Abstract
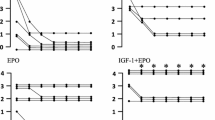
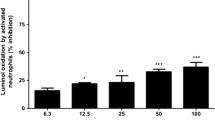
The immediate protective effect of erythropoietin (EPO) against ischemia in heart suggests a role beyond hematopoiesis and the treatment of anemia. We determined the role of JAK/STAT and Ras/Rac/MAPK in the protective effect of EPO against ischemia–reperfusion injury in infant rabbit heart. EPO (1.0 U/ml) administered 15 minutes prior to 30–minutes global ischemia and 35 minutes reperfusion resulted in increased recovery of postischemic ventricular developed pressure in rabbit hearts. EPO exerted its immediate cardioprotective effect via activation of multiple signaling pathways by: 1) phosphorylation and activation of JAK1/2, STAT3 and STAT5A but not of STAT1α and STAT5B, 2) phosphorylation and activation of PI3 kinase and its downstream kinases Akt and Rac, 3) activation of PKCε, Raf, MEK1/2, p42/44 MAPK and p38 MAPK. Pretreatment with Wortmannin abolished EPO–induced Akt activation and phosphorylation. Pretreatment with Chelerythrine followed by EPO treatment resulted in partial inhibition of Raf activation, and abolished PKCε and p38 MAPK activation without any effect on Akt, MEK1/2 and p42/44 MAPK. PD98059 abolished MEK1/2 and p42/44 MAPK activation with no effect on Akt, Raf and p38 MAPK activation. SB203580 inhibited only p38 MAPK activation by EPO. We can conclude EPO increases immediate cardioprotection through the activation of multiple signal transduction pathways.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agnello D, Bigini P, Villa P, Mennini T, Cerami A, Brines ML, Ghezzi P (2002) Erythropoietin exerts an anti-inflammatory effect on the CNS in a model of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Brain Res 952:128–134
Alblas J, Slager-Davidov R, Steenbergh PH, Sussenbach JS, van der Burg B (1998) The role of MAP kinase in TPA-mediated cell cycle arrest of human breast cancer cells. Oncogene 16:131–139
Ammarguellat F, Llovera M, Kelly PA, Goffin V (2001) Low doses of EPO activate MAP kinases but not JAK2-STAT5 in rat vascular smooth muscle cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 284:1031–1038
Arai A, Kanda E, Miura O (2002) Rac is activated by erythropoietin or interleukin-3 and is involved in activation of the Erk signaling pathway. Oncogene 21:2641–2651
Baker JE, Holman P, Gross GJ (1999) Preconditioning in immature rabbit hearts: role of KATP channels. Circulation 99:1249–1254
Boer AK, Drayer AL, Rui H, Vellenga E (2002) Prostaglandin-E2 enhances EPOmediated STAT5 transcriptional activity by serine phosphorylation of CREB. Blood 100:467–473
Booz GW, Day JN, Baker KM (2002) Interplay between the cardiac renin angiotensin system and JAK-STAT signaling: role in cardiac hypertrophy, ischemia/ reperfusion dysfunction, and heart failure. J Mol Cell Cardiol 34:1443–1453
Booz GW, Day JN, Speth R, Baker KM (2002) Cytokine G-protein signaling crosstalk in cardiomyocytes: attenuation of Jak-STAT activation by endothelin-1. Mol Cell Biochem 240:39–46
Brar BK, Stephanou A, Knight R, Latchman DS (2002) Activation of protein kinase B/Akt by urocortin is essential for its ability to protect cardiac cells against hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced cell death. J Mol Cell Cardiol 34:483–492
Burgering BM, Coffer PJ (1995) Protein kinase B (c-Akt) in phosphatidylinositol- 3-OH kinase signal transduction. Nature 376:599–602
Carroll MP, May WS (1994) Protein kinase C-mediated serine phosphorylation directly activates Raf-1 in murine hematopoietic cells. J Biol Chem 269:1249–1256
Chen C, Sytkowski AJ (2001) Erythropoietin activates two distinct signaling pathways required for the initiation and the elongation of c-myc. J Biol Chem 276:38518–38526
Devemy E, Billat C, Haye B (1997) Activation of Raf-1 and mitogen-activated protein kinases by erythropoietin and inositolphosphate- glycan in normal erythroid progenitor cells: involvement of protein kinase C. Cell Signal 9:41–46
Digicaylioglu M, Lipton SA (2001) Erythropoietin- mediated neuroprotection involves cross-talk between Jak2 and NF-kappaB signalling cascades. Nature 412:641–647
Dolznig H, Habermann B, Stangl K, Deiner EM, Moriggl R, Beug H, Mullner EW (2002) Apoptosis protection by the Epo target Bcl-X(L) allows factor-independent differentiation of primary erythroblasts. Curr Biol 12:1076–1085
Figueroa C, Tarras S, Taylor J, Vojtek AB (2003) Akt2 negatively regulates assembly of the POSH-MLK-JNK signaling complex. J Biol Chem 278:47922–47927
Figueroa C, Vojtek AB (2003) Akt negatively regulates translation of the ternary complex factor Elk-1. Oncogene 22:5554–5561
Franke TF, Kaplan DR, Cantley LC (1997) PI3K: downstream AKTion blocks apoptosis. Cell 88:435–437
Franke TF, Yang SI, Chan TO, Datta K, Kazlauskas A, Morrison DK, Kaplan DR, Tsichlis PN (1995) The protein kinase encoded by the Akt proto-oncogene is a target of the PDGF-activated phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. Cell 81:727–736
Hausenloy DJ, Mocanu MM, Yellon DM (2004) Cross-talk between the survival kinases during early reperfusion: its contribution to ischemic preconditioning. Cardiovasc Res 63:305–312
Hausenloy DJ, Mocanu MM, Yellon DM (2005) Ischemic Preconditioning Protects by Activating Pro-Survival Kinases at Reperfusion. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 288:H971–H976
Hu E, Kim JB, Sarraf P, Spiegelman BM (1996) Inhibition of adipogenesis through MAP kinase-mediated phosphorylation of PPARgamma. Science 274:2100–2103
Jiang BH, Aoki M, Zheng JZ, Li J, Vogt PK (1999) Myogenic signaling of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase requires the serinethreonine kinase Akt/protein kinase B. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:2077–2081
Kis A, Yellon DM, Baxter GF (2003) Second window of protection following myocardial preconditioning: an essential role for PI3 kinase and p70S6 kinase. J Mol Cell Cardiol 35:1063–1071
Light PE, Bladen C, Winkfein RJ, Walsh MP, French RJ (2000) Molecular basis of protein kinase C-induced activation of ATP-sensitive potassium channels. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:9058–9063
Mancini DM, Katz SD, Lang CC, LaManca J, Hudaihed A, Androne AS (2003) Effect of erythropoietin on exercise capacity in patients with moderate to severe chronic heart failure. Circulation 107:294–299
Michaud NR, Fabian JR, Mathes KD, Morrison DK (1995) 14-3-3 is not essential for Raf-1 function: identification of Raf-1 proteins that are biologically activated in a 14-3-3- and Ras-independent manner. Mol Cell Biol 15:3390–3397
Mocanu MM, Baxter GF, Yue Y, Critz SD, Yellon DM (2000) The p38 MAPK inhibitor, SB203580, abrogates ischaemic preconditioning in rat heart but timing of administration is critical. Basic Res Cardiol 95:472–478
Muslin AJ, Tanner JW, Allen PM, Shaw AS (1996) Interaction of 14-3-3 with signaling proteins is mediated by the recognition of phosphoserine. Cell 84:889–897
Okutani Y, Kitanaka A, Tanaka T, Kamano H, Ohnishi H, Kubota Y, Ishida T, Takahara J (2001) Src directly tyrosinephosphorylates STAT5 on its activation site and is involved in erythropoietininduced signaling pathway. Oncogene 20:6643–6650
Omura T, Yoshiyama M, Ishikura F, Kobayashi H, Takeuchi K, Beppu S, Yoshikawa J (2001) Myocardial ischemia activates the JAK-STAT pathway through angiotensin II signaling in in vivo myocardium of rats. J Mol Cell Cardiol 33:307–316
Pain T, Yang XM, Critz SD, Yue Y, Nakano A, Liu GS, Heusch G, Cohen MV, Downey JM (2000) Opening of mitochondrial K(ATP) channels triggers the preconditioned state by generating free radicals. Circ Res 87:460–466
Rafiee P, Shi Y, Kong X, Pritchard KA Jr, Tweddell JS, Litwin SB, Mussatto K, Jaquiss RD, Su J, Baker JE (2002) Activation of protein kinases in chronically hypoxic infant human and rabbit hearts: role in cardioprotection. Circulation 106:239–245
Rodriguez-Viciana P, Warne PH, Khwaja A, Marte BM, Pappin D, Das P, Waterfield MD, Ridley A, Downward J (1997) Role of phosphoinositide 3-OH kinase in cell transformation and control of the actin cytoskeleton by Ras. Cell 89:457–467
Shi Y, Rafiee P, Su J, Pritchard Jr K, Tweddell J, Baker J (2004) Acute cardioprotective effects of erythropoietin in infant rabbits are mediated by activation of protein kinases and potassium channels. Basic Res Cardiol 99:173–182
Silverberg DS, Wexler D, Blum M, Keren G, Sheps D, Leibovitch E, Brosh D, Laniado S, Schwartz D, Yachnin T, Shapira I, Gavish D, Baruch R, Koifman B, Kaplan C, Steinbruch S, Iaina A (2000) The use of subcutaneous erythropoietin and intravenous iron for the treatment of the anemia of severe, resistant congestive heart failure improves cardiac and renal function and functional cardiac class, and markedly reduces hospitalizations. J Am Coll Cardiol 35:1737–1744
Stephanou A, Brar BK, Scarabelli TM, Jonassen AK, Yellon DM, Marber MS, Knight RA, Latchman DS (2000) Ischemia-induced STAT-1 expression and activation play a critical role in cardiomyocyte apoptosis. J Biol Chem 275:10002–10008
Tilbrook PA, Colley SM, McCarthy DJ, Marais R, Klinken SP (2001) Erythropoietin- stimulated Raf-1 tyrosine phosphorylation is associated with the tyrosine kinase Lyn in J2E erythroleukemic cells. Arch Biochem Biophys 396:128–132
Tsang A, Hausenloy DJ, Mocanu MM, Yellon DM (2004) Postconditioning: a form of “modi.ed reperfusion” protects the myocardium by activating the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-Akt pathway. Circ Res 95:230–232
Xuan YT, Guo Y, Han H, Zhu Y, Bolli R (2001) An essential role of the JAK-STAT pathway in ischemic preconditioning. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:9050–9055
Yamaura G, Turoczi T, Yamamoto F, Siddqui MA, Maulik N, Das DK (2003) STAT signaling in ischemic heart: a role of STAT5A in ischemic preconditioning. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 285:H476–482
Zimmermann S, Moelling K (1999) Phosphorylation and regulation of Raf by Akt (protein kinase B). Science 286:1741–1744
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rafiee, P., Shi, Y., Su, J. et al. Erythropoietin protects the infant heart against ischemia–reperfusion injury by triggering multiple signaling pathways. Basic Res Cardiol 100, 187–197 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00395-004-0508-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00395-004-0508-1