Abstract.
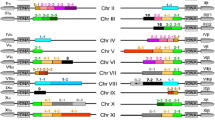
As part of the EULEISH international genome project, a region of 74,674 nucleotides from chromosome 21 of Leishmania major Friedlin was subcloned and sequenced; and 31 new coding sequences were predicted. Of particular interest was a unique coding strand switching region covering 1.6 kb of DNA; and this was subjected to further investigation. Bioinformatic analysis of this region revealed an unusually high AT composition, a lack of putative hairpins and a strong curvature of the DNA in agreement with the structural characteristics of similar regions of other Leishmania chromosomes. These observations and a comparison with the secondary DNA structure of four other Leishmania chromosomes and chromosomes of different organisms could suggest a functional role of this region in transcription and mitotic division.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tosato, V., Ciarloni, L., Ivens, A.C. et al. Secondary DNA structure analysis of the coding strand switch regions of five Leishmania major Friedlin chromosomes. Curr Genet 40, 186–194 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002940100246
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002940100246