Abstract
Purpose
Treatment and prognosis of gliomas depend on their histological tumour grade. The aim of the study was to evaluate the potential of [18F]fluoroethyltyrosine (FET) PET for non-invasive tumour grading in untreated patients.
Methods
Dynamic FET PET studies were performed in 54 patients who, based on MRI, were estimated to have low grade (LG; n = 20), intermediate (WHO II–III; n = 4) or high grade (HG; n = 30) tumours. For standard evaluation, tumour SUVmax and the ratio to background (SUVmax/BG) were calculated (sum image: 20–40 min). For dynamic evaluation, mean SUV values within a 90% isocontour ROI (SUV90) and the SUV90/BG ratios were determined for each time frame to evaluate the course of FET uptake. Results were correlated with histopathological findings from PET-guided stereotactic biopsies.
Results
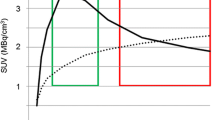
Histology revealed gliomas in all patients. Using the standard method a statistically significant difference (p = 0.001) was found between LG (n = 20; SUVmax/BG: 2.16 ± 0.98) and HG (n = 34; SUVmax/BG: 3.29 ± 1.06) gliomas (opt. threshold 2.58: SN71%/SP85%/area under ROC curve [AUC]:0.798), however, with a marked overlap between WHO II to IV tumours. Time activity curves showed slight increase in LG, whereas HG tumours presented with an early peak (10–20 min) followed by a decrease. Dynamic evaluation successfully separated LG from HG gliomas with higher diagnostic accuracy (SN94%/SP100%/AUC:0.967).
Conclusions
Based on the ratio-based method, a statistically significant difference was found between LG and HG gliomas. Due to the interindividual variability, however, no reliable individual grading was possible. In contrast, dynamic evaluation allowed LG and HG gliomas to be differentiated with high diagnostic power and, thus, should supplement the conventional method.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ohgaki H, Kleihues P. Population-based studies on incidence, survival rates, and genetic alterations in astrocytic and oligodendroglial gliomas. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 2005;64:479–89.
Kleihues P, Cavenee WK. Tumors of the nervous system. Pathology and genetics. Lyon, France: IARC Press; 2000.
Earnest Ft, Kelly PJ, Scheithauer BW, Kall BA, Cascino TL, Ehman RL, et al. Cerebral astrocytomas: histopathologic correlation of MR and CT contrast enhancement with stereotactic biopsy. Radiology 1988;166:823–7.
Pierallini A, Bonamini M, Bozzao A, Pantano P, Stefano DD, Ferone E, et al. Supratentorial diffuse astrocytic tumours: proposal of an MRI classification. Eur Radiol 1997;7:359–95.
Asari S, Makabe T, Katayama S, Itoh T, Tsuchida S, Ohmoto T. Assessment of the pathological grade of astrocytic gliomas using an MRI score. Neuroradiology 1994;36:308–10.
Glantz MJ, Burger PC, Herndon JE 2nd, Friedman AH, Cairncross JG, Vick NA, et al. Influence of the type of surgery on the histologic diagnosis in patients with anaplastic gliomas. Neurology 1991;41:1741–4.
Borbely K, Nyary I, Toth M, Ericson K, Gulyas B. Optimization of semi-quantification in metabolic PET studies with 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose and 11C-methionine in the determination of malignancy of gliomas. J Neurol Sci 2006;246:85–94.
Kracht LW, Miletic H, Busch S, Jacobs AH, Voges J, Hoevels M, et al. Delineation of brain tumor extent with [11C]L-methionine positron emission tomography: local comparison with stereotactic histopathology. Clin Cancer Res 2004;10:7163–70.
Pirotte B, Goldman S, Massager N, David P, Wikler D, Lipszyc M, et al. Combined use of 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose and 11C-methionine in 45 positron emission tomography-guided stereotactic brain biopsies. J Neurosurg 2004;101:476–83.
Van Laere K, Ceyssens S, Van Calenbergh F, de Groot T, Menten J, Flamen P, et al. Direct comparison of 18F-FDG and 11C-methionine PET in suspected recurrence of glioma: sensitivity, inter-observer variability and prognostic value. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2005;32:39–51.
Popperl G, Gotz C, Rachinger W, Gildehaus FJ, Tonn JC, Tatsch K. Value of O-(2-[18F]fluoroethyl)- L-tyrosine PET for the diagnosis of recurrent glioma. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2004;31:1464–70.
Rachinger W, Goetz C, Popperl G, Gildehaus FJ, Kreth FW, Holtmannspotter M, et al. Positron emission tomography with O-(2-[18F]fluoroethyl)-l-tyrosine versus magnetic resonance imaging in the diagnosis of recurrent gliomas. Neurosurgery 2005;57:505–11, discussion 505–511.
Popperl G, Gotz C, Rachinger W, Schnell O, Gildehaus FJ, Tonn JC, et al. Serial O-(2-[(18)F]fluoroethyl)-L: -tyrosine PET for monitoring the effects of intracavitary radioimmunotherapy in patients with malignant glioma. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2006;33:792–800.
Popperl G, Goldbrunner R, Gildehaus FJ, Kreth FW, Tanner P, Holtmannspotter M, et al. O-(2-[18F]fluoroethyl)-L-tyrosine PET for monitoring the effects of convection-enhanced delivery of paclitaxel in patients with recurrent glioblastoma. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2005;32:1018–25.
Torii K, Tsuyuguchi N, Kawabe J, Sunada I, Hara M, Shiomi S. Correlation of amino-acid uptake using methionine PET and histological classifications in various gliomas. Ann Nucl Med 2005;19:677–83.
Kracht LW, Friese M, Herholz K, Schroeder R, Bauer B, Jacobs A, et al. Methyl-[(11)C]- l-methionine uptake as measured by positron emission tomography correlates to microvessel density in patients with glioma. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2003;30:868–73.
Derlon JM, Bourdet C, Bustany P, Chatel M, Theron J, Darcel F, et al. [11C]L-methionine uptake in gliomas. Neurosurgery 1989;25:720–8.
Popperl G, Kreth FW, Herms J, Koch W, Mehrkens JH, Gildehaus FJ, et al. Analysis of 18F-FET PET for grading of recurrent gliomas: is evaluation of uptake kinetics superior to standard methods? J Nucl Med 2006;47:393–403.
Weckesser M, Langen KJ, Rickert CH, Kloska S, Straeter R, Hamacher K, et al. O-(2-[(18)F]fluorethyl)-L: -tyrosine PET in the clinical evaluation of primary brain tumours. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2005;32:422–9.
Kreth FW, Muacevic A, Medele R, Bise K, Meyer T, Reulen HJ. The risk of haemorrhage after image guided stereotactic biopsy of intra-axial brain tumours-a prospective study. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 2001;143:539–45, discussion 545–546.
Swets JA. ROC analysis applied to the evaluation of medical imaging techniques. Invest Radiol 1979;14:109–21.
Hanley JA, McNeil BJ. The meaning and use of the area under a receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve. Radiology 1982;143:29–36.
Kaschten B, Stevenaert A, Sadzot B, Deprez M, Degueldre C, Del Fiore G, et al. Preoperative evaluation of 54 gliomas by PET with fluorine-18-fluorodeoxyglucose and/or carbon-11-methionine. J Nucl Med 1998;39:778–85.
De Witte O, Goldberg I, Wikler D, Rorive S, Damhaut P, Monclus M, et al. Positron emission tomography with injection of methionine as a prognostic factor in glioma. J Neurosurg 2001;95:746–50.
Ceyssens S, Van Laere K, de Groot T, Goffin J, Bormans G, Mortelmans L. [11C]methionine PET, histopathology, and survival in primary brain tumors and recurrence. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2006;27:1432–7.
Weber WA, Wester HJ, Grosu AL, Herz M, Dzewas B, Feldmann HJ, et al. O-(2-[18F]fluoroethyl)-L-tyrosine and L-[methyl-11C]methionine uptake in brain tumours: initial results of a comparative study. Eur J Nucl Med 2000;27:542–9.
Stober B, Tanase U, Herz M, Seidl C, Schwaiger M, Senekowitsch-Schmidtke R. Differentiation of tumour and inflammation: characterisation of [methyl-3H]methionine (MET) and O-(2-[18F]fluoroethyl)-L-tyrosine (FET) uptake in human tumour and inflammatory cells. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2006;33:932–9.
Lahoutte T, Caveliers V, Camargo SM, Franca R, Ramadan T, Veljkovic E, et al. SPECT and PET amino acid tracer influx via system L (h4F2hc-hLAT1) and its transstimulation. J Nucl Med 2004;45:1591–6.
Fortin D, Cairncross GJ, Hammond RR. Oligodendroglioma: an appraisal of recent data pertaining to diagnosis and treatment. Neurosurgery 1999;45:1279–91, discussion 191.
Ogawa T, Shishido F, Kanno I, Inugami A, Fujita H, Murakami M, et al. Cerebral glioma: evaluation with methionine PET. Radiology 1993;186:45–53.
Di Chiro G. Positron emission tomography using [18F] fluorodeoxyglucose in brain tumors. A powerful diagnostic and prognostic tool. Invest Radiol 1987;22:360–71.
Delbeke D, Meyerowitz C, Lapidus RL, Maciunas RJ, Jennings MT, Moots PL, et al. Optimal cutoff levels of F-18 fluorodeoxyglucose uptake in the differentiation of low-grade from high-grade brain tumors with PET. Radiology 1995;195:47–52.
Gupta K, Radotra BD, Banerjee AK, Nijhawan R. Quantitation of angiogenesis and its correlation with vascular endothelial growth factor expression in astrocytic tumors. Anal Quant Cytol Histol 2004;26:223–9.
Miyagawa T, Oku T, Uehara H, Desai R, Beattie B, Tjuvajev J, et al. “Facilitated” amino acid transport is upregulated in brain tumors. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 1998;18:500–9.
Langen KJ, Jarosch M, Muhlensiepen H, Hamacher K, Broer S, Jansen P, et al. Comparison of fluorotyrosines and methionine uptake in F98 rat gliomas. Nucl Med Biol 2003;30:501–8.
Heiss P, Mayer S, Herz M, Wester HJ, Schwaiger M, Senekowitsch-Schmidtke R. Investigation of transport mechanism and uptake kinetics of O-(2-[18F]fluoroethyl)-L-tyrosine in vitro and in vivo. J Nucl Med 1999;40:1367–73.
Meier C, Ristic Z, Klauser S, Verrey F. Activation of system L heterodimeric amino acid exchangers by intracellular substrates. Embo J 2002;21:580–9.
Christensen HN. Role of amino acid transport and countertransport in nutrition and metabolism. Physiol Rev 1990;70:43–77.
Wester HJ, Herz M, Weber W, Heiss P, Senekowitsch-Schmidtke R, Schwaiger M, et al. Synthesis and radiopharmacology of O-(2-[18F]fluoroethyl)-L-tyrosine for tumor imaging. J Nucl Med 1999;40:205–12.
Acknowledgement
Part of this work was supported by grant 10-3163-Wi3 from Deutsche Krebshilfe.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pöpperl, G., Kreth, F.W., Mehrkens, J.H. et al. FET PET for the evaluation of untreated gliomas: correlation of FET uptake and uptake kinetics with tumour grading. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 34, 1933–1942 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-007-0534-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-007-0534-y