Abstract
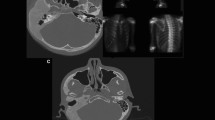
Facial nerve paralysis (FNP) is a rare occurrence in fibrous dysplasia (FD) of the temporal bone (FDTB). Eight such cases have been described in the literature. In none of these cases was the FNP the presenting symptom, and in all, a direct etiology for the paralysis was identified. We present the first case of recurrent, unilateral FNP as the sole otological manifestation of FDTB. We discuss possible etiological factors for the paralysis favoring a compressive, transient ischemia of the facial nerve. The authors suggest adding FDTB to the differential diagnosis of recurrent FNP.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sharp M (1970) Monostotic fibrous dysplasia of the temporal bone. J Laryngol Otol 84(7):697–708
Magu S, Mishra D, Sood A et al (2002) Fibrous dysplasia of the temporal bone. Neurol India 50:374–5
DiCaprio MR, Enneking WF (2005) Fibrous dysplasia. Pathophysiology. Evaluation, and treatment. J Bone Joint Surg Am 87(8):1848–64
Lustig L, Holliday M, McCarthy E et al (2001) Fibrous dysplasia involving the skull base and temporal bone. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 127:1239–1247
Chinski A, Beider B, Cohen D (1999) Fibrous dysplasia of the temporal bone. Int J Pediatr otorhinolaryngol 47:275–281
Smouha E, Edelstein D, Parisier S (1987) Fibrous dysplasia involving the temporal bone, report of three new cases. Am J Otol 8(2):103–107
Chee G, Chen J (2002) Fibrous dysplasia of the temporal bone. Otol Neurotol 23:405–406
Tweddle E, Holwell K (2005) Fibrous dysplasia of the temporal bone. J Surg 75:80–83
Megerian C, Sofferman R, McKenna M et al (1995) Fibrous dysplasia of the temporal bone: ten new cases demonstrating the spectrum of otologic sequelae. Am J Otol 16(4):408–419
Shlumberger H (1946) Fibrous dysplasia of single bones (monostotic fibrous dysplasia). Mil Surg 99:504–527
Cohen A, Rosenwasser H (1969) Fibrous dysplasia of the temporal bone. Arch Otolaryngol 89(3):447–459
Barrionuevo C, Marcallo F, Coelho A et al (1980) Fibrous dysplasia and the temporal bone. Arch Otolaryngol 106(5):298–301
Reddy K, Vinayak B, Jefferis A et al (1994) Fibrous dysplasia of the temporal bone. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 103(1):74–76
Sakamoto M, Hayashida T, Sugasawa M (2001) A case of fibrous dysplasia of the temporal bone: Evaluation of treatment performed 23 years ago. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 125:563–564
Eidlitz-Markus T, Gilai A, Mimouni M et al (2001) Recurrent facial nerve palsy in pediatric patients. Eur J Pediatr 160:659–663
Singhi P, Jain V (2003) Bell’s palsy in children. Semin Pediatr Neurol 10(4):289–297
Acknowledgments
The authors declare that prior consent was obtained from the patient referred to in this report regarding the publication of all included information.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zaytoun, G.M., Dagher, W.I. & Rameh, C.E. Recurrent facial nerve paralysis: an unusual presentation of fibrous dysplasia of the temporal bone. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 265, 255–259 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-007-0422-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-007-0422-x