Abstract.
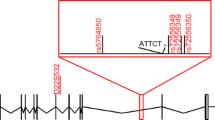
Spinocerebellar ataxia type 4 (SCA4) is an autosomal dominant disorder mapped to chromosome 16q22.1 in a large Utah kindred. The clinical phenotype is characterized by cerebellar ataxia with sensory neuropathy. We describe a five-generation family from northern Germany with similar clinical findings linked to the same locus. Haplotype analyses refined the gene locus to a 3.69 cM interval between D16S3019 and D16S512. Analysis of nine CAG/CTG tracts in this region revealed no evidence for a repeat expansion.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 28 October 2002, Received in revised form: 16 December 2002, Accepted: 19 December 2002
Correspondence to: Dr. Yorck Hellenbroich
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hellenbroich, Y., Bubel, S., Pawlack, H. et al. Refinement of the spinocerebellar ataxia type 4 locus in a large German family and exclusion of CAG repeat expansions in this region. J Neurol 250, 668–671 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-003-1052-x
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-003-1052-x