Abstract
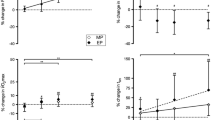
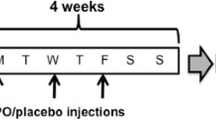
The effects of recombinant human erythropoietin (rHuEpo) treatment on aerobic power (VO2max) are well documented, but little is known about the effects of rHuEpo on submaximal exercise performance. The present study investigated the effect on performance (ergometer cycling, 20–30 min at 80% of maximal attainable workload), and for this purpose eight subjects received either 5,000 IU rHuEpo or placebo every second day for 14 days, and subsequently a single dose of 5,000 IU/placebo weekly/10 weeks. Exercise performance was evaluated before treatment and after 4 and 11 weeks of treatment. With rHuEpo treatment VO2max increased (P < 0.05) by 12.6 and 11.6% in week 4 and 11, respectively, and time-to-exhaustion (80% VO2max) was increased by 54.0 and 54.3% (P < 0.05) after 4 and 11 weeks of treatment, respectively. However, when normalizing the workload to the same relative intensity (only done at time point week 11), TTE was decreased by 26.8% as compared to pre rHuEpo administration. In conclusion, in healthy non-athlete subjects rHuEpo administration prolongs submaximal exercise performance by about 54% independently of the approximately 12% increase in VO2max.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Audran M, Gareau R, Matecki S, Durand F, Chenard C, Sicart M, Marion B, Bressolle F (1999) Effects of erythropoietin administration in training athletes and possible indirect detection in doping control. Med Sci Sports Exerc 31:639–645
Bassett DR, Howley ET (2000) Limiting factors for maximum oxygen uptake and determinants of endurance performance. Med Sci Sports Exerc 32:70–84
Berglund B, Ekblom B (1991) Effect of recombinant human erythropoietin treatment on blood pressure and some hematological parameters in healthy men. J Intern Med 229:125–130
Birkeland KI, Stray-Gundersen J, Hemmersbach P, Jostein H, Haug E, Bahr R (2000) Effect of rhEPO administration on serum levels of sTfR and cycling performance. Med Sci Sports Exerc 32:1238–1243
Brien AJ, Simon TL (1987) The effects of red blood cell infusion on 10-km race time. J Am Med Assoc 20:2761–2765
Burgomaster KA, Hughes CS, Heigenhauser GJ, Bradwell SN, Gibala MJ (2005) Six sessions of sprint interval training increases muscle oxidative potential and cycle endurance capacity in humans. J Appl Physiol 98:1895–1990
Calbet JAL, Lundby C, Koskolou M, Boushel R (2006) Importance of hemoglobin concentration to exercise: acute manipulations. Respir Physiol Neurobiol 151:132–140
di Prampero PE, Ferretti G (1990) Factors limiting maximal oxygen consumption in humans. Respir Physiol 80:113–127
Jelkmann W (2005) Effects of erythropoietin on brain function. Curr Pharm Biotechnol 6:65–79
Jeukendrup A, Saris WH, Brouns F, Kester AD (1996) A new validated endurance performance test. Med Sci Sports Exerc 28:266–270
Leddy J, Limprasertkul A, Patel S, Modlich F, Buyea C, Pendergast D, Lundgren C (2007) Isocapnic hyperpnea training improves performance in competitive male runners. Eur J Appl Physiol 99:665–676
Lucia A, Hoyos J, Perez M, Santalla A, Chicharro JL (2002) Inverse relationship between VO2max and economy/efficiency in world-class cyclists. Med Sci Sports Exerc 34:2079–2084
Lundby C, Thomsen JJ, Boushel R, Koskolou M, Warberg J, Calbet JAL, Robach P (2007) Erythropoietin treatment elevates haemoglobin concentration by increasing red cell volume and depressing plasma volume. J Physiol 578:309–314
McMahon FG, Vargas R, Ryan M, Jain AK, Abels RI, Perry B, Smith IL (1990) Pharmacokinetics and effects of recombinant human erythropoietin after intravenous and subcutaneous injections in healthy volunteers. Blood 76:1718–1722
Miskowiak K, Inkster B, Selvaraj S, Wise R, Goodwin GM, Harmer CJ (2007) Erythropoietin improves mood and modulates the cognitive and neural processing of emotion 3 days post administration. Neuropsychopharmacology
Ninot G, Connes P, Caillaud C (2006) Effects of recombinant human erythropoietin injections on physical self in endurance athletes. J Sports Sci 24:383–391
Parisotto R, Wu M, Ashenden MJ, Emslie KR, Gore CJ, Howe C, Kazlauskas R, Sharpe K, Trout GJ, Xie M (2001) Detection of recombinant human erythropoietin abuse in athletes utilizing markers of altered erythropoiesis. Haematologica 86:128–137
Rice L, Ruiz W, Driscoll T, Whitley CE, Tapia R, Hachey DL, Gonzales GF, Alfrey CP (2001) Neocytolysis on descent from altitude: a newly recognized mechanism for the control of red cell mass. Ann Intern Med 134:652–656
Russell G, Gore CJ, Ashenden MJ, Parisotto R, Hahn AG (2002) Effects of prolonged low doses of recombinant human erythropoietin during submaximal and maximal exercise. Eur J Appl Physiol 86:442–449
Turner DL, Hoppeler H, Noti C, Gurtner HP, Gerber H, Schena F, Kayser B, Ferretti G (1993) Limitations to VO2max in humans after blood retransfusion. Respir Physiol 92:329–341
Wagner PD (2000) New ideas on limitations to VO2max. Med Sci Sports Exerc 28:10–14
Warburton DER, Gledhill N, Quinney H (2000) Blood volume, aerobic power, and endurance performance: potential ergogenic effect of volume loading. Clin J Sport Med 10:59–66
Acknowledgments
This study was supported financially by Anti Doping Denmark (CL), Kunststyrelsen (CL), and by the Bundesamt für Sport (BASPO) in Magglingen, Switzerland.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thomsen, J.J., Rentsch, R.L., Robach, P. et al. Prolonged administration of recombinant human erythropoietin increases submaximal performance more than maximal aerobic capacity. Eur J Appl Physiol 101, 481–486 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-007-0522-8
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-007-0522-8