Abstract
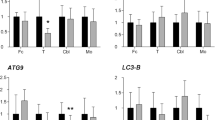
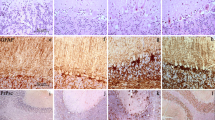
Although apoptosis has been implicated in the neuronal loss observed in prion diseases, the participation of apoptosis-related factors, like the Bcl-2 family of proteins, is still not clear. Moreover, there are conflicting data concerning the major role of apoptosis in the neuropathology associated with transmissible spongiform encephalopathies. Many studies have been developed in vitro or in experimentally infected animal models but, at present, little is known about this process in natural spontaneous and acquired prion diseases. In this work, the implication of Bax and Bcl-2 has been investigated by the analysis of their expression and protein distribution in medulla oblongata of naturally scrapie-infected sheep. Moreover, their spatial relationship with PrPSc deposition, neuronal vacuolation and neuropil spongiosis has also been analysed as well as the possible induction of neuronal apoptosis in this model. Real Time RT-PCR showed overexpression of the pro-apoptotic gene Bax in scrapie medullas, and immunohistochemistry confirmed its accumulation. No variation of Bcl-2 was observed at the level of gene expression or protein production. Bax distribution, PrPSc deposition, neuronal vacuolation and spongiosis were quantified in different medulla oblongata nuclei and their spatial relationship was evaluated. Bax staining showed a positive correlation with prion deposition, suggesting that this factor is involved in prion neurotoxicity in our natural model. Despite Bax overexpression, neuronal apoptosis was revealed neither by TUNEL nor by immunohistochemical detection of the activated form of caspase-3. This lack of apoptosis could be attributed to the relatively low number of neurons in this area or to the existence of neuroprotective mechanisms in medulla oblongata motor neurons.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acin C, Martin-Burriel I, Goldmann W, Lyahyai J, Monzon M, Bolea R, Smith A, Rodellar C, Badiola JJ, Zaragoza P (2004) Prion protein gene polymorphisms in healthy and scrapie-affected Spanish sheep. J Gen Virol 85:2103–2110
Adams JM, Cory S (1998) Matters of life and death: programmed cell death at Cold Spring Harbor. Science 281:1322–1326
Bendotti C, Calvaresi N, Chiveri L, Prelle A, Moggio M, Braga M, Silani V, De Biasi S (2001) Early vacuolization and mitochondrial damage in motoneurons of FALS mice are not associated with apoptosis or with changes in cytochrome oxidase histochemical reactivity. J Neurol Sci 191:25–33
Bolea R, Monleón E, Schiller I, Raeber A, Acín C, Monzón M, Martín-Burriel I, Struckmeyer T, Oesch B, Badiola JJ (2005) Comparison of immunohistochemistry and two rapid tests for detection of PrPsc in different brain regions of sheep with typical scrapie. J Vet Diagn Invest 14:467–469
Borner C (2003) The Bcl-2 protein family: sensors and checkpoints for life-or-death decisions. Mol Immunol 11:615–647
Bounhar Y, Zhang Y, Goodyer CG, LeBlanc A (2001) Prion protein protects human neurons against Bax-mediated apoptosis. J Biol Chem 276:39145–39149
Brown DR (2005) Neurodegeneration and oxidative stress: prion disease results from loss of antioxidant defence. Folia Neuropathol 43:229–243
Bruey JM, Ducasse C, Bonniaud P, Ravagnan L, Susin SA, Diaz-Latoud C, Gurbuxani S, Arrigo AP, Kroemer G, Solary E, Garrido C (2000) Hsp27 negatively regulates cell death by interacting with cytochrome c. Nat Cell Biol 2:645–652
Carimalo J, Corner S, Petit G, Peyrin JM, Boukhtouche F, Arbez N, Lemaigre-Dubreuil Y, Brugg B, Miguel MC (2005) Activation of the JNK-c-Jun pathway during the early phase of neuronal apoptosis induced by PrP106-126 and prion infection. Eur J Neurosci 21:2311–2319
Chiesa R, Drisaldi B, Quaglio E, Migheli A, Piccardo P, Ghetti B, Harris DA (2000) Accumulation of protease-resistant prion protein (PrP) and apoptosis of cerebellar granule cells in transgenic mice expressing a PrP insertional mutation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:5574–5579
Colliti M, Stefanon B, Wilde CJ (1999) Apoptotic cell death, bax and bcl-2 expression during sheep mammary gland involution. Anat Histol Embryol 28:257–264
Fairbairn DW, Carnahan KG, Thwaits RN, Gribsby RV, Holyoak GR, O’Neill KL (1994) Detection of apoptosis induced DNA cleavage in scrapie-infected sheep brain. FEMS Microbiol Lett 115:341–346
Forloni G, Bugiani O, Tagliavini F, Salmona M (1996) Apoptosis-mediated neurotoxicity induced by beta-amyloid and PrP fragments. Mol Chem Neuropathol 28:163–171
Freixes M, Rodriguez A, Dalfo E, Ferrer I (2006) Oxidation, glycoxidation, lipoxidation, nitration, and responses to oxidative stress in the cerebral cortex in Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Neurobiol Aging (in press)
García-Crespo D, Juste RA, Hurtado A (2005) Selection of ovine housekeeping genes for normalisation by real-time RT-PCR; analysis of PrP gene expression and genetic susceptibility to scrapie. BMC Vet Res 3:1746–6148
Giese A, Groschup MH, Hess B, Kretzschmar HA (1995) Neuronal cell death in scrapie-infected mice is due to apoptosis. Brain Pathol 5:213–221
Graeber MB, Moran LB (2002) Mechanisms of cell death in neurodegenerative diseases: fashion, fiction, and facts. Brain Pathol 12:385–390
Gray F, Chretien F, Adle-Biassette H, Dorandeu A, Ereau T, Deslise MB, Kopp N, Ironside JW, Vital C (1999) Neuronal apoptosis in Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 58:321–328
Hardt M, Baron T, Groschup MH (2000) A comparative study of immunohistochemical methods for detecting abnormal prion protein with monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies. J Comp Pathol 122:43–53
Jamieson E, Jeffrey M, Ironside JW, Fraser JR (2001) Activation of Fas and caspase 3 precedes PrPaccumulation in 87V scrapie. Neuroreport 12:3567–3572
Jesionek-Kupnicka D, Kordek R, Buczynski J, Liberski PP (2001) Apoptosis in relation to neuronal loss in experimental Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease in mice. Acta Neurobiol Exp (Wars) 61:3–9
Kim BH, Lee HG, Choi JK, Kim JI, Choi EK, Carp RI, Kim YS (2004) The cellular prion protein (PrPC) prevents apoptotic neuronal cell death and mitochondrial dysfunction induced by serum deprivation. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 124:40–50
Kovács GG, Kurucz I, Budka H, Ádori C, Müller F, Ács P, Klöppel S, Schätzl HM, Mayer J, László L (2001) Prominent stress response of Purkinje cells in Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Neurobiol Dis 8:881–889
Kretzschmar HA, Giese A, Brown DR, Herms J, Schmidt B, Groschup MH (1996) Cell death in prion disease. In: Court L, Dodet B (eds) Transmissible subacute spongiform encephalopathies: prion disease. Proceedings of the third international symposium on transmissible subacute spongiform encephalopathies: prion disease. Vak-de-Grace, Paris, France/Elsevier, Amsterdam/Oxford, Paris, pp97–106 (cited by 28)
Kuwahara C, Takeuchi AM, Nishimura T, Haraguchi K, Kubosaki A, Matsumoto Y, Saeki K, Matsumoto Y, Yokoyama T, Itohara S, Onodera T (1999) Prions prevent neuronal cell-line death. Nature 400:225–226
Liberski PP, Sikorska B, Bratosiewicz-Wasik J, Gajdusek DC, Brown P (2004) Neuronal cell death in transmissible spongiform encephalopathies (prion diseases) revisited: from apoptosis to autophagy. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 36:2473–2490
Lin PH, Pan Z, Zheng L, Li N, Danielpour D, Ma JJ (2005) Overexpression of Bax sensitises prostate cancer cells to TGF-B induced apoptosis. Cell Res 15:160–166
Lucassen PJ, Williams A, Chung WC, Fraser H (1995) Detection of apoptosis in murine scrapie. Neurosci Lett 198:185–188
Lyahyai J, Goldammer T, Beattie AE, Zaragoza P, Martin-Burriel I (2005) Positional and functional characterisation of apoptosis related genes belonging to the BCL2 family in sheep. Cytogenet Genome Res 109:519–526
de la Monte SM, Chiche J, von dem Bussche A, Sanyal S, Lahousse SA, Janssens SP, Bloch KD (2003) Nitric oxide synthase-3 overexpression causes apoptosis and impairs neuronal mitochondrial function: relevance to Alzheimer’s-type neurodegeneration. Lab Invest 83:287–298
O’Donovan CN, Tobin D, Cotter TG (2001) Prion protein frament PrP 106–126 induces apoptosis via mitochondrial disruption in human SH-SY5Y cells. J Biol Chem 276:45516–45523
Park SK, Choi SI, Jin JK, Choi EK, Kim JI, Carp RI, Kim YS (2000) Differential expression of Bax and Bcl-2 in the brains of hamsters infected with 263 K scrapie agent. Neuroreport 11:1677–1682
Puig B, Ferrer I (2001) Cell death signalling in the cerebellum in Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 102:207–215
Ray SK, Fidan M, Nowak MW, Wilford GG, Hogan EL, Banik NL (2000) Oxidative stress and Ca2 + influx upregulate calpain and induce apoptosis in PC12 cells. Brain Res 852:326–334
Roucou X, Gains M, LeBlanc AC (2004) Neuroprotective functions of prion protein. J Neurosci Res 75:153–161
Roucou X, Giannopoulus PN, Zhang Y, Jodoin J, Goodyer CG, LeBlanc A (2005) Cellular prion protein inhibits proapoptotic Bax conformational change in human neurons and in breast carcinoma MCF-7 cells. Cell Death Differ 12:783–795
Shou Y, Li N, Li L, Borowitz JL, Isom GE (2002) NF-kappaB-mediated up-regulation of Bcl-X(S) and Bax contributes to cytochrome c release in cyanide-induced apoptosis. J Neurochem 81:842–852
Siso S, Puig B, Varea R, Vidal E, Acin C, Prinz M, Montrasio F, Badiola J, Aguzzi A, Pumarola M, Ferrer I (2002) Abnormal synaptic protein expresión and cell death in murine scrapie. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 103:615–626
Stadelmann C, Deckwerth TL, Srinivasan A, Bancher C, Brück W, Jellinger K, Lassmann H (1999) Activation of Caspase-3 in single neurons and autophagic granules of granulovacuolar degenration in Alzheimer’s Disease. Am J Pathol 155:1459–1466
Unterberger U, Voigtländer T, Budka H (2005) Pathogenesis of prion diseases. Acta Neuropathol 109:32–48
Vandesompele J, De Preter K, Pattyn F, Poppe B, Van Roy N, De Paepe A, Speleman F (2002) Accurate normalization of real-time quantitative RT-PCR data by geometric averaging of multiple internal control genes. Genome Biol 3:research004.1–0034.12
White AR, Guirguis R, Braier MW, Jobling MF, Hill AF, Beyreuther K, Barrow CJ, Masters CL, Collins SJ, Cappai R (2001) Sublethal concentrations of prion peptide PrP106-126 or the amyloid beta peptide of Alzheimer’s disease activates expression of proapoptotic markers in primary cortical neurons. Neurobiol Dis 8:299–316
Yin XM, Oltvai ZN, Korsmeyer SJ (1994) BH1 and BH2 domains of Bcl-2 are required for inhibition of apoptosis and heterodimerization with Bax. Nature 369:321–323
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Nuria Segovia and Silvia Ruiz for their technical assistance. This work was performed as part of the EET2003-09890 project (CICYT/FEDER), Red CIEN (Carlos III Institute), Fondo de Investigación Sanitaria (PI020840) and Research Consolidated Groups from the Aragon Government. J. Lyahyai and C. Serrano were supported by AECI (MAE) and DGA doctoral grants, respectively, and I. Martín-Burriel by a research contract from the Ramón y Cajal Program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lyahyai, J., Bolea, R., Serrano, C. et al. Correlation between Bax overexpression and prion deposition in medulla oblongata from natural scrapie without evidence of apoptosis. Acta Neuropathol 112, 451–460 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-006-0094-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-006-0094-4