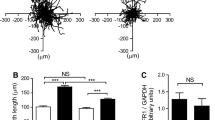
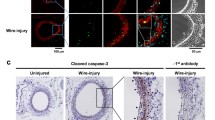
Abstract
Vascular smooth muscle cell (VSMC) proliferation and migration is responsible for intimal thickening that occurs in restenosis and atherosclerosis. Integrin-linked kinase (ILK) is a serine/threonine protein kinase implicated in signaling pathways involved in cell proliferation and migration. We studied the involvement of ILK in intimal thickening. ILK expression was significantly increased in two models of intimal thickening: balloon-injured rat carotid arteries and human saphenous vein organ cultures. Over-expression of a dominant negative ILK (DN-ILK) significantly reduced intimal thickening by approximately 50% in human saphenous vein organ cultures, demonstrating an important role in intimal thickening. ILK protein and activity was reduced on laminin and up-regulated on fibronectin, indicating ILK protein expression is modulated by extracellular matrix composition. Inhibition of ILK by siRNA knockdown and DN-ILK significantly decreased VSMC proliferation and migration while wild type ILK significantly increased proliferation and migration on laminin, confirming an essential role of ILK in both processes. Localization of paxillin and vinculin and protein levels of FAK and phospho-FAK indicated that inhibition of ILK reduced focal adhesion formation. Additionally, inhibition of ILK significantly attenuated the presence of the cell–cell complex proteins N-cadherin and β-catenin, and β-catenin signaling. We therefore suggest ILK modulates VSMC proliferation and migration at least in part by acting as a molecular scaffold in focal adhesions as well as modulating the stability of cell–cell contact proteins and β-catenin signaling. In summary, ILK plays an important role in intimal thickening by modulating VSMC proliferation and migration via regulation of cell–matrix and cell–cell contacts and β-catenin signaling.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bar H, Wende P, Watson L, Denger S, Van Eys G, Kreuzer J, Jahn L (2002) Smoothelin is an indicator of reversible phenotype modulation of smooth muscle cells in balloon-injured rat carotid arteries. Basic Res Cardiol 97:9–16
Bou-Gharios G, Ponticos M, Rajkumar V, Abraham D (2004) Extra-cellular matrix in vascular networks. Cell Prolif 37:207–220
Chen X, Gumbiner BM (2006) Crosstalk between different adhesion molecules. Curr Opin Cell Biol 18:572–578
Delcommenne M, Tan C, Gray V, Rue L, Woodgett J, Dedhar S (1998) Phosphoinositide-3-OH kinase-dependent regulation of glycogen synthase kinase 3 and protein kinase B/AKT by the integrin-linked kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:11211–11216
Dietrich T, Perlitz C, Licha K, Stawowy P, Atrott K, Tachezy M, Meyborg H, Stocker C, Grafe M, Fleck E, Schirner M, Graf K (2007) ED-B fibronectin (ED-B) can be targeted using a novel single chain antibody conjugate and is associated with macrophage accumulation in atherosclerotic lesions. Basic Res Cardiol 102:298–307
Dwivedi A, George SJ (2004) Cadherins, MMPs and proliferation. Trends Cardiovasc Med 14:100–105
Filipenko NR, Attwell S, Roskelley C, Dedhar S (2005) Integrin-linked kinase activity regulates Rac- and Cdc42-mediated actin cytoskeleton reorganization via [alpha]-PIX. Oncogene 24:5837
Friedrich EB, Clever YP, Wassmann S, Werner N, Bohm M, Nickenig G (2006) Role of integrin-linked kinase in vascular smooth muscle cells: regulation by statins and angiotensin II. Biochem Biophys Res Comm 349:883–889
George SJ, Angelini GD, Capogrossi MC, Baker AH (2001) Wild type p53 gene transfer inhibits neointima formation in human saphenous vein by modulation of smooth muscle cell migration and induction of apoptosis. Gene Ther 8:668–676
George SJ, Johnson JL, Angelini GD, Newby AC, Baker AH (1998) Adenovirus-mediated gene transfer of the human TIMP-1 gene inhibits SMC migration and neointima formation in human saphenous vein. Hum Gene Ther 9:867–877
George SJ, Williams A, Newby AC (1996) An essential role for platelet-derived growth factor in neointima formation in human saphenous vein in vitro. Atherosclerosis 120:227–240
Hannigan GE, Leung-Hagesteijn C, Fitz-Gibbon L, Coppolino MG, Radeva G, Filmus J, Bell J, Dedhar S (1996) Regulation of cell adhesion and anchorage-dependent growth by a new beta 1-integrin-linked protein kinase. Nature 379:91–96
Hedin U, Bottger BA, Forsberg E, Johansson S, Thyberg J (1988) Diverse effects of fibronectin and laminin on phenotypic properties of cultured smooth muscle cells. J Cell Biol 107:307–319
Hungerford J, Compton M, Matter M, Hoffstrom B, Otey C (1996) Inhibition of pp125FAK in cultured fibroblasts results in apoptosis. J Cell Biol 135:1383–1390
Jones M, Sabatini PJ, Lee FS, Bendeck MP, Langille BL (2002) N-cadherin upregulation and function in response of smooth muscle cells to arterial injury. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 22:1972–1977
Kappert K, Blaschke F, Meehan WP, Kawano H, Grill M, Fleck E, Hseuh WA, Law RE, Graf K (2001) Integrins αvβ3 and αvβ5 mediate VSMC migration and are elevated during neointima formation in the rat aorta. Basic Res Cardiol 96:42–49
Khyrul W, LaLonde DP, Brown M, Levinson H, Turner CE (2004) The integrin-linked kinase regulates cell morphology and motility in a Rho-associated kinase-dependent manner. J Biol Chem 279:54131–54139
Koutsouki E, Beeching CA, Slater SC, Blaschuk OW, Sala-Newby GB, George SJ (2005) N-cadherin-dependent cell–cell contacts promote human saphenous vein smooth muscle cell survival. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 25:982–988
Legate KR, Montanez E, Kudlacek O, Fassler R (2006) ILK, PINCH and parvin: the tIPP of integrin signalling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 7:20–31
Mackinnon AC, Qadota H, Norman KR, Moerman DG, Williams BD (2002) C. elegans PAT-4/ILK functions as an adaptor protein within integrin adhesion complexes. Curr Biol 12:787–797
Morla AO, Mogford JE (2000) Control of smooth muscle cell proliferation and phenotype by integrin through focal adhesion kinase. Biochem Biophys Res Comm 272:298–302
Nho RS, Xia H, Kahm J, Kleidon J, Diebold D, Henke CA (2005) Role of integrin-linked kinase in regulating phosphorylation of Akt and fibroblast survival in type I collagen matrices through a β1 integrin viability signaling pathway. J Biol Chem 280:26630–26639
Nikolopoulos SN, Turner CE (2001) Integrin-linked kinase (ILK) binding to paxillin LD1 motif regulates ILK localisation to focal adhesions. J Biol Chem 276:23499–23505
Nikolopoulos SN, Turner CE (2002) Molecular dissection of actopaxin-integrin-linked kinase–paxillin interactions and their role in subcellular localization. J Biol Chem 277:1568–1575
Novak A, Hsu S-C, Leung-Hagesteijn C, Radeva G, Papkoff J, Montesano R, Roskelley C, Grosschedl R, Dedhar S (1998) Cell adhesion and the integrin-linked kinase regulate the LEF-1 and β-catenin signaling pathways. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:4374–4379
Oloumi A, Syam S, Dedhar S (2006) Modulation of Wnt3a-mediated nuclear [beta]-catenin accumulation and activation by integrin-linked kinase in mammalian cells. Oncogene 25:7747
Persad S, Attwell S, Gray V, Mawji N, Deng JT, Leung D, Yan J, Sanghera J, Walsh MP, Dedhar S (2001) Regulation of protein kinase B/Akt-serine 473 phosphorylation by integrin-linked kinase: critical roles for kinase activity and amino acids arginine 211 and serine 343. J Biol Chem 276:27462–27469
Persad S, Dedhar S (2003) The role of integrin-linked kinase (ILK) in cancer progression. Cancer Metastasis Rev 22:375–384
Quasnichka H, Slater SC, Beeching CA, Boehm M, Sala-Newby GB, George SJ (2006) Regulation of smooth muscle cell proliferation by β-catenin/TCF signaling involves modulation of cyclin D1 and p21 expression. Circ Res 99:1329–1337
Sarkar R, Meinberg EG, Stanley JC, Gordon D, Webb RC (1996) Nitric oxide reversibly inhibits the migration of cultured vascular smooth muscle cells. Circ Res 78:225–230
Slater SC, Koutsouki E, Jackson CL, Bush RC, Angelini GD, Newby AC, George SJ (2004) R-cadherin: β-catenin complex and its association with vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 24:1204–1210
Taylor J, Mack CP, Nolan K, Regan CP, Owens GK, Parsons JT (2001) Selective expression of an endogenous inhibitor of FAK regulates proliferation and migration of vascular smooth muscle cells. Mol Cell Biol 21:1565–1572
Thyberg J, Blomgren K, Roy J, Tran PK, Hedin U (1997) Phenotypic modulation of smooth muscle cells after arterial injury is associated with changes in the distribution of laminin and fibronectin. J Histochem Cytochem 45:837–846
Uglow EB, Angelini GD, Newby AC, George SJ (2002) Vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation requires dismantling of N-cadherin cell–cell contacts. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 22:P59
Uglow EB, Slater S, Sala-Newby GB, Aguilera-Garcia CM, Angelini GD, Newby AC, George SJ (2003) Dismantling of cadherin-mediated cell–cell contacts modulates smooth muscle proliferation. Circ Res 92:1314–1321
Vouret-Craviari V, Boulter E, Grall D, Matthews C, Van Obberghen-Schilling E (2004) ILK is required for the assembly of matrix-forming adhesions and capillary morphogenesis in endothelial cells. J Cell Sci 117:4559–4569
Wang X, Xiao Y, Mou Y, Zhao Y, Blankesteijn M, Hall JL (2002) A role for the β-catenin/T-cell factor signaling cascade in vascular remodeling. Circ Res 90:340–347
Wilson DP, Sutherland C, Borman MA, Deng JT, MacDonald JA, Walsh MP (2005) Integrin-linked kinase is responsible for Ca2+-independent myosin diphosphorylation and contraction of vascular smooth muscle. Biochem J 392:641–648
Wozniak MA, Modzelewska K, Kwong L, Keely PJ (2004) Focal adhesion regulation of cell behaviour. Biochim Biophys Acta 1692:103–119
Yamaji S, Suzuki A, Sugiyama Y, Koide Y-I, Yoshida M, Kanamori H, Mohri H, Ohno S, Ishigatsubo Y (2001) A novel integrin-linked kinase-binding protein, affixin, is involved in the early stage of cell-substrate interaction. J Cell Biol 153:1251–1264
Yano H, Mazaki Y, Kurokawa K, Hanks SK, Matsuda M, Sabe H (2004) Roles played by a subset of integrin signaling molecules in cadherin-based cell–cell adhesion. J Cell Biol 166:283–295
Zervas C, SL G, Brown N (2001) Drosophila integrin-linked kinase is required at sites of integrin adhesion to link the cytoskeleton to the plasma membrane. J Cell Biol 152:1007–1018
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge the gift of wild-type and DN-ILK cDNA from Professor Shoukat Dedhar (Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, University of British Columbia, Vancouver, BC, Canada) and rat carotid arteries from Dr. Christopher L. Jackson (Bristol Heart Institute). We thank Dr. Jason Johnson and Jill Tarlton for their excellent technical assistance and the British Heart Foundation for funding this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Returned for 1. Revision: 14 August 2007 1. Revision received: 15 October 2007
Returned for 2. Revision: 8 November 2007 2. Revision received: 9 November 2007
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dwivedi, A., Sala-Newby, G.B. & George, S.J. Regulation of cell–matrix contacts and β-catenin signaling in VSMC by integrin-linked kinase: implications for intimal thickening. Basic Res Cardiol 103, 244–256 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00395-007-0693-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00395-007-0693-9