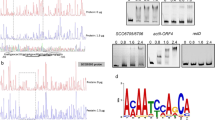
Abstract
GlnK is an important nitrogen sensor protein in Streptomyces coelicolor. Deletion of glnK results in a medium-dependent failure of aerial mycelium and spore formation and loss of antibiotic production. Thus, GlnK is not only a regulator of nitrogen metabolism but also of morphological differentiation and secondary metabolite production. Through a comparative transcriptomic approach between the S. coelicolor wild-type and a S. coelicolor glnK mutant strain, 142 genes were identified that are differentially regulated in both strains. Among these are genes of the ram and rag operon, which are involved in S. coelicolor morphogenesis, as well as genes involved in gas vesicle biosynthesis and ectoine biosynthesis. Surprisingly, no relevant nitrogen genes were found to be differentially regulated, revealing that GlnK is not an important nitrogen sensor under the tested conditions.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arcondéguy T, Jack R, Merrick M (2001) PII signal transduction proteins, pivotal players in microbial nitrogen control. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 65:80–105
Atkinson MR, Ninfa AJ (1998) Role of the GlnK signal transduction protein in the regulation of nitrogen assimilation in Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol 29:431–447
Battke F, Symons S, Nieselt K (2010) Mayday—integrative analytics for expression data. BMC Bioinforma 11:121
Battke F, Herbig A, Wentzel A, Jakobsen OM, Bonin M, Hodgson DA, Wohlleben W, Ellingsen TE, STREAM Consortium, Nieselt K (2011) A technical platform for generating reproducible expression data from Streptomyces coelicolor batch cultivations. Adv Exp Med Biol 696:3–15
Bierman M, Logan R, O’Brien K, Seno ET, Rao RN, Schoner BE (1992) Plasmid cloning vectors for the conjugal transfer of DNA from Escherichia coli to Streptomyces spp. Gene 116:43–49
Bolstad BM, Irizarry RA, Astrand M, Speed TP (2003) A comparison of normalization methods for high density oligonucleotide array data based on bias and variance. Bioinformatics 19:185–193
Boogerd FC, Ma H, Bruggeman FJ, van Heeswijk WC, García-Contreras R, Molenaar D, Krab K, Westerhoff HV (2011) AmtB-mediated NH3 transport in prokaryotes must be active and as a consequence regulation of transport by GlnK is mandatory to limit futile cycling of NH +4 /NH3. FEBS Lett 585:23–28
Bullock WO, Fernandez JM, Short JM (1987) Xl1-Blue, a high efficiency plasmid transforming recA Escherichia coli strain with beta galactosidase selection. Focus 5:376–378
Bursy J, Kuhlmann AU, Pittelkow M, Hartmann H, Jebbar M, Pierik AJ, Bremer E (2008) Synthesis and uptake of the compatible solutes ectoine and 5-hydroxyectoine by Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2) in response to salt and heat stresses. Appl Environ Microbiol 74:7286–7296
Chakraburtty R, Bibb MJ (1997) The ppGpp synthetase gene (relA) of Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2) plays a conditional role in antibiotic production and morphological differentiation. J Bacteriol 179:5854–5861
Chater KF, Bucca G, Dyson P, Fowler K, Gust B, Herron P, Hesketh A, Hotchkiss G, Kieser T, Mersinias V, Smith CP (2002) Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2): from genome sequence to function. Methods Microbiol 33:321–336
Claessen D, Rink R, de Jong W, Siebring J, de Vreugd P, Boersma FG, Dijkhuizen L, Wosten HA (2003) A novel class of secreted hydrophobic proteins is involved in aerial hyphae formation in Streptomyces coelicolor by forming amyloid-like fibrils. Genes Dev 17:1714–1726
Cole ST, Brosch R, Parkhill J, Garnier T, Churcher C, Harris D, Gordon SV, Eiglmeier K, Gas S, Barry CE 3rd, Tekaia F, Badcock K, Basham D, Brown D, Chillingworth T, Connor R, Davies R, Devlin K, Feltwell T, Gentles S, Hamlin N, Holroyd S, Hornsby T, Jagels K, Krogh A, McLean J, Moule S, Murphy L, Oliver K, Osborne J, Rajandream MA, Rogers J, Rutter S, Seeger K, Skelton J, Squares R, Squares S, Sulston JE, Taylor K, Whitehead S, Barrell BG (1998) Deciphering the biology of Mycobacterium tuberculosis from the complete genome sequence. Nature 393:537–544
D’Alia D, Eggle D, Nieselt K, Hu WS, Breitling R, Takano E (2011) Deletion of the signalling molecule synthase ScbA has pleiotropic effects on secondary metabolite biosynthesis, morphological differentiation and primary metabolism in Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). Microb Biotechnol 4:239–251
Fink D, Falke D, Wohlleben W, Engels A (1999) Nitrogen metabolism in Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2): modification of glutamine synthetase I by an adenylyltransferase. Microbiology 145:2313–2322
Fink D, Weißschuh N, Reuther J, Wohlleben W, Engels A (2002) Two transcriptional regulators GlnR and GlnRII are involved in regulation of nitrogen metabolism in Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). Mol Microbiol 46:331–347
Fischer M, Alderson J, van Keulen G, White J, Sawers RG (2011) The obligate aerobe Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2) synthesizes three active respiratory nitrate reductases. Microbiology 156(Pt 10):3166–3179
Flett F, Mersinias V, Smith CP (1997) High efficiency intergeneric conjugal transfer of plasmid DNA from Escherichia coli to methyl DNA-restricting streptomycetes. FEMS Microbiol Lett 155:223–229
Forchhammer K (2008) PII signal transducers: novel functional and structural insights. Trends Microbiol 16:65–72
Gautier L, Cope L, Bolstad BM, Irizarry RA (2004) affy—analysis of Affymetrix GeneChip data at the probe level. Bioinformatics 20:307–315
Hesketh A, Fink D, Gust B, Rexer H-U, Scheel B, Chater K, Wohlleben W, Engels A (2002) The GlnD and GlnK homologues of Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2) are functionally dissimilar to their nitrogen regulatory system counterparts from enteric bacteria. Mol Microbiol 46:319–330
Hodgson DA (2000) Primary metabolism and its control in streptomycetes: a most unusual group of bacteria. Adv Microb Physiol 42:47–238
Hopwood DA, Chater KF, Bibb MJ (1995) Genetics of antibiotic production in Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2), a model streptomycete. Biotechnology 28:65–102
Horinouchi S (2002) A microbial hormone, A-factor, as a master switch for morphological differentiation and secondary metabolism in Streptomyces griseus. Front Biosci 7:2045–2057
Ihaka R, Gentleman R (2005) R: a language for data analysis and graphics. J Comput Graph Stat 5:299–314
Jäger G, Battke F, Nieselt K (2011) TIALA - Time Series Alignment Analysis. In Proceedings of the 1st IEEE Symposium on Biological Data Visualization (IEEE VisWeek). Providence, USA
Jakoby M, Krämer R, Burkovski A (1999) Nitrogen regulation in Corynebacterium glutamicum: isolation of genes involved and biochemical characterization of corresponding proteins. FEMS Microbiol Lett 173:303–310
Kieser T, Bibb MJ, Buttner MJ, Chater KF, Hopwood DA (2000) Practical Streptomyces genetics. The John Innes Foundation, Norwich
Lewis RA, Shahi SK, Laing E, Bucca G, Efthimiou G, Bushell M, Smith CP (2011) Genome-wide transcriptomic analysis of the response to nitrogen limitation in Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). BMC Res Notes 4:78
MacNeil DJ, Gewain KM, Ruby CL, Dezeny G, Gibbons PH, MacNeil T (1992) Analysis of Streptomyces avermitilis genes required for avermectin biosynthesis utilizing a novel integration vector. Gene 111:61–88
Magasanik B (1996) Regulation of nitrogen utilization. In: Neidhardt FC, Curtiss IR, Ingraham JL, Lin ECC, Low KB, Magasanik B et al (eds) Escherichia coli and Salmonella: cellular and molecular biology. American Society for Microbiology Press, Washington, pp 1344–1356
Malin G, Lapidot A (1996) Induction of synthesis of tetrahydropyrimidine derivatives in Streptomyces strains and their effect on Escherichia coli in response to osmotic and heat stress. J Bacteriol 178:385–395
Manteca A, Alvarez R, Salazar N, Yagüe P, Sanchez J (2008) Mycelium differentiation and antibiotic production in submerged cultures of Streptomyces coelicolor. Appl Environ Microbiol 74:3877–3886
Merrick MJ, Edwards RA (1995) Nitrogen control in bacteria. Microbiol Rev 59:604–622
Nguyen KT, Willey JM, Nguyen LD, Nguyen LT, Viollier PH, Thompson CJ (2002) A central regulator of morphological differentiation in the multicellular bacterium Streptomyces coelicolor. Mol Microbiol 46:1223–1238
Nieselt K, Battke F, Herbig A, Bruheim P, Wentzel A, Jakobsen ØM, Sletta H, Alam MT, Merlo ME, Moore J, Omara WA, Morrissey ER, Juarez-Hermosillo MA, Rodríguez-García A, Nentwich M, Thomas L, Iqbal M, Legaie R, Gaze WH, Challis GL, Jansen RC, Dijkhuizen L, Rand DA, Wild DL, Bonin M, Reuther J, Wohlleben W, Smith MC, Burroughs NJ, Martín JF, Hodgson DA, Takano E, Breitling R, Ellingsen TE, Wellington EM (2010) The dynamic architecture of the metabolic switch in Streptomyces coelicolor. BMC Genomics 11:10
Nolden L, Ngouoto-Nkili C-E, Bendt AK, Krämer R, Burkovski A (2001) Sensing nitrogen limitation in Corynebacterium glutamicum: the role of glnK and glnD. Mol Microbiol 42:1281–1295
Pullan ST, Chandra G, Bibb MJ, Merrick M (2011) Genome-wide analysis of the role of GlnR in Streptomyces venezuelae provides new insights into global nitrogen regulation in actinomycetes. BMC Genomics 12:175
Reuther J, Wohlleben W (2007) Nitrogen metabolism in Streptomyces coelicolor: transcriptional and post-translational regulation. J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol 12:139–146
Rexer HU, Schäberle T, Wohlleben W, Engels A (2006) Investigation of the functional properties and regulation of three glutamine synthetase-like genes in Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). Arch Microbiol 186:447–458
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Manzanal T (1989) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor
San Paolo S, Huang J, Cohen SN, Thompson CJ (2006) rag genes: novel components of the RamR regulon that trigger morphological differentiation in Streptomyces coelicolor. Mol Microbiol 5:1167–1186
Shetty ND, Reddy MC, Palaninathan SK, Owen JL, Sacchettini JC (2010) Crystal structure of the apo and ATP bound Mycobacterium tuberculosis nitrogen regulatory PII protein. Protein Sci 19:1513–1524
Strösser J, Lüdke A, Schaffer S, Krämer R, Burkovski A (2004) Regulation of GlnK activity: modification, membrane sequestration and proteolysis as regulatory principles in the network of nitrogen control in Corynebacterium glutamicum. Mol Microbiol 54:132–147
Süsstrunk U, Pidoux J, Taubert S, Ullmann A, Thompson CJ (1998) Pleiotropic effects of cAMP on germination, antibiotic biosynthesis and morphological development in Streptomyces coelicolor. Mol Microbiol 30:33–46
van Keulen G, Hopwood DA, Dijkhuizen L, Sawers RG (2005) Gas vesicles in actinomycetes: old buoys in novel habitats? Trends Microbiol 13:350–354
Viollier PH, Minas W, Dale GE, Folcher M, Thompson CJ (2001) Role of acid metabolism in Streptomyces coelicolor morphological differentiation and antibiotic biosynthesis. J Bacteriol 183:3184–3192
Willey JM, Willems A, Kodani S, Nodwell JR (2006) Morphogenetic surfactants and their role in the formation of aerial hyphae in Streptomyces coelicolor. Mol Microbiol 59(3):731–742
Yang YH, Song E, Kim EJ, Lee K, Kim WS, Park SS, Hahn JS, Kim BG (2009) NdgR, an IclR-like regulator involved in amino-acid-dependent growth, quorum sensing, and antibiotic production in Streptomyces coelicolor. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 82:50–511
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge Anders Øverby, Sunniva Hoel, Øyvind M. Jakobsen, and Ingemar Nærdal for their excellent participation in fermentation experiments and the members of the STREAM consortium led by E. M. H. Wellington for their input and discussions. This project was supported by the EU-funded (FP6) ActinoGEN project (LSHM-CT-2004-005224) and grants of the ERA-NET SysMO Project [GEN2006-27745-E/SYS]: (P-UK-01-11-3i), “STREAM”, and the Research Council of Norway [project no. 181840/I30].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Eva Waldvogel and Alexander Herbig are the first authors of the article.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Fig. S1
Expression profiles of the 41 genes that show a variant expression profile in the SCglnK-3 mutant but not in the wild-type strain. The centroid profile is shown as a dotted blue line (JPEG 80 kb)
Fig. S2
Expression profiles of the nar2 operon (blue: wild-type; red: SC glnK-3). (JPEG 123 kb)
Fig. S3
Expression profiles of the ectABCD genes (blue: wild-type; red: SCglnK-3) (JPEG 116 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Waldvogel, E., Herbig, A., Battke, F. et al. The PII protein GlnK is a pleiotropic regulator for morphological differentiation and secondary metabolism in Streptomyces coelicolor . Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 92, 1219–1236 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-011-3644-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-011-3644-1