Abstract
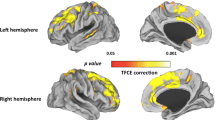
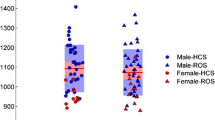
Brain abnormalities of schizophrenia probably consist of deviation related to the vulnerability and pathological changes in association with overt psychosis. We conducted a cross–sectional comparison in brain morphology between patients with overt schizophrenia and schizotypal disorder, a schizophrenia–spectrum disorder without florid psychotic episode. Voxelbased morphometry was applied to assess gray matter volume in 25 patients with schizophrenia, 25 patients with schizotypal disorder, and 50 healthy control subjects. In comparison with controls, schizophrenia patients showed gray matter reductions in the bilateral medial frontal, inferior frontal, medial temporal, and septal regions, and the left middle frontal, orbitofrontal, insula, and superior temporal regions, and an increased gray matter in the left basal ganglia. Schizotypal disorder patients showed reductions in the left inferior frontal, insula, superior temporal, and medial temporal regions. There was a significant reduction in the left orbitofrontal region of schizophrenia compared with schizotypal disorder. Gray matter reductions that are common to both patient groups such as those in the left medial temporal and inferior frontal regions may represent vulnerability to schizophrenia, and additional involvement of several frontal regions may be crucial to florid psychosis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
American Psychiatric Association (1994) Diagnostic Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, 4th Edition. Washington, D.C.: American Psychiatric Press
Ananth H, Popescu I, Critchley HD, Good CD, Frackowiak RSJ, Dolan RJ (2002) Cortical and subcortical gray matter abnormalities in schizophrenia determined through structural magnetic resonance imaging with optimized volumetric voxel-based morphometry. Am J Psychiatry 159:1497–1505
Andreasen NC (1983) Scale of the Assessment of Negative Symptoms (SANS). University of Iowa, Iowa city
Andreasen NC (1984) Scale of the Assessment of Positive Symptoms (SAPS). University of Iowa, Iowa city
Andreasen NC, Flaum M, Arndt S (1992) The Comprehensive Assessment of Symptoms and History (CASH) An instrument for assessing diagnosis and psychopathology. Arch Gen Psychiatry 49:615–623
Ashburner J, Friston K (1997) Multimodal image coregistration and partitioning: a unified framework. Neuroimage 6:209–217
Ashburner J, Friston KJ (1999) Nonlinear spatial normalization using basis functions. Hum Brain Mapp 7:254–266
Ashburner J, Friston KJ (2000) Voxel-based morphometry—the methods. Neuroimage 11:805–821
Ashburner J, Friston KJ (2001) Comments and controversies: why voxel-based morphometry should be used. Neuroimage 14:1238–1243
Ashburner J, Neelin P, Collins DL, Evans A, Friston K (1997) Incorporating prior knowledge into image registration. Neuroimage 6:344–352
Bookstein FL (2001) “Voxel-based morphometry” should not be used with imperfectly registered images. Neuroimage 14:1454–1462
Cannon TD, Thompson PM, van Erp TG, Toga AW, Poutanen VP, Huttunen M, Lonnqvist J, Standerskjold-Nordenstam CG, Narr KL, Khaledy M, Zoumalan CI, Dail R, Kaprio J (2002) Cortex mapping reveals regionally specific patterns of genetic and disease-specific gray-matter deficits in twins discordant for schizophrenia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:3228–3233
Dickey CC, McCarley RW, Voglmaier MM, Niznikiewicz MA, Seidman LJ, Hirayasu Y, Fischer I, Teh EK, Van Rhoads R, Jakab M, Kikinis R, Jolesz FA, Shenton ME (1999) Schizotypal personality disorder and MRI abnormalities of temporal lobe gray matter. Biol Psychiatry 45:1393–1402
Dickey CC, McCarley RW, Shenton ME (2002) The brain in schizotypal personality disorder: a review of structural MRI and CT findings. Harvard Rev Psychiatry 10:1–15
Dickey CC, McCarley RW, Voglmaier MM, Niznikiewicz MA, Seidman LJ, Demeo S, Frumin M, Shenton ME (2003) An MRI study of superior temporal gyrus volume in women with schizotypal personality disorder. Am J Psychiatry 160:2198–2201
Downhill JE, Buchsbaum MS, Hazlett EA, Barth S, Roitman SL, Nunn M, Lekarev O, Wei T, Shihabuddin L, Mitropoulou V, Silverman J, Siever L (2001) Temporal lobe volume determined by magnetic resonance imaging in schizotypal personality disorder and schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 48:187–199
Friston KJ, Frith CD, Liddle PF, Dolan RJ, Lammertsma AA, Frackowiak RSJ (1990) The relationship between global and local changes in PET scans. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 10:458–466
Friston KJ, Holms AP, Worsley KJ, Poline J-B, Frith CD, Frackowiak RSJ (1995) Statistical parametric maps in functional imaging: a general linear approach. Hum Brain Mapp 2:189–210
Gaser C, Volz HP, Kiebel S, Riehemann S, Sauer H (1999) Detecting structural changes in whole brain based on nonlinear deformations—application to schizophrenia research. Neuroimage 10:107–113
Good CD, Johnsrude IS, Ashburner J, Henson RN, Friston KJ, Frackowiak RSJ (2001) A voxel-based morphometric study of aging in 465 normal adult human brains. Neuroimage 14:21–36
Job DE, Whalley HC, McConnell S, Glabus M, Johnstone EC, Lawrie S (2002) Structural gray matter differences between firstepisode schizophrenics and normal control using vozel-based morphometry. Neuroimage 17:880–889
Job DE, Whalley HC, McConnell S, Glabus M, Johnstone EC, Lawrie SM (2003) Voxel-based morphometry of grey matter densities in subjects at high risk of schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 64:1–13
Kubicki M, Shenton ME, Salisbury DF, Hirayasu Y, Kasai K, Kikinis R, Jolesz FA, McCarley RW (2002) Voxel-based morphometric analysis of gray matter in first episode schizophrenia. Neuroimage 17:1711–1719
Kurachi M (2003) Pathogenesis of schizophrenia: part II temporo-frontal two-step hypothesis. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 5:9–15
Lawrie SM, Abukmeil SS (1998) Brain abnormality in schizophrenia—A systematic and quantitative review of volumetric magnetic resonance imaging studies. Br J Psychiatry 172:110–120
Lawrie SM, Whalley H, Kestelman JN, Abukmeil SS, Byrne M, Hodges A, Rimmington JE, Best JJ, Owens DG, Johnstone EC (1999) Magnetic resonance imaging of brain in people at high risk of developing schizophrenia. Lancet 353:30–33
Overall JE, Gorham DR (1962) The Brief Psychiatric Rating Scale. Psychol Rep 10:799–812
Paillère-Martinot ML, Caclin A, Artiges E, Poline JB, Joliot M, Mallet L, Recasens C, Attar-Levy D, Martinot JL (2001) Cerebral gray and white matter reductions and clinical correlates in patients with early onset schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 50:19–26
Pantelis C, Velakoulis D, McGorry PD, Wood SJ, Suckling J, Phillips LJ, Yung AR, Bullmore ET, Brewer W, Soulsby B, Desmond P, McGuire PK (2003) Neuroanatomical abnormalities before and after onset of psychosis: a cross-sectional and longitudinal MRI comparison. Lancet 361:281–288
Raine A, Lencz T, Yaralian P, Bihrle S, LaCasse L,Ventura, Colletti P (2002) Prefrontal structural and functional deficits in schizotypal Personality Disorder. Schizophr Bull 28:501–513
Seidman LJ, Faraone SV, Goldstein JM, Kremen WS, Horton NJ, Makris N,Toomey R, Kennedy D, Caviness VS, Tsuang MT (2002) Left hippocampal volume as a vulnerability indicator for schizophrenia: a magnetic resonance imaging morphometric study of nonpsychotic first-degree relatives. Arch Gen Psychiatry 59:839–849
Shenton ME, Dickey CC, Frumin M, McCarley RW (2001) A review of MRI findings in schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 49:1–52
Shihabuddin L, Buchsbaum MS, Hazlett EA, Silverman J, New A, Brickman AM, Mitropoulou V, Nunn M, Fleischman MB, Tang C, Siever LJ (2001) Striatal size and glucose metabolic rate in schizotypal personality disorder and schizophrenia. Arch Gen Psychiatry 58:877–884
Siever LJ, Koeningsberg HW, Harvey P, Mitropoulou V, Laruelle M, Abi-Dargham A, Goodman M, Buchsbaum M (2002) Cognitive and brain function in schizotypal personality disorder. Schizophr Res 54:157–167
Sigmundsson T, Suckling J, Maier M, Williams SCR, Bullmore ET, Greenwood K, Fukuda R, Ron M, Toone B (2001) Structural abnormalities in frontal, temporal and limbic regions and interconnecting white matter tracts in schizophrenic patients with prominent negative symptoms. Am J Psychiatry 158:234–243
Suzuki M, Nohara S, Hagino H, Kurokawa K, Yotsutsuji T, Kawasaki Y, Takahashi T, Matsui M, Watanabe N, Seto H, Kurachi M (2002) Regional changes in brain gray and white matter in patients with schizophrenia demonstrated with voxel-based analysis of MRI. Schizophr Res 55:41–54
Suzuki M, Zhou S-Y, Hagino H, Takahashi T, Kawasaki Y, Nohara S, Yamashita I, Matsui M, Seto H, Kurachi M (2004) Volume reduction of the right anterior limb of the internal capsule in patients with schizotypal disorder. Psychiatry Res Neuroimaging 130:213–225
Takahashi T, Suzuki M, Kawasaki Y, Kurokawa K, Hagino H, Yamashita I, Zhou SY, Nohara S, Nakamura K, Seto H, Kurachi M (2002) Volumetric magnetic resonance imaging study of the anterior cingulate gyrus in schizotypal disorder. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 252:268–277
Takahashi T, Suzuki M, Zhou S-Y, Hagino H, Kawasaki Y, Yamashita I, Nohara S, Nakamura K, Seto H, Kurachi K (2004) Lack of normal gender differences of the perigenual cingulate gyrus in schizophrenia spectrum disorders: a magnetic resonance imaging study. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci (in press)
Talairach J, Tournoux P (1988) Co-planar stereotaxic atlas of the human brain. Three-dimensional proportional system. New York: Thieme
Toru M (2001) Psychotropic manual, second edition. Tokyo: Igaku-Shoin
Van Erp TGM, Saleh PA, Rosso IM, Huttunen M, Lonnqvist J, Pirkola T, Salonen O, Valanne L, Poutanen VP, Standertskjold-Nordenstam CG, Cannon TD (2002) Contributions of genetic risk and fetal hypoxia to hippocampal volume in patients with schizophrenia or schizoaffective disorder, their unaffected siblings, and healthy unrelated volunteers. Am J Psychiatry 159:1514–1520
Volz H, Gaser C, Sauer H (2000) Supporting evidence for the model of cognitive dysmetria in schizophrenia: a structural magnetic resonance imaging study using deformation-based morphometry. Schizophr Res 46:45–56
Wilke M, Kaufmann C, Grabner A, Pütz B,Wetter TC, Auer DP (2001) Gray matter-changes and correlates of disease severity in schizophrenia: a statistical parametric mapping study. Neuroimage 13:814–824
World Health Organization (1993) The ICD-10 Classification of Mental and Behavioural Disorders. Diagnostic criteria for research. Geneva: World Health Organization
Worsley KJ, Marrett S, Neelin P, Vandal AC, Friston JJ, Evans AC (1996) A unified statistical approach for determining significant voxels in imagings of cerebral activation. Hum Brain Mapp 8:98–101
Wright IC, Ellison ZR, Sharma T, Friston KJ, Murray RM, McGuire PK (1999) Mapping of grey matter changes in schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 35:1–14
Wright IC, McGuire PK, Poline JB, Travere JM, Murray RM, Frith CD, Frackowiak RS, Friston KJ (1995) A voxel-based method for the statistical analysis of gray and white matter density applied to schizophrenia. Neuroimage 2:244–252
Wright IC, Rabe-Hesketh S, Woodruff PW, David AS, Murray RM, Bullmore ET (2000) Meta-analysis of regional brain volumes in schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry 157:16–25
Yoneyama E, Matsui M, Kawasaki Y, Nohara S, Takahashi T, Hagino H, Suzuki M, Seto H, Kurachi M (2003) Gray matter features of schizotypal disorder patients exhibiting the schizophrenia-related code types of the Minnesota Multiphasic Personality Inventory. Acta Psychiatr Scand 108:333–340
Yung AR, McGorry PD (1996) The prodromal phase of firstepisode psychosis: past and current conceptualizations. Schizophr Bull 22:353–370
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kawasaki, Y., Suzuki, M., Nohara, S. et al. Structural brain differences in patients with schizophrenia and schizotypal disorder demonstrated by voxel–based morphometry. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 254, 406–414 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00406-004-0522-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00406-004-0522-1