Abstract
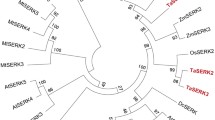
We report here the isolation and characterization of three SOMATIC EMBRYOGENESIS RECEPTOR KINASE (TaSERK) genes from wheat. TaSERKs belong to a small family of receptor-like kinase genes, share a conserved structure and extensive sequence homology with previously reported plant SERK genes. TaSERK genes are in general auxin inducible and expressed during embryogenesis in cell cultures. We show here that somatic embryogenesis in Triticum aestivum is associated with high SERK expression which could be enhanced with auxin application and is calcium dependent. TaSERK transcripts could also be enhanced by epibrassinolide and abscisic acid. TaSERK1 and TaSERK2 may have a role in somatic embryogenesis, whereas TaSERK3 appears to be a brassinosteroid-associated kinase (BAK) lacking an SPP motif but shares a characteristic C-terminal domain with other SERK proteins. Also, the transcripts of all the three TaSERK genes could be induced in zygotic and somatic tissues. Although our analysis suggests them to be involved in somatic embryogenesis, they may have a broader role in acquiring embryogenic competence in wheat.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- SE:
-
Somatic embryogenesis
- SERK:
-
Somatic embryogenesis receptor-like kinase
- RLK:
-
Receptor-like kinase
- 2,4-D:
-
2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid
References
Abel S, Nguyen MD, Theologis A (1995) The PS-IAA4/5-like family of early auxin-inducible mRNAs in Arabidopsis thaliana. J Mol Biol 251:533–549
Albertini E, Marconi G, Reale L, Barcaccia G, Porceddes A, Ferranti F, Falcinelli M (2005) SERK and APOSTART. Candidate genes for apomixis in Poa pratensis. Plant Physiol 138:2185–2194
Albrecht C, Russinova E, Hecht V, Baaijens E, de Vries S (2005) The Arabidopsis thaliana somatic embryogenesis receptor like kinases1 and 2 control male sporogenesis. Plant Cell 17:3337–3349
Anil VS, Rao KS (2000) Calcium-mediated signaling during sandalwood somatic embryogenesis. Role for exogenous calcium as second messenger. Plant Physiol 123:1301–1311
Baudino S, Hansen S, Brettschneider R, Hecht VFG, Dresselhaus T, Lorz H, Dumas C, Rogowsky PM (2001) Molecular characterization of two novel maize LRR receptor-like kinases, which belong to the SERK gene family. Planta 213:1–10
Becraft PW (2002) Receptor kinase signaling in plant development. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 18:163–192
Boutilier K, Offringa R, Sharma VK, Kieft H, Ouellet T, Zhang L, Hattori J, Liu C-M, van Lammeren AAM, Miki BLA, Custers JBN, van Lookeren Campage MM (2002) Ectopic expression of BABY BOOM triggers a conversion from vegetative to embryonic growth. Plant Cell 14:1737–1749
Braybrook SA, Stone SL, Park S, Bui AQ, Brandon HL, Fischer R, Goldberg RB, Harada JJ (2006) Genes directly regulated by LEAFY COTYLEDON2 provide insight into the control of embryo maturation and somatic embryogenesis. Pro Natl Acad Sci USA 103:3468–3473
Chugh A, Khurana P (2002) Gene expression during somatic embryogenesis-recent advances. Curr Sci 83:715–730
Colcombet J, Bossom-Dernier A, Ros-Palan R, Vena CE, Schroeder JI (2005) Arabidopsis SOMATIC EMBRYOGENESIS RECEPTOR KINASE1 and 2 are essential for tapetum development and microspore maturation. Plant Cell 17:3350–3361
Davletava S, Meszaros T, Miskolczi P, Obersschall A, Torok K, Magyar Z, Dudits D, Deak M (2001) Auxin and heat shock activation of a novel member of the calmodulin like domain protein kinase gene family in cultured alfalfa cells. J Exp Bot 52:215–221
Dellaporta SL, Wood J, Hicks JB (1983) A plant DNA minipreparation: version II. Plant Mol Biol Rep 4:19–21
Douville EM, Afar DE, Howell BW, Letwin K, Tannock L, Ben-David Y, Pawson T, Bell JC (1992) Multiple cDNAs encoding the esk kinase predict transmembrane and intracellular enzyme isoforms. Mol Cell Biol 12:2681–2689
Du L, Poovaiah BW (2005) Ca2+/calmodulin is critical for brassinosteroid biosynthesis and plant growth. Nature 437:741–745
Dudits D, Bogre L, Gyorgyey J (1991) Molecular and cellular approaches to the analysis of plant embryo development from somatic cells in vitro. J Cell Sci 99:475–484
Fambrini M, Durante C, Cionini G, Geri C, Giorgetti L, Michelotti, Salvini M, Pugliesi C (2006) Characterization of LEAFY COTYLEDON1-LIKE gene in Helianthus annuus and its relationship with zygotic and somatic embryogenesis. Dev Genes Evol 216:253–264
Feher A, Pasternak TP, Dudits D (2003) Transition of somatic cells to an embryogenic state. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 74:201–228
Gaj MD, Zhang S, Harada JJ, Lemaux G (2005) Leafy cotyledon genes are essential for induction of somatic embryogenesis of Arabidopsis. Planta 222:977–988
Hanks SK, Quinn AM, Hunter T (1988) The protein kinase family:conserved features and deduced phylogeny of the catalytic domains. Science 241:42–52
Harada JJ (2001) Role of Arabidopsis LEAFY COTYLEDON genes in seed development. J Plant Physiol 158:405–409
Hecht V, Vielle-Calzada J-P, Hartog MV, Schmidt ED, Boutilier K, Grossniklaus U, de Vries SC (2001) The Arabidopsis somatic embryogenesis receptor kinase 1 gene is expressed in developing ovules and embryos and enhances embryogenic competence in cultures. Plant Physiol 127:803–816
Hofmann K, Bucher P, Falquet L, Bairoch A (1999) The PROSITE database: its status in 1999. Nucl Acids Res 27:215–219
Hu H, Xiong L, Yang Y (2005) Rice SERK1 gene positively regulates somatic embryoenesis of cultured cell and host defense response against fungal infection. Planta 222:107–117
Ito Y, Takaya K, Kurata N (2005) Expression of SERK family receptor-like protein kinase genes in rice. Biochim Biophys Acta 1730:253–258
Jansen MAK, Booij H, Schel JHN, de Vries SC (1990) Calcium increases the yield of somatic embryos in carrot embryogenic suspension cultures. Plant Cell Rep 9:221–223
Khurana J, Chugh A, Khurana P (2002) Regeneration from mature and immature embryos and transient gene expression via Agrobacterium-mediated transformation in emmer wheat (Triticum dicoccum Schuble). Indian J Exp Biol 40:295–303
Krupa A, Anamika, Srinivasan N (2006) Genome-wide comparative analyses of domain organisation of repertoires of protein kinases of Arabidopsis thaliana and Oryza sativa. Gene 380:1–13
Kwong RM, Bui AQ, Lee IL, Kwong LW, Fischer RL, Goldberg RB, Harada JJ (2003) LEAFY COTYLEDON-LIKE defines a class of regulators essential for embryo development. Plant Cell 15:5–18
Li J, Wen J, Lease KA, Doke JT, Tax FE, Walker JC (2002) BAK1, an Arabidopsis LRR receptor-like protein kinase, interacts with BRI1 and modulates brassinosteroid signaling. Cell 110:213–222
Li L, Xu J, Xu Z-H, Xue H-W (2005) Brassinosteroids stimulate plant tropisms through modulation of polar auxin transport in Brassica and Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 17(10):2738–2753
Lotan T, Ohto M, Yee KM, West MAL, Lo R, Kwong RW, Yamagishi K, Fischer RL, Goldberg RB, Harada JJ (1998) Arabidopsis LEAFY COTYLEDON1 is sufficient to induce embryo development in vegetative cells. Cell 93:1195–1205
Mahalakshmi A, Khurana JP, Khurana P (2003) Rapid induction of somatic embryogenesis by 2,4-D in leaf base cultures of wheat (Triticum aestivum L). Plant Biotech 20:267–273
Mahalakshmi A, Singla B, Khurana JP, Khurana P (2007) Role of calcium-calmodulin in auxin-induced somatic embryogenesis in leaf base cultures of wheat (Triticum aestivum var. HD 2329). Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 88:167–174
Mordhorst AP, Toonen MAJ, de Vries SC (1997) Plant embryogenesis. Crit Rev Plant Sci 16:535–576
Mordhorst AP, Voerman KJ, Hartog MV, Meijer EA, van Went J, Koornneef M, de Vries SC (1998) Somatic embryogenesis in Arabidopsis thaliana is facilitated by mutations in genes repressing meristematic cell divisions. Genetics 149:549–563
Nakai K, Kanehisa M (1992) A knowledge base for predicting protein localization sites in eukaryotic cells. Genomics 14:215–219
Nakamura A, Higuchi K, Goda H, Fujiwara MT, Sawa S, Koshiba T, Shimada Y, Yoshida S (2003) Brassinolide induces IAA5, IAA19, and DR5, a synthetic auxin response element in Arabidopsis, implying a cross talk point of brassinosteroid and auxin signaling. Plant Physiol 133:1843–1853
Nakamura A, Nakajima N, Shimada H, Hayashi K, Nozaki H, Asami T, Yoshida S, Fujioka S (2006) Arabidopsis Aux/IAA genes are involved in brassinosteroid-mediated growth responses in a manner dependent on organ type. Plant J 45:193–205
Nam KH, Li J (2002) BRI1.BAK1, a receptor kinase pair mediating brassinosteriod signaling. Cell 110:203–212
Nolan KE, Irwanto RR, Rose RJ (2003) Auxin up-regulates MtSERK1 expression in both Medicago truncatula root-forming and embryogenic cultures. Plant Physiol 133:218–230
Nomura K, Komamine A (1995) Physiological and biochemical aspects of somatic embryogenesis. In: Thorpe TA (ed) In vitro embryogenesis in plants. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, pp 249–266
Overvoorde PI, Grimes HD (1994) The role of calcium and calmodulin in carrot somatic embryo. Plant Cell Physiol 35:135–144
Patnaik D, Khurana P (2005) Identifictaion of a phosphoprotein expressed during somatic embryogenesis in wheat leaf base cultures. J Plant Biochem Biotech 14:149–154
Russinova E, Borst JW, Kwaaitaal M, Cano-Delgado A, Yin Y, Chory J, de Vries SC (2004) Heterodimerization and endocytosis of Arabidopsis brassinosteroid receptors BRI1 and AtSERK3 (BAK1). Plant Cell 16:3216–3229
Sasse J (1999) Physiological actions of brassinosteroids. In: Sakurai A, Yokota T, Clouse SD (ed) Brassinosteroids: steroidal plant hormones. Springer-Verlag, Tokyo, pp 137–161
Schmidt EDL, Guzzo F, Toonen MAJ, de Vries SC (1997) A leucine rich repeat containing receptor-like kinase marks somatic plant cells competent to form embryos. Development 124:2049–2062
Shah K, Gadella TW Jr, van Erp H, Hecht V, de Vries SC (2001a) Subcellular localization and oligomerization of the Arabidopsis thaliana somatic embryogenesis receptor kinase 1 protein. J Mol Biol 309(3):641–655
Shah K, Vervoort J, de Vries SC (2001b) Role of threonines in Arabidopsis thaliana somatic embryogenesis receptor kinase 1 activation loop in phopsphorylation. J Biol Chem 276:41263–41269
Shah K, Schmidt ED, Vlak JM, de Vries SC (2001c) Expression of the Daucus carota somatic embryogenesis receptor kinase (DcSERK) protein in insect cells. Biochimie 83:415–421
Shah K, Russinova E, Gadela TWJ Jr, Willemse J, de Vries SC (2002) The Arabidopsis kinase-associated protein phosphatase controls internalization of the somatic embryogenesis receptor kinase 1. Genes Dev 16:1707–1720
Shimada T, Kita M, Endo T, Fujii H, Ueda T, Moriguchi T, Omura M (2003) Expressed sequence tags of ovary tissue cDNA library in Citrus unshiu Marc. cDNA. Plant Sci 165:167–168
Shimada T, Hirabayashi T, endo T, Fujii H, Kita M, Omura M (2005) Isolation and characterization of the somatic embryogenesis receptor-like kinase gene homologue (CiSERK1) from Citrus unshiu Marc. Sci Horticult 103:233–238
Shiu SH, Bleecker AB (2001) Receptor-like kinases from Arabidopsis form a monophyletic gene family related to animal receptor kinases. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:10763–10768
Singla B, Khurana JP, Khurana P (2006) An early auxin-responsive Aux/IAA gene from wheat (Triticum aestivum) is induced by epibrassinolide and differentially regulated by light and calcium. J Exp Bot 57:4059–4070
Singla B, Tyagi AK, Khurana JP, Khurana P (2007) Analysis of expression profile of selected genes expressed during auxin-induced somatic embryogenesis in leaf base system of wheat (Triticum aestivum) and their possible interactions. Plant Mol Biol 65:677–692
Snedden WA, Fromm H (2001) Calmodulin as a versatile signal transducer in plants. New Phytol 151:35–66
Somleva MN, Schmidt EDL, de Vries SC (2000) Embryogenic cells in Dactylis glomerata L. (Poaceae) explants identified by cell tracking and by SERK expression. Plant Cell Rep 19:718–726
Stone SL, Kwong LW, Yee KM, Pelletier J, Lepiniec L, Fischer RL, Goldberg RB, Harada JJ (2001) LEAFY COTYLEDON2 encodes B3 domain transcription factor that induces embryo development. Pro Natl Acad Sci USA 98:11806–11811
Thibaud-Nissen F, Shealy RT, Khanna A, Vodkin LO (2003) Clustering of microarray data reveals transcript patterns associated with somatic embryogenesis in soybean. Plant Physiol 132:118–136
Thomas C, Meyer D, Himber C, Steinmetz A (2004) Spatial expression of a sunflower SERK gene during induction of somatic embryogenesis and shoot organogenesis. Plant Physiol Biochem 42:35–42
Torii KU (2004) Leucine-rich repeat receptor kinases in plants: structure, function, and signal transduction pathways. Int Rev Cytol 234:1–46
Ullrich A, Schlessinger J (1990) Signal transduction by receptors with tyrosine kinase activity. Cell 61:203–212
Walker JC (1994) Structure and function of the receptor-like protein kinases of higher plants. Plant Mol Biol 26:1599–1609
Yang T, Poovaiah BW (2003) Calcium/calmodulin-mediated signal network in plants. Trends Plant Sci 8:505–512
Yazawa K, Takahata K, Kamada H (2004) Isolation of the gene encoding carrot leafy cotyledon 1 and expression analysis during somatic and zygotic embryogenesis. Plant Physiol Biochem 42:215–223
Zhang S, Wong L, Meng L, Lemaux PG (2002) Similarity of expression patterns of knotted1 and ZmLEC1 during somatic embryogenesis in maize (Zea mays L.). Planta 215:191–194
Zuo J, Niu QW, Frugis G, Chua NH (2002) The WUSCHEL gene promotes vegetative-to-embryonic transition in Arabidopsis. Plant J 30:349–359
Acknowledgments
B.S. acknowledges the award of Senior Research Fellowship from the University Grants Commission, New Delhi. This research work was financially supported by the Department of Biotechnology, Government of India, and the University Grants Commission, New Delhi.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by P. Kumar.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
299_2008_505_MOESM1_ESM.doc
Supplementary Figure 1 Alignment of deduced amino acid sequence of TaSERK1 and TaSERK2 with sequences of other SERK proteins. Conserved domains I to XI are marked with lines at the top and labeled. The hydrophobic amino acid in the signal peptide sequence is highly conserved, depicted by dark gray color, highlighted in purple and blue color is the ATP-binding region and the activation loop, respectively. Red color in sub domain VIII of protein kinase shows the threonine at position 468. The active site of SERK proteins is depicted by brown color. Pink colors show the glycosylation sites and gray color highlights the membrane spanning region. In fluorescent blue color are the 15 invariant amino acids. (DOC 52 kb)
299_2008_505_MOESM2_ESM.ppt
Supplementary Figure 2 Southern analysis of wheat genomic DNA with TaSERK1 probe. An aliquot of 20 μg wheat (T. aestivum) DNA was digested with restriction endonuclease, BglII and Southern hybridization carried out under stringent conditions. (A) The kinase domain and the C-terminal region were used as a probe for highlighting the gene family, and (B) the 3’UTR region was used for specificity. (PPT 3222 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singla, B., Khurana, J.P. & Khurana, P. Characterization of three somatic embryogenesis receptor kinase genes from wheat, Triticum aestivum . Plant Cell Rep 27, 833–843 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-008-0505-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-008-0505-1