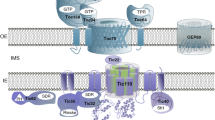
Abstract
The targeting of proteins, including the insertion and translocation of proteins in or across membranes, is a fundamental process within a cell, and a variety of specialized mechanisms for protein transport have been developed during evolution. The signal recognition particle (SRP) is found in the cytoplasm of most, if not all, eukaryotes and prokaryotes where it plays a central role in the co-translational insertion of membrane proteins into the endoplasmic reticulum and plasma membrane, respectively. SRP is a ribonucleoprotein consisting of an RNA and at least one polypeptide of ~54 kDa (SRP54). Interestingly, chloroplasts contain a specialized type of signal recognition particle. Chloroplast SRP (cpSRP) contains a SRP54 homologue but differs strikingly from cytosolic SRP in various aspects of structure and function. In contrast to cytosolic SRP, it contains a novel protein subunit (cpSRP43) and lacks RNA. CpSRP is also distinctive in its ability to interact with its substrate, light-harvesting chlorophyll a/b-binding protein, post-translationally. Furthermore, it is remarkable that the 54 kDa subunit of cpSRP is also involved in the co-translational transport of chloroplast-encoded thylakoid proteins, and is therefore able to switch between the co- and post-translational means of interaction with its respective substrate proteins.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdallah F, Salamini F, Leister D (2000) A prediction of the size and evolutionary origin of the proteome of chloroplasts of Arabidopsis. Trends Plant Sci 5:141–142
Amin P, Sy DA, Pilgrim ML, Parry DH, Nussaume L, Hoffman NE (1999) Arabidopsis mutants lacking the 43- and 54-kilodalton subunits of the chloroplast signal recognition particle have distinct phenotypes. Plant Physiol 121:61–70
Beck K, Eisner G, Trescher D, Dalbey RE, Brunner J, Muller M (2001) YidC, an assembly site for polytopic Escherichia coli membrane proteins located in immediate proximity to the SecYE translocon and lipids. EMBO Rep 2:709–714
Bernstein HD (2000) The biogenesis and assembly of bacterial membrane proteins. Curr Opin Microbiol 3:203–209
Bork P (1993) Hundreds of ankyrin-like repeats in functionally diverse proteins: mobile modules that cross phyla horizontally? Proteins 17:363–374
Chen M, Samuelson JC, Jiang F, Muller M, Kuhn A, Dalbey RE (2002) Direct interaction of YidC with the Sec-independent Pf3 coat protein during its membrane protein insertion. J Biol Chem 277:7670–7675
Cline K, Mori H (2001) Thylakoid Delta pH-dependent precursor proteins bind to a cpTatC-Hcf106 complex before Tha4-dependent transport. J Cell Biol 154:719–729
DeLille J, Peterson EC, Johnson T, Moore M, Kight A, Henry R (2000) A novel precursor recognition element facilitates posttranslational binding to the signal recognition particle in chloroplasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:1926–1931
Eichacker LA, Henry R (2001) Function of a chloroplast SRP in thylakoid protein export. Biochim Biophys Acta 1541:120–134
Eissenberg JC, Elgin SC (2000) The HP1 protein family: getting a grip on chromatin. Curr Opin Genet Dev 10:204–210
Franklin AE, Hoffman NE (1993) Characterization of a chloroplast homologue of the 54-kDa subunit of the signal recognition particle. J Biol Chem 268:22175–22180
Fröderberg L, Houben E, Samuelson JC, Chen MY, Park SK, Phillips GJ, Dalbey R, Luirink J, de Gier JWL (2003) Versatility of inner membrane protein biogenesis in Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol 47:1015–1027
Gier JW de, Luirink J (2001) Biogenesis of inner membrane proteins in Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol 40:314–322
Glick BS, Von Heijne G (1996) Saccharomyces cerevisiae mitochondria lack a bacterial-type Sec machinery. Protein Sci 5:2651–2652
Groves MR, Mant A, Kuhn A, Koch J, Dubel S, Robinson C, Sinning I (2001) Functional characterization of recombinant chloroplast signal recognition particle. J Biol Chem 276:27778–27786
Hell K, Herrmann JM, Pratje E, Neupert W, Stuart RA (1998) Oxa1p, an essential component of the N-tail protein export machinery in mitochondria. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:2250–2255
Hell K, Neupert W, Stuart RA (2001) Oxa1p acts as a general membrane insertion machinery for proteins encoded by mitochondrial DNA. EMBO J 20:1281–1288
High S, Henry R, Mould RM, Valent Q, Meacock S, Cline K, Gray JC, Luirink J (1997) Chloroplast SRP54 interacts with a specific subset of thylakoid precursor proteins. J Biol Chem 272:11622–11628
Hoffman NE, Franklin AE (1994) Evidence for a stromal GTP requirement for the integration of a chlorophyll a/b-binding polypeptide into thylakoid membranes. Plant Physiol 105:295–304
Hoober JK, Eggink LL (1999) Assembly of light-harvesting complex II and biogenesis of thylakoid membranes in chloroplasts. Photosynth Res 61:197–215
Houben EN, Scotti PA, Valent QA, Brunner J, de Gier JL, Oudega B, Luirink J (2000) Nascent Lep inserts into the Escherichia coli inner membrane in the vicinity of YidC, SecY and SecA. FEBS Lett 476:229–233
Hutin C, Havaux M, Carde JP, Kloppstech K, Meiherhoff K, Hoffman N, Nussaume L (2002) Double mutation cpSRP43--/cpSRP54-- is necessary to abolish the cpSRP pathway required for thylakoid targeting of the light-harvesting chlorophyll proteins. Plant J 29:531–543
Jansson S (1999) A guide to the Lhc genes and their relatives in Arabidopsis. Trends Plant Sci 4:236–240
Jiang F, Yi L, Moore M, Chen M, Rohl T, van Wijk KJ, de Gier JW, Henry R, Dalbey R (2002) Chloroplast YidC homologue Albino3 can functionally complement the bacterial YidC depletion strain and promote membrane insertion of both bacterial and chloroplast thylakoid proteins. J Biol Chem 277:19281–19288
Johnson AE, van Waes MA (1999) The translocon: a dynamic gateway at the ER membrane. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 15:799–842
Jonas-Straube E, Hutin C, Hoffman NE, Schünemann D (2001) Functional analysis of the protein-interacting domains of chloroplast SRP43. J Biol Chem 276:24654–24660
Keenan RJ, Freymann DM, Stroud RM, Walter P (2001) The signal recognition particle. Ann Rev Biochem 70:755–775
Kermorgant M, Bonnefoy N, Dujardin G (1997) Oxa1p, which is required for cytochrome c oxidase and ATP synthase complex formation, is embedded in the mitochondrial inner membrane. Curr Genet 31:302–307
Kim SJ, Jansson S, Hoffman NE, Robinson C, Mant A (1999) Distinct “assisted” and “spontaneous” mechanisms for the insertion of polytopic chlorophyll-binding proteins into the thylakoid membrane. J Biol Chem 274:4715–4721
Klimyuk VI, Persello-Cartieaux F, Havaux M, Contard-David P, Schuenemann D, Meiherhoff K, Gouet P, Jones JD, Hoffman NE, Nussaume L (1999) A chromodomain protein encoded by the arabidopsis CAO gene is a plant- specific component of the chloroplast signal recognition particle pathway that is involved in LHCP targeting. Plant Cell 11:87–99
Klostermann E, Droste Gen Helling I, Carde JP, Schünemann D (2002) The thylakoid membrane protein ALB3 associates with the cpSecY-translocase in Arabidopsis thaliana. Biochem J 368:777–781
Kogata N, Nishio K, Hirohashi T, Kikuchi S, Nakai M (1999) Involvement of a chloroplast homologue of the signal recognition particle receptor protein, FtsY, in protein targeting to thylakoids. FEBS Lett 447:329–333
Koonin EV, Zhou S, Lucchesi JC (1995) The chromo superfamily: new members, duplication of the chromo domain and possible role in delivering transcription regulators to chromatin. Nucleic Acids Res 23:4229–33
Laan M van der, Houben EN, Nouwen N, Luirink J, Driessen AJ (2001) Reconstitution of Sec-dependent membrane protein insertion: nascent FtsQ interacts with YidC in a SecYEG-dependent manner. EMBO Rep 2:519–523
Leeuw E de, te Kaat K, Moser C, Menestrina G, Demel R, de Kruijff B, Oudega B, Luirink J, Sinning I (2000) Anionic phospholipids are involved in membrane association of FtsY and stimulate its GTPase activity. EMBO J 19:531–541
Li X, Henry R, Yuan J, Cline K, Hoffman NE (1995) A chloroplast homologue of the signal recognition particle subunit SRP54 is involved in the posttranslational integration of a protein into thylakoid membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92:3789–3793
Luirink J, ten Hagen-Jongman CM, van der Weijden CC, Oudega B, High S, Dobberstein B, Kusters R (1994) An alternative protein targeting pathway in Escherichia coli: studies on the role of FtsY. EMBO J 13:2289–2296
Martoglio B, Dobberstein B (1996) Snapshots of membrane-translocating proteins. Trends in Cell Biol 6:142–147
Moore M, Harrison MS, Peterson EC, Henry R (2000) Chloroplast Oxa1p homolog Albino3 is required for post-translational integration of the light harvesting chlorophyll-binding protein into thylakoid membranes. J Biol Chem 275:1529–1532
Mori H, Cline K (2001) Post-translational protein translocation into thylakoids by the Sec and DeltapH-dependent pathways. Biochim Biophys Acta 1541:80–90
Mori H, Summer EJ, Ma X, Cline K (1999) Component specificity for the thylakoidal Sec and Delta pH-dependent protein transport pathways. J Cell Biol 146:45–56
Mutka SC, Walter P (2001) Multifaceted physiological response allows yeast to adapt to the loss of the signal recognition particle-dependent protein-targeting pathway. Mol Biol Cell 12:577–588
Nilsson R, van Wijk KJ (2002) Transient interaction of cpSRP54 with elongating nascent chains of the chloroplast-encoded D1 protein: “cpSRP54 caught in the act.” FEBS Lett 524:127–133
Nilsson R, Brunner J, Hoffman NE, van Wijk KJ (1999) Interactions of ribosome nascent chain complexes of the chloroplast- encoded D1 thylakoid membrane protein with cpSRP54. EMBO J 18:733–742
Payan LA, Cline K (1991) A stromal protein factor maintains the solubility and insertion competence of an imported thylakoid membrane protein. J Cell Biol 112:603–613
Pilgrim ML, van Wijk KJ, Parry DH, Sy DA, Hoffman NE (1998) Expression of a dominant negative form of cpSRP54 inhibits chloroplast biogenesis in Arabidopsis. Plant J 13:177–186
Rapoport TA, Jungnickel B, Kutay U (1996) Protein transport across the eukaryotic endoplasmic reticulum and bacterial inner membranes. Annu Rev Biochem 65:271–303
Robinson C, Thompson SJ, Woolhead C (2001) Multiple pathways used for the targeting of thylakoid proteins in chloroplasts. Traffic 2:245–251
Samuelson JC, Chen M, Jiang F, Moller I, Wiedmann M, Kuhn A, Phillips GJ, Dalbey RE (2000) YidC mediates membrane protein insertion in bacteria. Nature 406:637–641
Samuelson JC, Jiang F, Yi L, Chen M, de Gier JW, Kuhn A, Dalbey RE (2001) Function of YidC for the insertion of M13 procoat protein in Escherichia coli: translocation of mutants that show differences in their membrane potential dependence and Sec requirement. J Biol Chem 276:34847–34852
Schleiff E, Klösgen RB (2001) Without a little help from “my” friends: direct insertion of proteins into chloroplast membranes? Biochim Biophys Acta 1541:22–33
Schünemann D, Gupta S, Persello-Cartieaux F, Klimyuk VI, Jones JDG, Nussaume L, Hoffman NE (1998) A novel signal recognition particle targets light-harvesting proteins to the thylakoid membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:10312–10316
Schünemann D, Amin P, Hoffman NE (1999) Functional divergence of the plastid and cytosolic forms of the 54-kDa subunit of signal recognition particle. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 254:253–258
Scotti PA, Urbanus ML, Brunner J, de Gier JW, von Heijne G, van der Does C, Driessen AJ, Oudega B, Luirink J (2000) YidC, the Escherichia coli homologue of mitochondrial Oxa1p, is a component of the Sec translocase. EMBO J 19:542–549
Sedgwick SG, Smerdon SJ (1999) The ankyrin repeat: a diversity of interactions on a common structural framework. Trends Biochem Sci 24:311–316
Sundberg E, Slagter JG, Fridborg I, Cleary SP, Robinson C, Coupland G (1997) ALBINO3, an Arabidopsis nuclear gene essential for chloroplast differentiation, encodes a chloroplast protein that shows homology to proteins present in bacterial membranes and yeast mitochondria. Plant Cell 9:717–730
Tu CJ, Schünemann D, Hoffman NE (1999) Chloroplast FtsY, chloroplast signal recognition particle, and GTP are required to reconstitute the soluble phase of light-harvesting chlorophyll protein transport into thylakoid membranes. J Biol Chem 274:27219–27224
Tu CJ, Peterson EC, Henry R, Hoffman NE (2000) The L18 domain of light-harvesting chlorophyll proteins binds to chloroplast signal recognition particle 43. J Biol Chem 275:13187–13190
Urbanus ML, Scotti PA, Froderberg L, Saaf A, de Gier JW, Brunner J, Samuelson JC, Dalbey RE, Oudega B, Luirink J (2001) Sec-dependent membrane protein insertion: sequential interaction of nascent FtsQ with SecY and YidC. EMBO Rep 2:524–529
Valent QA (2001) Signal recognition particle-mediated protein targeting in Escherichia coli. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 79:17–31
Valent QA, Scotti PA, High S, de Gier JW, von Heijne G, Lentzen G, Wintermeyer W, Oudega B, Luirink J (1998) The Escherichia coli SRP and SecB targeting pathways converge at the translocon. EMBO J 17:2504–2512
Vothknecht UC, Westhoff P (2001) Biogenesis and origin of thylakoid membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta 1541:91–101
Woolhead CA, Thompson SJ, Moore M, Tissier C, Mant A, Rodger A, Henry R, Robinson C (2001) Distinct Albino3-dependent and -independent pathways for thylakoid membrane protein insertion. J Biol Chem 276:40841–40846
Yamamoto HY, Bassi R (1996) Carotenoids: Localization and function. In: Ort DR, Yocum CF (eds) Oxygenic photosynthesis: the light reactions. Kluwer, The Netherlands, pp 539–563
Yuan J, Kight A, Goforth RL, Moore M, Peterson EC, Sakon J, Henry R (2002) ATP stimulates signal recognition particle (SRP)/FtsY-supported protein integration in chloroplasts. JBiol Chem 277:32400–32404
Zelazny A, Seluanov A, Cooper A, Bibi E (1997) The NG domain of the prokaryotic signal recognition particle receptor, FtsY, is fully functional when fused to an unrelated integral membrane polypeptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:6025–6029
Zhang LX, Paakkarinen V, Suorsa M, Aro EM (2001) A SecY homologue is involved in chloroplast-encoded D1 protein biogenesis. J Biol Chem 276:37809–37814
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by S. Hohmann
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schünemann, D. Structure and function of the chloroplast signal recognition particle. Curr Genet 44, 295–304 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00294-003-0450-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00294-003-0450-z