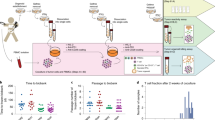
Abstract
Objective
Chronic inflammation and cancer development are associated with dysregulated immune responses and the presence of regulatory T cells (Treg). To study the role of Treg in tumor cell escape from immune surveillance, an in vitro model simulating the tumor microenvironment and promoting the induction and expansion of IL-10+ Treg type 1 (Tr1) was established.
Methods
An in vitro co-culture system (IVA) included an irradiated head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cell line, immature dendritic cells (iDC), CD4+CD25− T cells and cytokines, IL-2 (10 IU/ml), IL-10 (20 IU/ml), IL-15 (20 IU/ml) ± 1 nM rapamycin. Autologous iDC and CD4+CD25− T cells were obtained from the peripheral blood of 15 normal donors. Co-cultures were expanded for 10 days. Proliferating lymphocytes were phenotyped by multi-color flow cytometry. Their suppressor function was measured in CFSE inhibition assays ± neutralizing anti-IL-10 mAb and using transwell cultures. Culture supernatants were tested for IL-4, IL-10, TGF-β and IFN-γ in ELISA.
Results
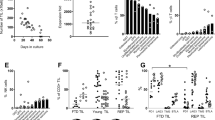
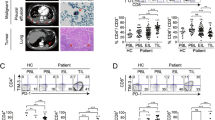
In the IVA, low doses of IL-2, IL-10 and IL-15 promoted induction and expansion of CD3+CD4+CD25−IL2Rβ+IL2Rγ+FoxP3+CTLA-4+IL-10+ cells with suppressor activity (mean suppression ± SD = 58 ± 12%). These suppressor cells produced IL-10 (mean ± SD = 535 ± 12 pg/ml) and TGF-β (mean ± SD = 512 ± 38 pg/ml), but no IL-4 or IFN-γ. Suppressor function of co-cultures correlated with the percent of expanding IL-10+ Tr1 cells (r 2 = 0.9; P < 0.001). The addition of rapamycin enriched Tr1 cells in all co-cultures. Neutralizing anti-IL-10 mAb abolished suppressive activity. Suppression was cell-contact independent.
Conclusion
The tumor microenvironment promotes generation of Tr1 cells which have the phenotype distinct from that of CD4+CD25highFoxP3+ nTreg and mediate IL-10 dependent immune suppression in a cell-contact independent manner. Tr1 cells may play a critical role in cancer progression.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abraham RT, Wiederrecht GJ (1996) Immunopharmacology of rapamycin. Annu Rev Immunol 14:483–510
Assenmacher M, Lohning M, Scheffold A, Richter A, Miltenyi S, Schmitz J, Radbruch A (1998) Commitment of individual Th1-like lymphocytes to expression of IFN-gamma versus IL-4 and IL-10: selective induction of IL-10 by sequential stimulation of naive Th cells with IL-12 and IL-4. J Immunol 161:2825–2832
Bacchetta R, Bigler M, Touraine JL, Parkman R, Tovo PA, Abrams J, de Waal Malefyt R, de Vries JE, Roncarolo MG (1994) High levels of interleukin 10 production in vivo are associated with tolerance in SCID patients transplanted with HLA mismatched hematopoietic stem cells. J Exp Med 179:493–502
Bacchetta R, Sartirana C, Levings MK, Bordignon C, Narula S, Roncarolo MG (2002) Growth and expansion of human T regulatory type 1 cells are independent from TCR activation but require exogenous cytokines. Eur J Immunol 32:2237–2245
Baecher-Allan C, Hafler DA (2004) Suppressor T cells in human diseases. J Exp Med 200:273–276
Baecher-Allan C, Anderson DE (2006) Regulatory cells and human cancer. Semin Cancer Biol 16:98–105
Barchet W, Price JD, Cella M, Colonna M, MacMillan SK, Cobb JP, Thompson PA, Murphy KM, Atkinson JP, Kemper C (2006) Complement-induced regulatory T cells suppress T-cell responses but allow for dendritic-cell maturation. Blood 107:1497–1504
Barrat FJ, Cua DJ, Boonstra A, Richards DF, Crain C, Savelkoul HF, de Waal-Malefyt R, Coffman RL, Hawrylowicz CM, O’Garra A (2002) In vitro generation of interleukin 10-producing regulatory CD4 (+) T cells is induced by immunosuppressive drugs and inhibited by T helper type 1 (Th1)- and Th2-inducing cytokines. J Exp Med 195:603–616
Battaglia M, Gregori S, Bacchetta R, Roncarolo MG (2006) Tr1 cells: from discovery to their clinical application. Semin Immunol 18:120–127
Battaglia M, Stabilini A, Draghici E, Gregori S, Mocchetti C, Bonifacio E, Roncarolo MG (2006) Rapamycin and interleukin-10 treatment induces T regulatory type 1 cells that mediate antigen-specific transplantation tolerance. Diabetes 55:40–49
Bluestone JA, Abbas AK (2003) Natural versus adaptive regulatory T cells. Nat Rev Immunol 3:253–257
Curiel TJ, Coukos G, Zou L, Alvarez X, Cheng P, Mottram P, Evdemon-Hogan M, Conejo-Garcia JR, Zhang L, Burow M, Zhu Y, Wei S, Kryczek I, Daniel B, Gordon A, Myers L, Lackner A, Disis ML, Knutson KL, Chen L, Zou W (2004) Specific recruitment of regulatory T cells in ovarian carcinoma fosters immune privilege and predicts reduced survival. Nat Med 10:942–949
de Waal Malefyt R, Haanen J, Spits H, Roncarolo MG, te Velde A, Figdor C, Johnson K, Kastelein R, Yssel H, de Vries JE (1991) Interleukin 10 (IL-10) and viral IL-10 strongly reduce antigen-specific human T cell proliferation by diminishing the antigen-presenting capacity of monocytes via downregulation of class II major histocompatibility complex expression. J Exp Med 174:915–924
Furtado GC, Curotto de Lafaille MA, Kutchukhidze N, Lafaille JJ (2002) Interleukin 2 signaling is required for CD4(+) regulatory T cell function. J Exp Med 196:851–857
Giri JG, Anderson DM, Kumaki S, Park LS, Grabstein KH, Cosman D (1995) IL-15, a novel T cell growth factor that shares activities and receptor components with IL-2. J Leukoc Biol 57:763–766
Groux H, O’Garra A, Bigler M, Rouleau M, Antonenko S, de Vries JE, Roncarolo MG (1997) A CD4+ T-cell subset inhibits antigen-specific T-cell responses and prevents colitis. Nature 389:737–742
Heo DS, Snyderman C, Gollin SM, Pan S, Walker E, Deka R, Barnes EL, Johnson JT, Herberman RB, Whiteside TL (1989) Biology, cytogenetics, and sensitivity to immunological effector cells of new head and neck squamous cell carcinoma lines. Cancer Res 49:5167–5175
Inobe J, Slavin AJ, Komagata Y, Chen Y, Liu L, Weiner HL (1998) IL-4 is a differentiation factor for transforming growth factor-beta secreting Th3 cells and oral administration of IL-4 enhances oral tolerance in experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. Eur J Immunol 28:2780–2790
Ito M, Hiramatsu H, Kobayashi K, Suzue K, Kawahata M, Hioki K, Ueyama Y, Koyanagi Y, Sugamura K, Tsuji K, Heike T, Nakahata T (2002) NOD/SCID/gamma(c) (null) mouse: an excellent recipient mouse model for engraftment of human cells. Blood 100:3175–3182
Jonuleit H, Schmitt E, Schuler G, Knop J, Enk AH (2000) Induction of interleukin 10-producing, nonproliferating CD4 (+) T cells with regulatory properties by repetitive stimulation with allogeneic immature human dendritic cells. J Exp Med 192:1213–1222
Levings MK, Sangregorio R, Galbiati F, Squadrone S, de Waal Malefyt R, Roncarolo MG (2001) IFN-alpha and IL-10 induce the differentiation of human type 1 T regulatory cells. J Immunol 166:5530–5539
Levings MK, Gregori S, Tresoldi E, Cazzaniga S, Bonini C, Roncarolo MG (2005) Differentiation of Tr1 cells by immature dendritic cells requires IL-10 but not CD25+CD4+ Tr cells. Blood 105:1162–1169
Levings MK, Roncarolo MG (2005) Phenotypic and functional differences between human CD4+CD25+ and type 1 regulatory T cells. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 293:303–326
Liu W, Putnam AL, Xu-Yu Z, Szot GL, Lee MR, Zhu S, Gottlieb PA, Kapranov P, Gingeras TR, Fazekas de St Groth B, Clayberger C, Soper DM, Ziegler SF, Bluestone JA (2006) CD127 expression inversely correlates with FoxP3 and suppressive function of human CD4+ T reg cells. J Exp Med 203:1701–1711
Malek TR, Bayer AL (2004) Tolerance, not immunity, crucially depends on IL-2. Nat Rev Immunol 4:665–674
Mocellin S, Marincola FM, Young HA (2005) Interleukin-10 and the immune response against cancer: a counterpoint. J Leukoc Biol 78:1043–1051
Morgan DA, Ruscetti FW, Gallo R (1976) Selective in vitro growth of T lymphocytes from normal human bone marrows. Science 193:1007–1008
Roncarolo MG, Gregori S, Battaglia M, Bacchetta R, Fleischhauer K, Levings MK (2006) Interleukin-10-secreting type 1 regulatory T cells in rodents and humans. Immunol Rev 212:28–50
Sakaguchi S, Ono M, Setoguchi R, Yagi H, Hori S, Fehervari Z, Shimizu J, Takahashi T, Nomura T (2006) Foxp3CD25CD4 natural regulatory T cells in dominant self-tolerance and autoimmune disease. Immunol Rev 212:8–27
Schaefer C, Kim GG, Albers A, Hoermann K, Myers EN, Whiteside TL (2005) Characteristics of CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells in the peripheral circulation of patients with head and neck cancer. Br J Cancer 92:913–920
Shevach EM (2004) Fatal attraction: tumors beckon regulatory T cells. Nat Med 10:900–901
Stassen M, Schmitt E, Jonuleit H (2004) Human CD(4+)CD(25+) regulatory T cells and infectious tolerance. Transplantation 77:S23–S25
Steinbrink K, Wolfl M, Jonuleit H, Knop J, Enk AH (1997) Induction of tolerance by IL-10-treated dendritic cells. J Immunol 159:4772–4780
Strauss L, Whiteside TL, Knights A, Bergmann C, Knuth A, Zippelius A (2007) Selective in vitro survival of naturally occuring human CD4+CD25+FOXP3+ regulatory T cells with rapamycin. J Immunol 178(1):320–329
Sugamura K, Asao H, Kondo M, Tanaka N, Ishii N, Ohbo K, Nakamura M, Takeshita T (1996) The interleukin-2 receptor gamma chain: its role in the multiple cytokine receptor complexes and T cell development in XSCID. Annu Rev Immunol 14:179–205
Suzuki H, Kundig TM, Furlonger C, Wakeham A, Timms E, Matsuyama T, Schmits R, Simard JJ, Ohashi PS, Griesser H et al (1995) Deregulated T cell activation and autoimmunity in mice lacking interleukin-2 receptor beta. Science 268:1472–1476
Whiteside TL (2006) Immune suppression in cancer: effects on immune cells, mechanisms and future therapeutic intervention. Semin Cancer Biol 16:3–15
Woo EY, Chu CS, Goletz TJ, Schlienger K, Yeh H, Coukos G, Rubin SC, Kaiser LR, June CH (2001) Regulatory CD4(+)CD25(+) T cells in tumors from patients with early-stage non-small cell lung cancer and late-stage ovarian cancer. Cancer Res 61:4766–4772
You S, Thieblemont N, Alyanakian MA, Bach JF, Chatenoud L (2006) Transforming growth factor-beta and T-cell-mediated immunoregulation in the control of autoimmune diabetes. Immunol Rev 212:185–202
Zhang M, Tang H, Guo Z, An H, Zhu X, Song W, Guo J, Huang X, Chen T, Wang J, Cao X (2004) Splenic stroma drives mature dendritic cells to differentiate into regulatory dendritic cells. Nat Immunol 5:1124–1133
Acknowledgments
Research described in this article was supported in part by Philip Morris USA, Inc. and Philip Morris International (SL, RZ and TLW) and by the NIH grant PO-1 DE12321 (TLW).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bergmann, C., Strauss, L., Zeidler, R. et al. Expansion and characteristics of human T regulatory type 1 cells in co-cultures simulating tumor microenvironment. Cancer Immunol Immunother 56, 1429–1442 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00262-007-0280-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00262-007-0280-9