Abstract
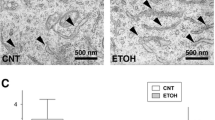
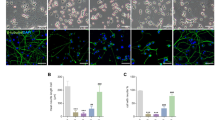
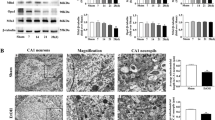
In the present study, we analyze the effects of ethanol on the Golgi structure and membrane transport in differentiated PC12 cells, which are used as a model of neurons. Chronic exposure to moderate doses of ethanol induces Golgi fragmentation, a common characteristic of many neurodegenerative diseases. Alcohol impaired the lateral linking of stacks without causing microtubule damage. Extensive immunocytochemical and western blot analyses of representative Golgi proteins showed that few, but important, proteins are significantly affected. Thus, alcohol exposure induced a significant ER-to-Golgi transport delay, the retention of the GTPase Rab1 in the Golgi membranes and the accumulation of tethering factor p115 in the cytosol. These modifications would explain the observed fragmentation. The amount of p115 and the stacking protein GRASP65 increased in alcohol-treated cells, which might be a mechanism to reverse Golgi damage. Importantly, the overexpression of GTP-tagged Rab1 but not of a dominant-negative Rab1 mutant, restored the Golgi morphology, suggesting that this protein is the main target of alcohol. Taken together, our results support the view that alcohol and neurodegenerative diseases such as Parkinson have similar effects on intracellular trafficking and provide new clues on the neuropathology of alcoholism.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allan BB, Moyer BD, Balch WE (2000) Rab1 recruitment of p115 into a cis-SNARE complex: programming budding COPII vesicles for fusion. Science 289:444–448
Babia T, Ayala I, Valderrama F, Mato E, Bosch M, Santaren JF, Renau-Piqueras J, Kok JW, Thomson TM, Egea G (1999) N-Ras induces alterations in Golgi complex architecture and in constitutive protein transport. J Cell Sci 112:477–489
Bailly E, McCaffrey M, Touchot N, Zahraoui A, Goud B, Bornens M (1991) Phosphorylation of two small GTP-binding proteins of the Rab family by p34cdc2. Nature 350:715–718
Barr FA, Puype M, Vandekerckhove J, Warren G (1997) GRASP65, a protein involved in the stacking of Golgi cisternae. Cell 91:253–262
Brandon E, Szul T, Alvarez C, Grabski R, Benjamin R, Kawai R, Sztul E (2006) On and off membrane dynamics of the ER-golgi tethering factor p115 in vivo. Mol Biol Cell 17:2996–3008
Braza-Boïls A, Tomás M, Marín MP, Megías L, Sancho-Tello M, Fornas E, Renau-Piqueras J (2006) Glycosylation is altered by ethanol in rat hippocampal cultured neurons. Alcohol Alcohol 41:494–504
Chiu R, Novikov L, Mukherjee S, Shields D (2002) A caspase cleavage fragment of p115 induces fragmentation of the Golgi apparatus and apoptosis. J Cell Biol 159:637–648
Cooper AA, Gitler AD, Cashikar A et al (2006) Alpha-synuclein blocks ER-Golgi traffic and Rab1 rescues neuron loss in Parkinson’s models. Science 313:324–328
Dinter A, Berger EG (1998) Golgi-disturbing agents. Histochem Cell Biol 109:571–590
Durán JM, Valderrama F, Castel S, Magdalena J, Tomás M, Hosoya H, Renau-Piqueras J, Malhotra V, Egea G (2003) Myosin motors and not actin comets are mediators of the actin-based Golgi-to-endoplasmic reticulum protein transport. Mol Biol Cell 14:445–459
Eckardt MJ, File SE, Gessa GL, Grant KA, Guerri C, Hoffman PL, Kalant H, Koob GF, Li TK, Tabakoff B (1998) Effects of moderate alcohol consumption on the central nervous system. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 22:998–1040
Fan J, Hu Z, Zeng L, Lu W, Tang X, Zhang J, Li T (2008) Golgi apparatus and neurodegenerative diseases. Int J Dev Neurosci 26:523–534
Gonatas NK, Gonatas JO, Stieber A (1998) The involvement of the Golgi apparatus in the pathogenesis of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, Alzheimer’s disease, and ricin intoxication. Histochem Cell Biol 109:591–600
Gonatas NK, Stieber A, Gonatas JO (2006) Fragmentation of the Golgi apparatus in neurodegenerative diseases and cell death. J Neurol Sci 246:21–30
Goodlett CR, Horn KH (2001) Mechanisms of alcohol-induced damage to the developing nervous system. Alcohol Res Health 25:175–184
Guerri C, Bazinet A, Riley EP (2009) Foetal alcohol spectrum disorders and alterations in brain and behaviour. Alcohol Alcohol 44:108–114
Harper C (2009) The neuropathology of alcohol-related brain damage. Alcohol Alcohol 44:136–140
Kim JA, Druse MJ (1996) Deficiency of essential neurotrophic factors in conditioned media produced by ethanol-exposed cortical astrocytes. Brain Res Dev Brain Res 96:1–10
Klausner RD, Donaldson JG, Lippincott-Schwartz J (1992) Brefeldin A: insights into the control of membrane traffic and organelle structure. J Cell Biol 116:1071–1080
Lane JD, Lucocq J, Pryde J, Barr FA, Woodman PG, Allan VJ, Lowe M (2002) Caspase-mediated cleavage of the stacking protein GRASP65 is required for Golgi fragmentation during apoptosis. J Cell Biol 156:495–509
Levine TP, Rabouille C, Kieckbusch RH, Warren G (1996) Binding of the vesicle docking protein p115 to Golgi membranes is inhibited under mitotic conditions. J Biol Chem 271:17304–17311
Linstedt AD, Jesch SA, Mehta A, Lee TH, Garcia-Mata R, Nelson DS, Sztul E (2000) Binding relationships of membrane tethering components. The giantin N terminus and the GM130N terminus compete for binding to the p115 C terminus. J Biol Chem 275:10196–10201
Lowe M, Gonatas NK, Warren G (2000) The mitotic phosphorylation cycle of the cis-Golgi matrix protein GM130. J Cell Biol 149:341–356
Lucocq J (2008) Quantification of structures and gold labeling in Transmission Electron Microscopy. Methods Cell Biol 88:59–82
Majoul I, Schmidt T, Pomasanova M, Boutkevich E, Kozlov Y, Söling HD (2002) Differential expression of receptors for Shiga and Cholera toxin is regulated by the cell cycle. J Cell Sci 115:817–826
Marmillot P, Rao MN, Lakshman MR (2001) Chronic ethanol exposure in rats affects rabs-dependent hepatic trafficking of apolipoprotein E and transferrin. Alcohol 25:195–200
Martinez-Alonso E, Egea G, Ballesta J, Martinez-Menarguez JA (2005) Structure and dynamics of the Golgi complex at 15 degrees C: low temperature induces the formation of Golgi-derived tubules. Traffic 6:32–44
Mayhew TM (2011) Mapping the distributions and quantifying the labelling intensities of cell compartments by immunoelectron microscopy: progress towards a coherent set of methods. J Anat 219:647–660
Miller MW (1992) Development of the central nervous system: effects of alcohol and opiates. In: Miller M, Alan R (eds) Lis, New York, pp 47–69
Miñana R, Climent E, Barettino D, Segui JM, Renau-Piqueras J, Guerri C (2000) Alcohol exposure alters the expression pattern of neural cell adhesion molecules during brain development. J Neurochem 75:954–964
Mitrovic S, Ben-Tekaya H, Koegler E, Gruenberg J, Hauri HP (2008) The cargo receptors Surf4, endoplasmic reticulum-Golgi intermediate compartment (ERGIC)-53, and p25 are required to maintain the architecture of ERGIC and Golgi. Mol Biol Cell 19:1890–1976
Moyer BD, Allan BB, Balch WE (2001) Rab1 interaction with a GM130 effector complex regulates COPII vesicle cis-Golgi tethering. Traffic 2:268–276
Nakagomi S, Barsoum MJ, Bossy-Wetzel E, Sütterlin C, Malhotra V, Lipton SA (2008) A Golgi fragmentation pathway in neurodegeneration. Neurobiol Dis 29:221–231
Nakamura N, Lowe M, Levine TP, Rabouille C, Warren G (1997) The vesicle docking protein p115 binds GM130, a cis-Golgi matrix protein, in a mitotically regulated manner. Cell 89:445–455
Orci L, Amherdt M, Ravazzola M, Perrelet A, Rothman JE (2000) Exclusion of Golgi residents from transport vesicles budding from Golgi cisternae in intact cells. J Cell Biol 150:1263–1270
Plutner H, Cox AD, Pind S, Khosravi-Far R, Bourne JR, Schwaninger R, Der CJ, Balch WE (1991) Rab1b regulates vesicular transport between the endoplasmic reticulum and successive Golgi compartments. J Cell Biol 115:31–43
Ramirez IB, Lowe M (2009) Golgins and GRASPs: holding the Golgi together. Semin Cell Dev Biol 20:770–779
Renau-Piqueras J, Miragall F, Guerri C, Báguena-Cervellera R (1987) Prenatal exposure to alcohol alters the Golgi apparatus of newborn rat hepatocytes. A cytochemical study. J Histochem Cytochem 35:221–228
Renau-Piqueras J, Guasch R, Azorín I, Seguí JM, Guerri C (1997) Prenatal alcohol exposure affects galactosyltransferase activity and glycoconjugates in the Golgi apparatus of fetal rat hepatocytes. Hepatology 25:343–350
Saraste J, Lahtinen U, Goud B (1995) Localization of the small GTP-binding protein rab1p to early compartments of the secretory pathway. J Cell Sci 108:1541–1552
Shorter J, Warren G (2002) Golgi architecture and inheritance. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 18:379–420
Shorter J, Beard MB, Seemann J, Dirac-Svejstrup AB, Warren G (2002) Sequential tethering of Golgins and catalysis of SNAREpin assembly by the vesicle-tethering protein p115. J Cell Biol 157:45–62
Sombers LA, Colliver TL, Ewing AG (2002) Differentiated PC12 cells: a better model system for the study of the VMAT’s effects on neuronal communication. Ann N Y Acad Sci 971:86–88
Stenmark H (2009) Rab GTPases as coordinators of vesicle traffic. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 10:513–525
Storrie B, White J, Röttger S, Stelzer EH, Suganuma T, Nilsson T (1998) Recycling of golgi-resident glycosyltransferases through the ER reveals a novel pathway and provides an explanation for nocodazole-induced Golgi scattering. J Cell Biol 143:1505–1521
Streissguth AP, Sampson PD, Olson HC, Bookstein FL, Barr HM, Scott M, Feldman J, Mirsky AF (1994) Maternal drinking during pregnancy: attention and short-term memory in 14-year-old offspring. A longitudinal prospective study. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 18:202–218
Tomás M, Fornas E, Megías L, Durán JM, Portolés M, Guerri C, Egea G, Renau-Piqueras J (2002) Ethanol impairs monosaccharide uptake and glycosylation in cultured rat astrocytes. J Neurochem 83:601–612
Tomás M, Marín P, Megías L, Egea G, Renau-Piqueras J (2005) Ethanol perturbs the secretory pathway in astrocytes. Neurobiol Dis 20:773–784
Tomás M, Martínez-Alonso E, Ballesta J, Martínez-Menárguez JA (2010) Regulation of ER-Golgi intermediate compartment tubulation and mobility by COPI coats, motor proteins and microtubules. Traffic 11:616–625
Vallés S, Lindo L, Montoliu C, Renau-Piqueras J, Guerri C (1994) Prenatal exposure to ethanol induces changes in the nerve growth factor and its receptor in proliferating astrocytes in primary culture. Brain Res 656:281–286
Weibel ER (1979) Stereological methods. Practical methods for biological morphometry, vol 1. Academic Press, London
Williams M (1977) Stereological techniques. In: Glauert AM (ed) Practical methods in electron microscopy, vol 6, part 2, chap 2. North Holland/American Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 1–84
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to the Image Analysis Service of the University of Murcia for help with the 3D reconstruction. This work was supported by grants from the Ministerio de Ciencia e Innovación (Spain) (BFU2008-00477/BMC and Consolider COAT CSD2009-00016) and Fundación Séneca de la Comunidad Autónoma de la Región de Murcia (04542/GERM/06) to JAM-M, from the Ministerio de Ciencia e Innovación (SAF2008-00305) and Red de Trastornos Adictivos (RTA, RETICS, ISCIII, grant RD06/0001/0009) to JR-P and from Ministerio de Ciencia e Innovación (BFU2010-17116) to MMM. MPM and GE-P are recipients of RTA fellowships.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
418_2012_970_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
Supplementary figure 1. Alcohol does not affect the microtubule cytoskeleton. Representative immunofluorescence images of distribution of α-tubulin and acetylated α-tubulin in control and ethanol-exposed cells. No differences concerning the distribution of these cytoskeletal proteins were found. Bar 25 μm. Supplementary figure 2. Alcohol does not affect the level of expression of proteins involved in ER-Golgi trafficking. Cell lysates obtained from control and ethanol-treated cell were separated by SDS-PAGE and immunolabelled with different antibodies. (PDF 1103 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tomás, M., Marín, M.P., Martínez-Alonso, E. et al. Alcohol induces Golgi fragmentation in differentiated PC12 cells by deregulating Rab1-dependent ER-to-Golgi transport. Histochem Cell Biol 138, 489–501 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-012-0970-z
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-012-0970-z