Abstract
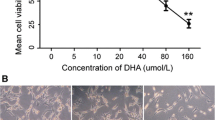
Dihydroartemisinin, a more water-soluble metabolite of artemisinin derivatives, is a safe and most effective antimalarial analog of artemisinin. In the present study, we investigated the antiangiogenic activity of dihydroartemisinin in vitro and in vivo, and investigated dihydroartemisinin-induced apoptosis in human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC). Dihydroartemisinin markedly reduced VEGF binding to its receptors on the surface of HUVEC. The expression levels of two major VEGF receptors, Flt-1 and KDR/flk-1, on HUVEC were lower following dihydroartemisinin treatment as shown by an immunocytochemical staining assay. The in vivo antiangiogenic activity was evaluated in the model of chicken chorioallantoic membrane (CAM) neovascularization. Dihydroartemisinin significantly inhibited CAM angiogenesis at low concentrations (5–30 nmol/100 μl per egg). We also investigated both qualitatively and quantitatively the induction of HUVEC apoptosis by dihydroartemisinin. A dose-related (5–80 μM) and time-dependent (6–36 h) increase in dihydroartemisinin-induced HUVEC apoptosis was observed by flow cytometry. Our results suggest that the antiangiogenic effect induced by dihydroartemisinin might occur by induction of cellular apoptosis and inhibition of expression of VEGF receptors. These findings and the known low toxicity of dihydroartemisinin indicate that it might be a promising candidate angiogenesis inhibitor.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Folkman J (1995) Angiogenesis in cancer, vascular, rheumatoid and other disease. Nat Med 1:27–31
Folkman J (1995) Clinical applications of research on angiogenesis. N Engl J Med 333:1757–1763
Folkman J, Klagsbrun M (1987) Angiogenic growth factors. Science 235:442–447
Folkman J (1971) Tumor angiogenesis: therapeutic implications. N Engl J Med 285:1182–1186
Kim KJ, Li B, Winer J (1993) Inhibition of vascular endothelial growth factor-induced angiogenesis suppresses tumor growth in vivo. Nature 362:841–844
Klagsbrun M, Moses MA (1999) Molecular angiogenesis. Chem Biol 6:217–224
Keck PJ, Hauser SD, Krivi G, Sanzo K, Warren T, Feder J, Conolly DT (1989) Vascular permeability factor, an endothelial cell mitogen related to PDGF. Science 246:1309–1312
Morbidelli L, Chang CH, Douglas JG, Granger HJ, Ledda F, Ziche M (1996) Nitric oxide mediates effect of VEGF on coronary venular endothelium. Am J Physiol 270:411–415
Ferrara N, Houck I, Jakeman L, Leung DW (1992) Molecular and biological properties of the vascular endothelial growth factor family of proteins. Endocr Rev 13:18–42
Shen BO, Lee DR, Zioncheck TF (1999) Vascular endothelial growth factor governs endothelial nitric-oxide synthase expression via KDR/Flk-1 receptor and a protein kinase C signaling pathway. J Biol Chem 274:33057–33063
Fong GH, Rossant J, Gertsenstein M, Breitman ML (1995) Role of the Flt-1 receptor tyrosine kinase in regulating the assembly of vascular endothelium. Nature 376:66–70
Ferrar N, Davis-Smyth T (1997) The biology of vascular endothelial growth factor. Edocr Rev 18:4–25
Claffey KP, Brow LF, Aguila LF (1996) Expression of vascular permeability factor/vascular endothelial growth factor by melanoma cells increases tumor growth, angiogenesis, and experimental metastasis. Cancer Res 56:172–182
Rak J, Kerbel RS (1996) Treating cancer by inhibiting angiogenesis: new hopes and potential pitfalls. Cancer Metastasis Res 56:231–236
Veikkola T, Karkkainen M, Claesson-Welsh K, Alitalo K (2000) Regulation of angiogenesis via vascular endothelial growth factor receptors. Cancer Res 60:203–212
Steller H (1995) Mechanisms and genes of cellular suicide. Science 267:1445–1448
Willie AH, Kerr JFR, Currie AR (1980) Cell death: the significance of apoptosis. Int Rev Cytol 68:251–308
Meredith JE, Fazeli B, Schwartz MA (1993) The extracellular matrix as a cell survival factor. Mol Biol Cell 4:953–961
Re F, Zanetti A, Sironi M, Poleutarutti N, Lanfrancone L, Dejana E, Colotta F (1994) Inhibition of anchorage-dependent cell spreading triggers apoptosis in cultured human endothelial cells. J Cell Biol 127:537–546
Klayman DL (1985) Qinghaosu (artemisinin): an antimalarial drug from China. Science 228:1049–1055
Woerdenbag HJ, Pras N, van Uden W, Wallart TE, Beekman AC, Lugt CB (1994) Progress in the research of artemisinin-related antimalarials: an update. Pharm World Sci 16:169–180
Tu Y (1999) The development of new antimalarial drugs: qinghaosu and dihydro-qinghaosu. Chin J Med 112:976–977
Janse CJ, Waters AP, Kos J, Lugt CB (1994) Comparison of in vivo and in vitro antimalarial activity of artemisinin, dihydroartemisinin and sodium artesunate in the Plasmodium berghei rodent model. Int J Parasitol 24:589–594
Efferth T, Dunstan H, Sauerbrey A, Miyachi H, Chitambar CR (2001) The anti-malarial artesunate is also active against cancer. Int J Oncol 18:767–773
Wu JM, Shan F, Wu GS, Li Y, Ding J, Xiao D, Han JX, Atassi G, Leonce S, Renard P (2001) Synthesis and cytotoxicity of artemisinin derivatives containing cyanoarylmethyl group. Eur J Med Chem 36:469–479
Efferth T, Ocbrich A, Bauer R (2002) mRNA expression profiles for the response of human tumor cell lines to the antimalarial drugs artesunate, arteether, and artemether. Biochem Pharmacol 64:617–623
Moore JC, Lai H, Li JR, Ren RL, McDougall JA, Singh NP, Chou CK (1995) Oral administration of dihydroartemisinin and ferrous sulfate retarded implanted fibrosarcoma growth in the rat. Cancer Lett 98:83–87
Yang X-P, Pan Q-C, Liang Y-L, Zikang Y-L (1997) The anti-tumor activity of artesunate (in Chinese). Ai Zheng 16:186–187
Chen HH, Zhou HJ, Fang X (2003) Inhibition of human cancer cell line growth and human umbilical vein endothelial cell angiogenesis by artemisinin derivatives in vitro. Pharmacol Res 48:231–236
Jackson JK, Burt HM, Oktaba AM, Hunter W, Scheid MP, Mouhajir F, Lauener RW (1998) The antineoplastic ether lipid, S-phosphonate, selectively induces apoptosis in human leukemic cells and exhibits antiangiogenic and apoptotic activity on the chorioallantoic membrane of the chick embryo. Cancer Chem Pharm 42:326–332
Reed A, Califano J, Cairus P (1996) High frequency of P16 inactivation in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Res 56:3630–3633
Cotter TG, Martin TG (1996) Techniques in apoptosis. A user’s guide. Portland Press, London, pp 7–9
Kum-Diaka J, Rodrigue R, Doudazi G (1998) Influence of genistein on the growth and proliferation of testicular cell lines. Biol Cell 90:349–354
Darzynkiewiez Z, Bruno S, Del Bino G, Gorczyca W, Hotz MA, Lassota P, Traganos F (1992) Features of apoptotic cells measured by flow cytometry. Cytometry 13:795–803
Zhang F, Gosser DK Jr, Meshnick SR (1992) Hemin-catalyzed decomposition of artemisinin (qinghaosu). Biochem Pharmacol 43:1805–1809
Berman PA, Adams PA (1997) Artemisinin enhances heme-catalysed oxidation of lipid membranes. Free Radic Biol Med 22:1283–1288
Reizenstein P (1991) Iron, free radical and cancer. Med Oncol Tumor Pharmacother 8:229–233
Trowbridge IS, Newman RA, Domingo DL, Saurage C (1984) Transferrin receptors: structure and function. Biochem Pharmacol 33:925–932
Singh NP, Lai H (2001) Selective toxicity of dihydroartemisinin and holotransferrin toward human breast cancer cells. Life Sci 79:49–56
Lai H, Singh NP (1995) Selective cancer cell cytotoxicity from exposure to dihydroartemisinin and holotransferrin. Cancer Lett 91:41–46
Hanahan D (1997) Signaling vascular morphogenesis and maintenance. Science 277:48–50
Alon T, Hemo I, Itin A, Pe’er J, Stone J, Keshet E (1995) Vascular endothelial growth factor acts as a survival factor for newly formed retinal vessels and has implications for retinopathy of prematurity. Nat Med 1:1024–1028
Thakker GD, Muller WA, Rosengart TK (1999) The role of phosphatidylinositol 3′-kinase in vascular endothelial growth factor signaling. J Biol Chem 274:10002–10007
Gerber HP, Dixit V, Ferrara N (1998) Vascular endothelial growth factor induced expression of the antiapoptotic proteins Bcl-2 and AI in vascular endothelial cells. J Biol Chem 273:13313–13316
Benakis A, Paris M, Loutan L, Plessas CT, Plassas ST (1997) Pharmacokinetics of artemisinin and artesunate after oral administration in healthy volunteers. Am J Trop Med Hyg 56:17–23
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by a Grant-in-Aid for New Drug Research from the National Key Laboratories of the Chinese Academy of Sciences and by funds for scientific research from Zhejiang University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, HH., Zhou, HJ., Wang, WQ. et al. Antimalarial dihydroartemisinin also inhibits angiogenesis. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 53, 423–432 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-003-0751-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-003-0751-4