Summary.
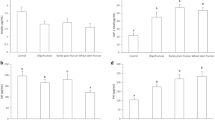
Background: Inulin-type fructans or chains with mainly β[2–1] linked fructose molecules escape the ingestion procedure in the small intestine and are fermented by the microflora, and are known to increase colonic absorption of minerals in animals. The fermentation rate in the large bowel into short-chain fatty acids depends on the molecular mass and the structure of these food ingredients. It is thought that this colonic fermentation is the basis for the reported increase in mineral absorption. Aim of the study: The purpose of the present study was twofold: a) to compare different types of fructans that differ in the sugar chain length and in chain branching; b) to determine the potential synergistic effect of a combination of inulin-type fructans with different chain lengths. Methods: For this purpose, 50 adult male Wistar rats weighing 170 g each were used in this study. The rats were distributed into 5 groups and fed for 28 days a fiber-free basal purified diet or diet containing 10 % oligofructose (OF) (DPav 4), or 10 % HP-inulin (DPav 25), a blend of 50 % OF and 50 % HP-inulin, or a branched-chain inulin. Results: During the first period, the rats went into a gradual adaptation, during which the rats received 2.5 % for 1 week and then 5 % for 1 week of the tested products. During the last 4 days of the experiment, feces and urine were monitored for mineral balance study. The animals were then sacrificed and blood, cecum and tibia were sampled for mineral status assessment. Our results showed that the ingestion of all the tested fructans led to a considerable cecal fermentation. All tested compounds increased the intestinal absorption and balance of Mg significantly. Interestingly, in the present experimental set-up, all tested compounds increased the intestinal absorption and balance of Ca numerically, but only the blend OF + HP-inulin increased apparent intestinal absorption and balance of Ca significantly. Conclusions: The different types of fructans studied in the present experiment seem to have similar activity on mineral absorption. However, the combination of OF and HP-inulin showed synergistic effects on intestinal Ca absorption and balance in rats. Further studies with other combinations of fructans need to be done to extend these findings.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 5 August 2002, Accepted: 4 November 2002
Correspondence to: Charles Coudray
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Coudray, C., Tressol, J., Gueux, E. et al. Effects of inulin-type fructans of different chain length and type of branching on intestinal absorption and balance of calcium and magnesium in rats. Eur J Nutr 42, 91–98 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-003-0390-x
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-003-0390-x