Abstract
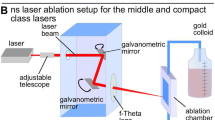
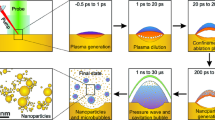
Femtosecond laser radiation has been used to ablate a gold target in pure deionized water to produce gold colloids. The dimensional distribution of nanoparticles is characterized by the simultaneous presence of two distinct particle populations: one with low dispersion, having a mean particle size of 5–20 nm, and one with high dispersion, having a much larger particle size. By changing the target position with respect to the radiation focus, we study the influence of the plasma formed after the laser pulse in front of the target, during nanofabrication process. We show that the most intense plasma is produced by positioning the target slightly before the geometric focal point. Here, the plasma intensity was found to correlate with the amount of ablated material as well as with the mean size of nanoparticles associated with the second, highly dispersed, distribution of nanoparticles; this suggests the involvement of plasma-related processes in the ablation of material, and the formation of relatively large particles. The thermal heating of the target by the plasma, and its mechanical erosion by the collapse of a plasma-induced cavitation bubble are discussed as possible ablation mechanisms. The gold nanoparticles produced in ultrapure water are of importance for biosensing applications.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
D.A. Schultz: Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 14, 13 (2003)
I. Lisiecki, M.P. Pileni: J. Am. Chem. Soc. 115, 3887 (1993)
A. Fojtik, A. Henglein: Ber. Bunsen-Ges. Phys. Chem. 97, 252 (1993)
J. Nedderson, G. Chumanov, T.M. Cotton: Appl. Spectrosc. 47, 1959 (1993)
M. Prochazka, J. Stepanek, B. Vlckova, I. Srnova, P. Maly: J. Mol. Struct. 410, 213 (1997)
F. Mafuné, J.-Y. Kohno, Y. Takeda, T. Kondow, H. Sawabe: J. Phys. Chem. B 104, 8333 (2000)
F. Mafuné, J.-Y. Kohno, Y. Takeda, T. Kondow, H. Sawabe: J. Phys. Chem. B 104, 9111 (2000)
F. Mafuné, J.-Y. Kohno, Y. Takeda, T. Kondow: J. Phys. Chem. B 105, 5114 (2001)
F. Mafuné, J.-Y. Kohno, Y. Takeda, T. Kondow: J. Phys. Chem. B 107, 4218 (2003)
Y.-H. Chen, C.S. Yeh: Coll. Surf. A 197, 133 (2002)
A.V. Kabashin, M. Meunier, C. Kingston, J.H.T. Luong: J. Phys. Chem. B 107, 4527 (2003)
J.-P. Sylvestre, A.V. Kabashin, E. Sacher, M. Meunier, J.H.T. Luong: J. Am. Chem. Soc. 126, 7176 (2004)
J.-S Jeon, C.-S. Yeh: J. Chin. Chem. Soc. 45, 721 (1998)
A.V. Simakin, V.V. Voronov, G.A. Shafeev, R. Brayner, F. Bozon-Verduraz: Chem. Phys. Lett. 348, 182 (2001)
S.I. Dolgaev, A.V. Simakin, V.V. Voronov, G.A. Shafeev, F. Bozon-Verduraz: Appl. Surf. Sci. 186, 546 (2002)
T. Tsuji, K. Iryo, N. Watanabe, M. Tsuji: Appl. Surf. Sci. 202, 80 (2002)
T. Tsuji, T. Kakita, M. Tsuji: Appl. Surf. Sci. 206, 314 (2003)
A.V. Kabashin, M. Meunier: J. Appl. Phys. 94, 7941 (2003)
G. Compagnini, A.A. Scalisi, O. Puglisi: Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 4, 2787 (2002)
J. Szejtli: Chem. Rev. 98, 1743 (1998)
A. Brodeur, S.L. Chin: Phys. Rev. Lett. 80, 4406 (1998)
A. Vogel, J. Noack, K. Nahen, D. Theisen, S. Busch, U. Parlitz, D.X. Hammer, G.D. Noojin, B.A. Rockwell, R. Birngruber: Appl. Phys. B 68, 271 (1999)
P.K. Kennedy, D.X. Hammer, B.A. Rockwell: Prog. Quantum Electr. 21, 155 (1997)
J.F. Ready, D.F. Farson, Eds.: LIA Handbook of Laser Materials Processing (Springer, Heidelberg 2001)
L.A. Chiu, A.A. Seraphin, K.D. Kolenbrander: J. Electron. Mater. 23, 347 (1994)
D.B. Geohegan, A.A. Puretzky, G. Duscher, S.J. Pennycook: Appl. Phys Lett. 72, 2987 (1998)
W. Liu, O. Kosareva, I.S. Golubstov, A. Iwasaki, A. Becker, V.P. Kandidov, S.L. Chin: Appl. Phys. B 76, 215 (2003)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
PACS
81.07.-b; 81.16.-c
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sylvestre, JP., Kabashin, A., Sacher, E. et al. Femtosecond laser ablation of gold in water: influence of the laser-produced plasma on the nanoparticle size distribution. Appl. Phys. A 80, 753–758 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-004-3081-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-004-3081-4