Abstract
Purpose
Ovarian cancer is the leading cause of death among all gynecological malignancies in Western countries. Although therapy for ovarian cancer has been greatly improved in the past 20 years, the overall survival for patients with advanced ovarian cancer has not changed significantly. The poor survival rates in patients with advanced ovarian cancer are due both to late diagnosis and to lack of effective drugs for the majority of patients who have a relapse and develop resistance to current chemotherapy agents used for ovarian cancer. Thus, developing and discovering effective novel drugs with different molecular structures from conventional chemotherapy agents have become an urgent clinical need.
Methods
Ovarian cancer cells were treated with lovastatin and atorvastatin. Apoptosis in these cells and tumor formation in soft agar were determined. The molecular mechanism by which statins suppress ovarian cancer cell growth was evaluated.
Results
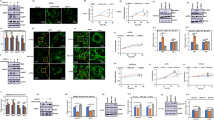
Both lovastatin and atorvastatin effectively induced apoptosis in ovarian cancer cells and suppressed anchorage-independent growth of these cells in soft agar. Further investigation of the molecular mechanism has revealed that the expression of Cdc42 and Rac1, small GTPase family members, was highly induced in the cells by these statins along with the activation of Jun N-terminal kinases (JNK). In addition, Bim, a proapoptotic protein, was significantly induced by these statins.
Conclusions
Our findings provide new insight into the molecular mechanism by which statins induce apoptosis in ovarian cancer cells and may lead to novel therapies for advanced ovarian cancer.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sharma S, Odunsi K (2005) Targeted therapy for epithelial ovarian cancer. Expert Opin Ther Targets 9(3):501–513
American Cancer Society, http://www.cancer.org
Ozols RF (2005) Treatment goals in ovarian cancer. Int J Gynecol Cancer 15(Suppl 1):3–11
Du Bois A, Pfisterer J (2005) Future options for first-line therapy of advanced ovarian cancer. Int J Gynecol Cancer 15(Suppl 1):42–50
Bookman MA (2005) Gemcitabine monotherapy in recurrent ovarian cancer: from the bench to the clinic. Int J Gynecol Cancer 15(Suppl 1):12–17
Caslake MJ, Packard CJ (2004) Phenotypes, genotypes and response to statin therapy. Curr Opin Lipidol 15(4):387–392
Stein EA (2003) The power of statins: aggressive lipid lowering. Clin Cardiol 26(4 Suppl 3):III25–31
Schmitz G, Drobnik W (2003) Pharmacogenomics and pharmacogenetics of cholesterol-lowering therapy. Clin Chem Lab Med 41(4):581–589
Chan KK, Oza AM, Siu LL (2003) The statins as anticancer agents. Clin Cancer Res 9(1):10–19
Cafforio P, Dammacco F, Gernone A, Silvestris F (2005) Statins activate the mitochondrial pathway of apoptosis in human lymphoblasts and myeloma cells. Carcinogenesis 26(5):883–891
Muck AO, Seeger H, Wallwiener D (2004) Inhibitory effect of statins on the proliferation of human breast cancer cells. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther 42(12):695–700
Koyuturk M, Ersoz M, Altiok N (2004) Simvastatin induces proliferation inhibition and apoptosis in C6 glioma cells via c-jun N-terminal kinase. Neurosci Lett 370(2–3):212–217
Otsuki T, Sakaguchi H, Hatayama T, Fujii T, Tsujioka T, Sugihara T, Takata A, Hyodoh F, Eto M (2004) Effects of an HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor, simvastatin, on human myeloma cells. Oncol Rep 11(5):1053–1058
Collisson EA, Kleer C, Wu M, De A, Gambhir SS, Merajver SD, Kolodney MS (2003) Atorvastatin prevents RhoC isoprenylation, invasion, and metastasis in human melanoma cells. Mol Cancer Ther 2(10):941–948
Gliemroth J, Feyerabend T, Gerlach C, Arnold H, Terzis AJ (2003) Proliferation, migration, and invasion of human glioma cells exposed to fractionated radiotherapy in vitro. Neurosurg Rev 26(3):198–205
Holstein SA, Knapp HR, Clamon GH, Murry DJ, Hohl RJ (2005) Pharmacodynamic effects of high dose lovastatin in subjects with advanced malignancies. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 30:1–10
Issat T, Nowis D, Jakobisiak M, Golab J (2004) Lovastatin potentiates antitumor effects of saquinavir against human lymphoma cells. Oncol Rep 12(6):1371–1375
Kozar K, Kaminski R, Legat M, Kopec M, Nowis D, Skierski JS, Koronkiewicz M, Jakobisiak M, Golab J (2004) Cerivastatin demonstrates enhanced antitumor activity against human breast cancer cell lines when used in combination with doxorubicin or cisplatin. Int J Oncol 24(5):1149–1157
Agarwal B, Bhendwal S, Halmos B, Moss SF, Ramey WG, Holt PR (1999) Lovastatin augments apoptosis induced by chemotherapeutic agents in colon cancer cells. Clin Cancer Res 5(8):2223–2229
Feleszko W, Jakóbisiak M (2000) Lovastatin potentiates antitumor activity and attenuates cardiotoxicity of doxorubicin in three tumor models in mice. Clin Cancer Res 6(5):2044–2052
Xiao H, Zhang Q, Lin Y, Reddy BS, Yang CS (2008) Combination of atorvastatin and celecoxib synergistically induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in colon cancer cells. Int J Cancer 122(9):2115–2124
Turner SJ, Zhuang S, Zhang T, Boss GR, Pilz RB (2008) Effects of lovastatin on Rho isoform expression, activity, and association with guanine nucleotide dissociation inhibitors. Biochem Pharmacol 75(2):405–413
Bokoch GM, Diebold BA (2002) Current molecular models for NADPH oxidase regulation by Rac GTPase. Blood 100(8):2692–2696
Rul W, Zugasti O, Roux P, Peyssonnaux C, Eychene A, Franke TF, Lenormand P, Fort P, Hibner U (2002) Activation of ERK, controlled by Rac1 and Cdc42 via Akt, is required for anoikis. Ann NY Acad Sci 973:145–148
Frost JA, Steen H, Shapiro P, Lewis T, Ahn N, Shaw PE, Cobb MH (1991) Cross-cascade activation of ERKs and ternary complex factors by Rho family proteins. EMBO J 16(21):6426–6438
Clerk A, Pham FH, Fuller SJ, Sahai E, Aktories K, Marais R, Marshall C, Sugden PH (2001) Regulation of mitogen-activated protein kinases in cardiac myocytes through the small G protein Rac1. Mol Cell Biol 21(4):1173–1184
Keely PJ, Westwick JK, Whitehead IP, Der CJ, Parise LV (1997) Cdc42 and Rac1 induce integrin-mediated cell motility and invasiveness through PI(3)K. Nature 390(6660):632–636
Aznar S, Lacal JC (2001) Rho signals to cell growth and apoptosis. Cancer Lett 165(1):1–10
Chuang TH, Hahn KM, Lee JD, Danley DE, Bokoch GM (1997) The small GTPase Cdc42 initiates an apoptotic signaling pathway in Jurkat T lymphocytes. Mol Biol Cell 8(9):1687–1698
Subauste MC, Von Herrath M, Benard V, Chamberlain CE, Chuang TH, Chu K, Bokoch GM, Hahn KM (2000) Rho family proteins modulate rapid apoptosis induced by cytotoxic T lymphocytes and Fas. J Biol Chem 275(13):9725–9733
Minden A, Lin A, Claret FX, Abo A, Karin M (1995) Selective activation of the JNK signaling cascade and c-Jun transcriptional activity by the small GTPases Rac and Cdc42Hs. Cell 81(7):1147–1157
Coso OA, Chiariello M, Yu JC, Teramoto H, Crespo P, Xu N, Miki T, Gutkind JS (1995) The small GTP-binding proteins Rac1 and Cdc42 regulate the activity of the JNK/SAPK signaling pathway. Cell 81(7):1137–1146
Teramoto H, Coso OA, Miyata H, Igishi T, Miki T, Gutkind JS (1996) Signaling from the small GTP-binding proteins Rac1 and Cdc42 to the c-Jun N-terminal kinase/stress-activated protein kinase pathway. A role for mixed lineage kinase 3/protein-tyrosine kinase 1, a novel member of the mixed lineage kinase family. J Biol Chem 271(44):27225–27228
Chuang TH, Hahn KM, Lee JD, Danley DE, Bokoch GM (1997) The small GTPase Cdc42 initiates an apoptotic signaling pathway in Jurkat T lymphocytes. Mol Biol Cell 8(9):1687–1698
Melichar B, Ferrandina G, Verschraegen CF, Loercher A, Abbruzzese JL, Freedman RS (1998) Growth inhibitory effects of aromatic fatty acids on ovarian tumor cell lines. Clin Cancer Res 4(12):3069–3076
van de Donk NW, Kamphuis MM, van Kessel B, Lokhorst HM, Bloem AC (2003) Inhibition of protein geranylgeranylation induces apoptosis in myeloma plasma cells by reducing Mcl-1 protein levels. Blood 102(9):3354–3362
Erl W, Hristov M, Neureuter M, Yan ZQ, Hansson GK, Weber PC (2003) HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors induce apoptosis in neointima-derived vascular smooth muscle cells. Atherosclerosis 169:251–258
Kaneta S, Satoh K, Kano S, Kanda M, Ichihara K (2003) All hydrophobic HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors induce apoptotic death in rat pulmonary vein endothelial cells. Atherosclerosis 170:237–243
Zhu BK, Wang P, Zhang XD, Jiang CC, Chen LH, Avery-Kiejda KA, Watts R, Hersey P (2008) Activation of Jun N-terminal kinase is a mediator of vincristine-induced apoptosis of melanoma cells. Anticancer Drugs 19(2):189–200
Avall-Lundqvist EH, Peterson CO (1996) Serum cholesterol and apolipoprotein B levels may reflect disease activity in ovarian cancer patients. Acta Oncol 35(8):1007–1010
Risch HA, Jain M, Marrett LD, Howe GR (1994) Dietary fat intake and risk of epithelial ovarian cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst 86(18):1409–1415
Biswas SC, Shi Y, Sproul A, Greene LA (2007) Pro-apoptotic Bim induction in response to nerve growth factor deprivation requires simultaneous activation of three different death signaling pathways. J Biol Chem 282(40):29368–29374
Bennett BL, Sasaki DT, Murray BW, O’Leary EC, Sakata ST, Xu W, Leisten JC, Motiwala A, Pierce S, Satoh Y, Bhagwat SS, Manning AM, Anderson DW (2001) SP600125, an anthrapyrazolone inhibitor of Jun N-terminal kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98(24):13681–13686
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, H., Liang, SL., Kumar, S. et al. Statins induce apoptosis in ovarian cancer cells through activation of JNK and enhancement of Bim expression. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 63, 997–1005 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-008-0830-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-008-0830-7