycolysis, the tricarboxylic acid cycle, gluconeogenesis, sugar uptake, amino acid metabolism, and fatty acid β-oxidation. Our study reveals potential target genes for xylose fermentation improvement and provides insights into the mechanisms underlying xylose fermentation in S. stipitis.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agbogbo FK, Coward-Kelly G (2008) Cellulosic ethanol production using the naturally occurring xylose-fermenting yeast, Pichia stipitis. Biotechnol Lett 30:1515–1524
Alper H, Stephanopoulos G (2009) Engineering for biofuels: exploiting innate microbial capacity or importing biosynthetic potential? Nat Rev Microbiol 7:715–723
Anders S, Huber W (2010) Differential expression analysis for sequence count data. Genome Biol 11:R106
Cho JY, Jeffries TW (1998) Pichia stipitis genes for ethanol dehydrogenase with fermentative and respiratory functions. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:1350–1358
Fiaux J, Cakar ZP, Sonderegger M, Wüthrich K, Szyperski T, Sauer U (2003) Metabolic-flux profiling of the yeasts Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Pichia stipitis. Eukaryot Cell 2:170–180
Freese S, Passoth V, Klinner U (2011) A mutation in the COX5 gene of the yeast Scheffersomyces stipitis alters utilization of amino acids as carbon source, ethanol formation and activity of cyanide insensitive respiration. Yeast 28:309–320
Gancedo JM (1998) Yeast carbon catabolite repression. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 62:334–361
Han JDJ, Bertin N, Hao T, Goldberg DS, Berriz GF, Zhang LV, Dupuy D, Walhout AJM, Cusick ME, Roth FP, Vidal M (2004) Evidence for dynamically organized modularity in the yeast protein–protein interaction network. Nature 430:88–93
Hartwell LH, Hopfield JJ, Leibler S, Murray AW (1999) From molecular to modular cell biology. Nature 402:C47–C52
Jeffries TW, Jin YS (2004) Metabolic engineering for improved fermentation of pentoses by yeasts. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 63:495–509
Jeffries TW, Van Vleet JRH (2009) Pichia stipitis genomics, transcriptomics, and gene clusters. FEMS Yeast Res 9:793–807
Jeffries TW, Grigoriev IV, Grimwood J, Laplaza JM, Aerts A, Salamov A, Schmutz J, Lindquist E, Dehal P, Shapiro H, Jin YS, Passoth V, Richardson PM (2007) Genome sequence of the lignocellulose-bioconverting and xylose-fermenting yeast Pichia stipitis. Nat Biotechnol 25:319–326
Jeong H, Mason SP, Barabási AL, Oltvai ZN (2001) Lethality and centrality in protein networks. Nature 411:41–42
Jin YS, Laplaza JM, Jeffries TW (2004) Saccharomyces cerevisiae engineered for xylose metabolism exhibits a respiratory response. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:6816–6825
Jin YS, Alper H, Yang YT, Stephanopoulos G (2005) Improvement of xylose uptake and ethanol production in recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae through an inverse metabolic engineering approach. Appl Environ Microbiol 71:8249–8256
Jojima T, Omumasaba CA, Inui M, Yukawa H (2010) Sugar transporters in efficient utilization of mixed sugar substrates: current knowledge and outlook. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 85:471–480
Kosman DJ (2003) Molecular mechanisms of iron uptake in fungi. Mol Microbiol 47:1185–1197
Kurtzman CP, Suzuki M (2010) Phylogenetic analysis of ascomycete yeasts that form coenzyme Q-9 and the proposal of the new genera Babjeviella, Meyerozyma, Millerozyma, Priceomyces, and Scheffersomyces. Mycoscience 51:2–14
La Grange DC, Den Haan R, Van Zyl WH (2010) Engineering cellulolytic ability into bioprocessing organisms. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 87:1195–1208
Li H, Durbin R (2009) Fast and accurate short read alignment with Burrows–Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics 25:1754–1760
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-ΔΔCt method. Methods 25:402–408
Ma M, Liu ZL (2010) Mechanisms of ethanol tolerance in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 87:829–845
Margeot A, Hahn-Hägerdal B, Edlund M, Slade R, Monot F (2009) New improvements for lignocellulosic ethanol. Curr Opin Biotechnol 20:372–380
Marguerat S, Bähler J (2010) RNA-seq: from technology to biology. Cell Mol Life Sci 67:569–579
Matsushika A, Inoue H, Kodaki T, Sawayama S (2009) Ethanol production from xylose in engineered Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains: current state and perspectives. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 84:37–53
Moriya H, Johnston M (2004) Glucose sensing and signaling in Saccharomyces cerevisiae through the Rgt2 glucose sensor and casein kinase I. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:1572–1577
Mortazavi A, Williams BA, McCue K, Schaeffer L, Wold B (2008) Mapping and quantifying mammalian transcriptomes by RNA-Seq. Nat Method 5:621–628
Mussatto SI, Dragone G, Guimarães PMR, Silva JPA, Carneiro LM, Roberto IC, Vicente A, Domingues L, Teixeira JA (2010) Technological trends, global market, and challenges of bio-ethanol production. Biotechnol Adv 28:817–830
Nagalakshmi U, Wang Z, Waern K, Shou C, Raha D, Gerstein M, Snyder M (2008) The transcriptional landscape of the yeast genome defined by RNA sequencing. Science 320:1344–1349
Özcan S, Johnston M (1999) Function and regulation of yeast hexose transporters. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 63:554–569
Ozsolak F, Milos PM (2011) RNA sequencing: advances, challenges and opportunities. Nat Rev Genet 12:87–98
Passoth V, Schäfer B, Liebel B, Weierstall T, Klinner U (1998) Molecular cloning of ethanol dehydrogenase genes of the yeast Pichia stipitis and identification of the fermentative ADH. Yeast 14:1311–1325
Platta HW, Erdmann R (2007) Peroxisomal dynamics. Trends Cell Biol 17:474–484
Rhodes DR, Tomlins SA, Varambally S, Mahavisno V, Barrette T, Kalyana-Sundaram S, Ghosh D, Pandey A, Chinnaiyan AM (2005) Probabilistic model of the human protein–protein interaction network. Nat Biotechnol 23:951–959
Rodicio R, Heinisch JJ (2010) Together we are strong—cell wall integrity sensors in yeasts. Yeast 27:531–540
Rolland F, Winderickx J, Thevelein JM (2002) Glucose-sensing and -signalling mechanisms in yeast. FEMS Yeast Res 2:183–201
Rutherford K, Parkhill J, Crook J, Horsnell T, Rice P, Rajandream MA, Barrell B (2000) Artemis: sequence visualization and annotation. Bioinformatics 16:944–945
Salusjärvi L, Kankainen M, Soliymani R, Pitkänen JP, Penttilä M, Ruohonen L (2008) Regulation of xylose metabolism in recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Microb Cell Fact 7:18
Salwinski L, Miller CS, Smith AJ, Pettit FK, Bowie JU, Eisenberg D (2004) The database of interacting proteins: 2004 update. Nucleic Acids Res 32:D449–D451
Schüller HJ (2003) Transcriptional control of nonfermentative metabolism in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Curr Genet 43:139–160
Stephanopoulos G (2007) Challenges in engineering microbes for biofuels production. Science 315:801–804
Toivari MH, Aristidou A, Ruohonen L, Penttilä M (2001) Conversion of xylose to ethanol by recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae: importance of xylulokinase (XKS1) and oxygen availability. Metab Eng 3:236–249
Trapnell C, Pachter L, Salzberg SL (2009) TopHat: discovering splice junctions with RNA-Seq. Bioinformatics 25:1105–1111
Van Vleet JH, Jeffries TW (2009) Yeast metabolic engineering for hemicellulosic ethanol production. Curr Opin Biotechnol 20:300–306
Van Vleet JH, Jeffries TW, Olsson L (2008) Deleting the para-nitrophenyl phosphatase (pNPPase), PHO13, in recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae improves growth and ethanol production on d-xylose. Metab Eng 10:360–369
Vandesompele J, De Preter K, Pattyn F, Poppe B, Van Roy N, De Paepe A, Speleman F (2002) Accurate normalization of real-time quantitative RT-PCR data by geometric averaging of multiple internal control genes. Genome Biol 3:research0034.1–0034.11
Visser WF, Van Roermund CWT, Ijlst L, Waterham HR, Wanders RJA (2007) Metabolite transport across the peroxisomal membrane. Biochem J 401:365–375
Weber C, Farwick A, Benisch F, Brat D, Dietz H, Subtil T, Boles E (2010) Trends and challenges in the microbial production of lignocellulosic bioethanol fuels. Appl Microb Biotechnol 87:1303–1315
Westholm JO, Nordberg N, Murén E, Ameur A, Komorowski J, Ronne H (2008) Combinatorial control of gene expression by the three yeast repressors Mig1, Mig2 and Mig3. BMC Genomic 9:601
Wilhelm BT, Landry JR (2009) RNA-Seq—quantitative measurement of expression through massively parallel RNA-sequencing. Methods 48:249–257
Wilhelm BT, Marguerat S, Goodhead I, Bähler J (2010) Defining transcribed regions using RNA-seq. Nat Protoc 5:255–266
Young MD, Wakefield MJ, Smyth GK, Oshlack A (2010) Gene ontology analysis for RNA-seq: accounting for selection bias. Genome Biol 11:R14
Yun C-W, Bauler M, Moore RE, Klebba PE, Philpott CC (2001) The role of the FRE family of plasma membrane reductases in the uptake of siderophore-iron in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem 276:10218–10223
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Ministry of Agriculture of China—the China Modern Agriculture Research System (CARS-42) and the Key Program of Transgenic Plant Breeding (2008ZX08003-002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary materials
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOC 1.54 mb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yuan, T., Ren, Y., Meng, K. et al. RNA-Seq of the xylose-fermenting yeast Scheffersomyces stipitis cultivated in glucose or xylose. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 92, 1237–1249 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-011-3607-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-011-3607-6