Abstract
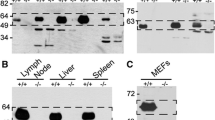
Stabilin-2, the hepatic hyaluronan receptor, has recently been cloned by us. Together with stabilin-1, stabilin-2 constitutes a novel family of fasciclin-like hyaluronan receptor homologues. Here, we analyzed expression of stabilin-2 (mStab-2) in a broad array of C57BL/6 mouse organs and tissues. While northern blot analysis showed positive expression of mStab-2 mRNA confined to liver and spleen, immunohistochemistry demonstrated mStab-2 protein expression in the endothelial sinuses of liver, lymph nodes, spleen, and bone marrow, and in specialized structures of eye, heart, brain, and kidney. Expression of mStab-2 was detected in corneal and lens epithelium, in mesenchymal cells of the heart valves, in the ependymal cells lining the ventricles in the brain, and in the prismatic epithelial cells covering the renal papillae. In pathological conditions, such as tumor growth or wound healing processes, mStab-2 was not expressed in the newly formed vasculature or other tissue components. Based on these results, we suggest that mStab-2 might be involved in the clearance of hyaluronan from the lymph or the blood circulation via the network of endothelial sinuses. At the other mStab-2-positive tissues sites that are either avascular and/or demarcate a solid/liquid interface, mStab-2 may serve to maintain tissue integrity by supporting extracellular matrix turnover or it may contribute to maintaining fluidity of bodily liquids by resorption of hyaluronan.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
al-Awqati Q, Goldberg MR (1998) Architectural patterns in branching morphogenesis in the kidney. Kidney Int 54:1832–1842
Balazs M, Horvath G, Grama L, Balogh P (2001) Phenotypic identification and development of distinct microvascular compartments in the postnatal mouse spleen. Cell Immunol 212:126–137
Bruni JE (1998) Ependymal development, proliferation, and functions: a review. Microsc Res Tech 41:2–13
Burke EJ, Mehlhorn U, Allen SJ (1994) Hyaluronan in cerebrospinal fluid after head injury. Acta Neurol 16:103–109
Camenisch TD, Spicer AP, Brehm-Gibson T, Biesterfeldt J, Augustine ML, Calabro A Jr, Kubalak S, Klewer SE, McDonald JA (2000) Disruption of hyaluronan synthase-2 abrogates normal cardiac morphogenesis and hyaluronan-mediated transformation of epithelium to mesenchyme. J Clin Invest 106:349–360
Chen WY, Abatangelo G (1999) Functions of hyaluronan in wound repair. Wound Repair Regen 7:79–89
Csoka TB, Frost GI, Wong T, Stern R (1997) Purification and microsequencing of hyaluronidase isozymes from human urine. FEBS Lett 417:307–310
Csoka AB, Frost GI, Stern R (2001) The six hyaluronidase-like genes in the human and mouse genomes. Matrix Biol 20:499–508
Deed R, Rooney P, Kumar P, Norton JD, Smith J, Freemont AJ, Kumar S (1997) Early-response gene signalling is induced by angiogenic oligosaccharides of hyaluronan in endothelial cells. Inhibition by non-angiogenic, high-molecular-weight hyaluronan. Int J Cancer 71:251–256
Eggli PS, Graber W (1993) Ultrastructural distribution of hyaluronan in rat cornea. Exp Eye Res 56:693–699
Eriksson S, Fraser JR, Laurent TC, Pertoft H, Smedsrød B (1983) Endothelial cells are a site of uptake and degradation of hyaluronic acid in the liver. Exp Cell Res 144:223–228
Evanko SP, Angello JC, Wight TN (1999) Formation of hyaluronan- and versican-rich pericellular matrix is required for proliferation and migration of vascular smooth muscle cells. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 19:1004–1013
Farber SJ, van Praag D (1970) Composition of glycosaminoglycans (mucopolysaccharides) in rabbit renal papillae. Biochim Biophys Acta 208:219–226
Fraser JR, Laurent TC (1989) Turnover and metabolism of hyaluronan. Ciba Found Symp 143:41–59
Fraser JR, Laurent TC, Pertoft H, Baxter E (1981) Plasma clearance, tissue distribution and metabolism of hyaluronic acid injected intravenously in the rabbit. Biochem J 200:415–424
Fraser JR, Appelgren LE, Laurent TC (1983) Tissue uptake of circulating hyaluronic acid. A whole body autoradiographic study. Cell Tissue Res 233:285–293
Fraser JR, Engstrom-Laurent A, Nyberg A, Laurent TC (1986) Removal of hyaluronic acid from the circulation in rheumatoid disease and primary biliary cirrhosis. J Lab Clin Med 107:79–85
Fraser JR, Kimpton WG, Laurent TC, Cahill RN, Vakakis N (1988) Uptake and degradation of hyaluronan in lymphatic tissue. Biochem J 256:153–158
Gakunga P, Frost G, Shuster S, Cunha G, Formby B, Stern R (1997) Hyaluronan is a prerequisite for ductal branching morphogenesis. Development 124:3987–3997
Gato A, Martin C, Alonso MI, Martinez-Alvarez C, Moro JA (2001) Chondroitin sulphate proteoglycan is involved in lens vesicle morphogenesis in chick embryos. Exp Eye Res 73:469–478
Goerdt S, Walsh LJ, Murphy GF, Pober JS (1991) Identification of a novel high molecular weight protein preferentially expressed by sinusoidal endothelial cells in normal human tissues. J Cell Biol 113:1425–1437
Goerdt S, Bhardwaj R, Sorg C (1993) Inducible expression of MS-1 high-molecular-weight protein by endothelial cells of continuous origin and by dendritic cells/macrophages in vivo and in vitro. Am J Pathol 142:1409–1422
Hansell P, Maric C, Alcorn D, Goransson V, Johnsson C, Hallgren R (1999) Renomedullary interstitial cells regulate hyaluronan turnover depending on growth media osmolality suggesting a role in renal water handling. Acta Physiol Scand 165:115–116
Henderson DJ, Copp AJ (1998) Versican expression is associated with chamber specification, septation, and valvulogenesis in the developing mouse heart. Circ Res 83:523–322
Inoue S, Osmond DG (2001) Basement membrane of mouse bone marrow sinusoids shows distinctive structure and proteoglycan composition: a high resolution ultrastructural study. Anat Rec 264:294–304
Knepper MA, Saidel GM, Hascall VC, Dwyer T (2003) Concentration of solutes in the renal inner medulla: interstitial hyaluronan as a mechano-osmotic transducer. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 284:433–446
Knudson CB, Knudson W (1993) Hyaluronan-binding proteins in development, tissue homeostasis, and disease. FASEB J 7:1233–1241
Kresse H, Grossmann A (1970) Comparative study of the mucopolysaccharide and collagen content in different topographical zones of the kidney of rat, dog and pig. Z Klin Chem Klin Biochem 8:420–424
Laurent TC, Fraser JR (1992) Hyaluronan. FASEB J 6:2397–2404
Laurent TC, Fraser JR, Pertoft H, Smedsrød B (1986) Removal of hyaluronic acid from the circulation in rheumatoid disease and primary biliary cirrhosis. J Lab Clin Med 107:79–85
Laurent TC, Laurent UB, Fraser JR (1996) The structure and function of hyaluronan: An overview. Immunol Cell Biol 74:1–7
Lechner MS, Dressler GR (1997) The molecular basis of embryonic kidney development. Mech Dev 2:105–120
Lerner LE, Schwartz DM, Hwang DG, Howes EL, Stern R (1998) Hyaluronan and CD44 in the human cornea and limbal conjunctiva. Exp Eye Res 67:481–484
McCourt PA, Smedsrød B, Melkko J, Johansson S (1999) Characterization of a hyaluronan receptor on rat sinusoidal liver endothelial cells and its functional relationship to scavenger receptors. Hepatology 30:1276–1286
Meyer K, Palmer JW (1934) The polysaccharide of the vitreous humor. J Biol Chem 107:629–634
Øynebråten I, Hansen B, Smedsrød B, Uhlin-Hansen L (2000) Serglycin secreted by leukocytes is efficiently eliminated from the circulation by sinusoidal scavenger endothelial cells in the liver. J Leukoc Biol 67:183–188
Petrides PE, Dittmann KH (1990) How do normal and leukemic white blood cells egress from the bone marrow? Morphological facts and biochemical riddles. Blut 61:3–13
Pitcock JA, Lyons H, Brown PS, Rightsel WA, Muirhead EE (1988) Glycosaminoglycans of the rat renomedullary interstitium: ultrastructural and biochemical observations. Exp Mol Pathol 49:373–387
Pohl M, Sakurai H, Stuart RO, Nigam SK (2000a) Role of hyaluronan and CD44 in in vitro branching morphogenesis of ureteric bud cells. Dev Biol 224:312–325
Pohl M, Stuart RO, Sakurai H, Nigam SK (2000b) Branching morphogenesis during kidney development. Annu Rev Physiol 62:595–620
Politz O, Gratchev A, McCourt PA, Schledzewski K, Guillot P, Johansson S, Svineng G, Franke P, Kannicht C, Kzhyshkowska J, Longati P, Velten FW, Johansson S, Goerdt S (2002) Stabilin-1 and -2 constitute a novel family of fasciclin-like hyaluronan receptor homologues. Biochem J 362:155–164
Prevo R, Banerji S, Ferguson DJ, Clasper S, Jackson DG (2001) Mouse LYVE-1 is an endocytic receptor for hyaluronan in lymphatic endothelium. J Biol Chem 276:19420–19430
Rooney P, Kumar S, Ponting J, Wang M (1995) The role of hyaluronan in tumour neovascularization. Int J Cancer 60:632–636
Saika S, Kawashima Y, Miyamoto T, Okada Y, Tanaka S, Yamanaka O, Ohnishi Y, Ooshima A, Yamanaka A (1998) Immunolocalization of hyaluronan and CD44 in quiescent and proliferating human lens epithelial cells. J Cataract Refract Surg 24:1266–1270
Saika S, Miyamoto T, Tanaka S, Tanaka T, Ishida I, Ohnishi Y, Ooshima A, Ishiwata T, Asano G, Chikama T, Shiraishi A, Liu CY, Kao CW, Kao WW (2003) Response of lens epithelial cells to injury: role of lumican in epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 44:2094–2102
Smedsrød B, Pertoft H, Eriksson S, Fraser JR, Laurent TC (1984) Studies in vitro on the uptake and degradation of sodium hyaluronate in rat liver endothelial cells. Biochem J 223:617–626
Smedsrød B, Kjellen L, Pertoft H (1985) Endocytosis and degradation of chondroitin sulphate by liver endothelial cells. Biochem J. 229:63–71
Snook T (1950) A comparative study of the vascular arrangements in mammalian spleens. Am J Anat 87:31–78
Tanihara H, Inatani M, Koga T, Yano T, Kimura A (2002) Proteoglycans in the eye. Cornea 21:62–69
Toole BP (1997) Hyaluronan in morphogenesis. J Intern Med 242:35–40
Toole BP (2002) Hyaluronan promotes the malignant phenotype. Glycobiology 12:37–42
Turley EA (1992) Molecular mechanisms of cell motility. Cancer Metastasis Rev 11:1–3
Walsh EC, Stainier DY (2001) UDP-glucose dehydrogenase required for cardiac valve formation in zebrafish. Science 293:1670–1673
Weigel JA, Raymond RC, McGary C, Singh A, Weigel PH (2003) A blocking antibody to the hyaluronan receptor for endocytosis (HARE) inhibits hyaluronan clearance by perfused liver. J Biol Chem 278:9808–9812
Wells AF, Larsson E, Tengblad A, Fellstrom B, Tufveson G, Klareskog L, Laurent TC (1990) The localization of hyaluronan in normal and rejected human kidneys. Transplantation 50:240–243
West DC, Hampson IN, Arnold F, Kumar S (1985) Angiogenesis induced by degradation products of hyaluronic acid. Science 228:1324–1326
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG), the Dr. Mildred-Scheel Stiftung für Krebsforschung, and the Tumorzentrum Heidelberg/Mannheim.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Falkowski, M., Schledzewski, K., Hansen, B. et al. Expression of stabilin-2, a novel fasciclin-like hyaluronan receptor protein, in murine sinusoidal endothelia, avascular tissues, and at solid/liquid interfaces. Histochem Cell Biol 120, 361–369 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-003-0585-5
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-003-0585-5