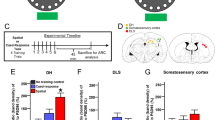
Abstract
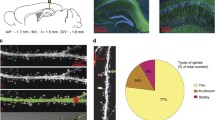
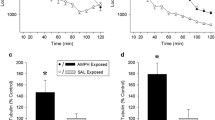
Activity-regulated cytoskeleton-associated protein (Arc) integrates information from multiple intracellular signaling cascades and, in turn, regulates cytoskeletal proteins involved in structural synaptic modifications. The purposes of the present study were: (1) to determine if the retrieval of contextual memories would induce Arc in hippocampal and amygdalar neurons; (2) use unbiased stereology at the ultrastructural level to quantify synapses contacting Arc-labeled (Arc+) and unlabeled (Arc−) postsynaptic structures in brain regions in which the amount of Arc integrated density (ID) correlated strongly with the degree of amphetamine conditioned place preference (AMPH CPP). The retrieval of contextual memories increased the Arc ID in the dentate gyrus, cornu ammonis (CA)1, and CA3 fields of the hippocampus and the basolateral, lateral, and central nuclei of the amygdala but not the primary auditory cortex, a control region. Stereological quantification of Arc+ and Arc− synapses in the basolateral nucleus of the amygdala (BLA) was undertaken because the strongest relationship between the amount of Arc ID and AMPH CPP was observed in the BLA. The retrieval of contextual memories increased the number and density of asymmetric (presumed excitatory) synapses contacting Arc+ spines and dendrites of BLA neurons, symmetric (presumed inhibitory or modulatory) synapses contacting Arc+ dendrites of BLA neurons, and multisynaptic boutons contacting Arc+ postsynaptic structures. Thus, the retrieval of contextual memories increases Arc in the amygdala and hippocampus, an effect that could be important for approach behavior to a drug-associated context.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beaulieu C, Somogyi P (1990) Targets and quantitative distribution of GABAergic synapses in the visual cortex of the cat. Eur J Neurosci 2(4):296–303
Bothwell S, Meredith GE, Phillips J, Staunton H, Doherty C, Grigorenko E, Glazier S, Deadwyler SA, O’Donovan CA, Farrell M (2001) Neural hypertrophy in the neocortex of patients with temporal lobe epilepsy. J Neurosci 21(13):4789–4800
Brinley-Reed M, Mascagni F, McDonald AJ (1995) Synaptology of prefrontal cortical projections to the basolateral amygdala: an electron microscopic study in the rat. Neurosci Lett 202(1–2):45–48
Calverley RK, Bedi KS, Jones DG (1988) Estimation of the numerical density of synapses in rat neocortex: comparison of the ‘disector’ with an ‘unfolding’ method. J Neurosci Methods 23(3):195–205
Carlsen J, Heimer L (1986) A correlated light and electron microscopic immunocytochemical study of cholinergic terminals and neurons in the rat amygdaloid body with special emphasis on the basolateral amygdaloid nucleus. J Comp Neurol 244(1):121–136
Daberkow DP, Riedy MD, Kesner RP, Keefe KA (2007) Arc mRNA induction in striatal efferent neurons associated with response learning. Eur J Neurosci 26(1):228–241
Day M, Wang Z, Ding J, An X, Ingham CA, Shering AF, Wokosin D, Ilijic E, Sun Z, Sampson AR, Mugnaini E, Deutch AY, Sesack SR, Arbuthnott GW, Surmeier DJ (2006) Selective elimination of glutamatergic synapses on striatopallidal neurons in Parkinson disease models. Nat Neurosci 9(2):251–259
De Groot DM (1988) Comparison of methods for the estimation of the thickness of ultrathin tissue sections. J Microsc 151(Pt 1):23–42
de Groot DM, Bierman EP (1986) A critical evaluation of methods for estimating the numerical density of synapses. J Neurosci Methods 18(1–2):79–101
Dragunow M, Peterson MR, Robertson HA (1987) Presence of c-fos-like immunoreactivity in the adult rat brain. Eur J Pharmacol 135(1):113–114
Dudai Y, Eisenberg M (2004) Rites of passage of the engram: reconsolidation and the lingering consolidation hypothesis. Neuron 44(1):93–100
Everitt BJ, Morris KA, O’Brien A, Robbins TW (1991) The basolateral amygdala-ventral striatal system and conditioned place preference: further evidence of limbic-striatal interactions underlying reward-related processes. Neuroscience 42(1):1–18
Ferbinteanu J, McDonald RJ (2001) Dorsal/ventral hippocampus, fornix, and conditioned place preference. Hippocampus 11(2):187–200
Fujimoto T, Tanaka H, Kumamaru E, Okamura K, Miki N (2004) Arc interacts with microtubules/microtubule-associated protein 2 and attenuates microtubule-associated protein 2 immunoreactivity in the dendrites. J Neurosci Res 76(1):51–63
Geinisman Y (2000) Structural synaptic modifications associated with hippocampal LTP and behavioral learning. Cereb Cortex 10(10):952–962
Geinisman Y, Berry RW, Disterhoft JF, Power JM, Van der Zee EA (2001) Associative learning elicits the formation of multiple-synapse boutons. J Neurosci 21(15):5568–5573
Gundersen HJ, Bagger P, Bendtsen TF, Evans SM, Korbo L, Marcussen N, Møller A, Nielson K, Nyengaard JR, Pakkenberg B, Sorensen FB, Vesterby A, West MJ (1988) The new stereological tools: disector, fractionator, nucleator and point sampled intercepts and their use in pathological research and diagnosis. APMIS 96(10):857–881
Guzowski JF, McNaughton BL, Barnes CA, Worley PF (1999) Environment-specific expression of the immediate-early gene Arc in hippocampal neuronal ensembles. Nat Neurosci 2(12):1120–1124
Guzowski JF, Lyford GL, Stevenson GD, Houston FP, McGaugh JL, Worley PF, Barnes CA (2000) Inhibition of activity-dependent arc protein expression in the rat hippocampus impairs the maintenance of long-term potentiation and the consolidation of long-term memory. J Neurosci 20(11):3993–4001
Guzowski JF, Setlow B, Wagner EK, McGaugh JL (2001) Experience-dependent gene expression in the rat hippocampus after spatial learning: a comparison of the immediate-early genes Arc, c-fos, and zif268. J Neurosci 21(14):5089–5098
Hearing MC, Schochet TL, See RE, McGinty JF (2010) Context-driven cocaine-seeking in abstinent rats increases activity-regulated gene expression in the basolateral amygdala and dorsal hippocampus differentially following short and long periods of abstinence. Neuroscience 170(2):570–579
Helmstetter FJ, Bellgowan PS (1994) Effects of muscimol applied to the basolateral amygdala on acquisition and expression of contextual fear conditioning in rats. Behav Neurosci 108(5):1005–1009
Hetzel A, Meredith GE, Rademacher DJ, Rosenkranz JA (2012) Effect of amphetamine place conditioning on excitatory synaptic events in the basolateral amygdala ex vivo. Neuroscience 206:7–16
Holland PC, Bouton ME (1999) Hippocampus and context in classical conditioning. Curr Opin Neurobiol 9(2):195–202
Honecker H, Coper H (1975) Kinetics and metabolism of amphetamine in the brain of rats of different ages. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 291(2):111–121
Hsu EH, Schroeder JP, Packard MG (2002) The amygdala mediates memory consolidation for an amphetamine conditioned place preference. Behav Brain Res 129(1–2):93–100
Hung AC, Huang HM, Tsay HJ, Lin TN, Kuo JS, Sun SH (2000) ATP-stimulated c-fos and zif268 mRNA expression is inhibited by chemical hypoxia in a rat brain-derived type 2 astrocyte cell line, RBA-2. J Cell Biochem 77(2):323–332
Hunter A, Stewart MG (1993) Long-term increases in the numerical density of synapses in the chick lobus parolfactorius after passive avoidance training. Brain Res 605(2):251–255
Ingham CA, Hood SH, Taggart P, Arbuthnott GW (1998) Plasticity of synapses in the rat neostriatum after unilateral lesion of the nigrostriatal dopaminergic pathway. J Neurosci 18(12):4732–4743
Ito R, Robbins TW, McNaughton BL, Everitt BJ (2006) Selective excitotoxic lesions of the hippocampus and basolateral amygdala have dissociable effects on appetitive cue and place conditioning based on path integration in a novel Y-maze procedure. Eur J Neurosci 23(11):3071–3080
Jeffery KJ, Anderson MI, Hayman R, Chakraborty S (2004) A proposed architecture for the neural representation of spatial context. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 28(2):201–218
Kelly MP, Deadwyler SA (2002) Acquisition of a novel behavior induces higher levels of Arc mRNA than does overtrained performance. Neuroscience 110(4):617–626
Kelly MP, Deadwyler SA (2003) Experience-dependent regulation of the immediate-early gene arc differs across brain regions. J Neurosci 23(16):6443–6451
Kolb B, Teskey GC (2012) Age, experience, injury, and the changing brain. Dev Psychobiol 54(3):311–325
Kozell LB, Meshul CK (2001) The effects of acute or repeated cocaine administration on nerve terminal glutamate within the rat mesolimbic system. Neuroscience 106(1):16–25
Kozell LB, Meshul CK (2004) Nerve terminal glutamate immunoreactivity in the rat nucleus accumbens and ventral tegmental area after a short withdrawal from cocaine. Synapse 51(4):224–232
Kuo YM, Liang KC, Chen HH, Cherng CG, Lee HT, Lin Y, Huang AM, Liao RM, Yu L (2007) Cocaine- but not methamphetamine-associated memory requires de novo protein synthesis. Neurobiol Learn Mem 87(1):93–100
Lanahan A, Worley P (1998) Immediate-early genes and synaptic function. Neurobiol Learn Mem 70(1–2):37–43
Li R, Nishijo H, Wang Q, Uwano T, Tamura R, Ohtani O, Ono T (2001) Light and electron microscopic study of cholinergic and noradrenergic elements in the basolateral nucleus of the rat amygdala: evidence for interactions between the two systems. J Comp Neurol 439(4):411–425
Link W, Konietzko U, Kauselmann G, Krug M, Schwanke B, Frey U, Kuhl D (1995) Somatodendritic expression of an immediate early gene is regulated by synaptic activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92(12):5734–5738
Lyford GL, Yamagata K, Kaufmann WE, Barnes CA, Sanders LK, Copeland NG, Gilbert DJ, Jenkins NA, Lanahan AA, Worley PF (1995) Arc, a growth factor and activity-regulated gene, encodes a novel cytoskeleton-associated protein that is enriched in neuronal dendrites. Neuron 14(2):433–445
McCutcheon JE, Marinelli M (2009) Age matters. Eur J Neurosci 29(5):997–1014
McDonald AJ, Betette RL (2001) Parvalbumin-containing neurons in the rat basolateral amygdala: morphology and co-localization of Calbindin-D(28 k). Neuroscience 102(2):413–425
McDonald AJ, Mascagni F (2001) Colocalization of calcium-binding proteins and GABA in neurons of the rat basolateral amygdala. Neuroscience 105(3):681–693
Moga DE, Calhoun ME, Chowdhury A, Worley P, Morrison JH, Shapiro ML (2004) Activity-regulated cytoskeletal-associated protein is localized to recently activated excitatory synapses. Neuroscience 125(1):7–11
Mokin M, Lindahl JS, Keifer J (2006) Immediate-early gene-encoded protein Arc is associated with synaptic delivery of GluR4-containing AMPA receptors during in vitro classical conditioning. J Neurophysiol 95(1):215–224
Morshedi MM, Rademacher DJ, Meredith GE (2009) Increased synapses in the medial prefrontal cortex are associated with repeated amphetamine administration. Synapse 63(2):126–135
Mouton PR (2002) Principles and practices of unbiased stereology: an introduction for bioscientists. The Johns Hopkins University Press, Baltimore
Mueller D, Stewart J (2000) Cocaine-induced conditioned place preference: reinstatement by priming injections of cocaine after extinction. Behav Brain Res 115(1):39–47
Mueller D, Perdikaris D, Stewart J (2002) Persistence and drug-induced reinstatement of a morphine-induced conditioned place preference. Behav Brain Res 136(2):389–397
Muller J, Corodimas KP, Fridel Z, LeDoux JE (1997) Functional inactivation of the lateral and basal nuclei of the amygdala by muscimol infusion prevents fear conditioning to an explicit conditioned stimulus and to contextual stimuli. Behav Neurosci 111(4):683–691
Muller JF, Mascagni F, McDonald AJ (2005) Coupled networks of parvalbumin- immunoreactive interneurons in the rat basolateral amygdala. J Neurosci 25(32):7366–7376
Muller JF, Mascagni F, McDonald AJ (2007) Postsynaptic targets of somatostatin-containing interneurons in the rat basolateral amygdala. J Comp Neurol 500(3):513–529
Muller JF, Mascagni F, McDonald AJ (2009) Dopaminergic innervation of pyramidal cells in the rat basolateral amygdala. Brain Struct Funct 213(3):275–288
Nicholson DA, Geinisman Y (2009) Axospinous synaptic subtype-specific differences in structure, size, ionotropic receptor expression, and connectivity in apical dendritic regions of rat hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons. J Comp Neurol 512(3):399–418
Nikam SS, Tennekoon GI, Christy BA, Yoshino JE, Rutkowski JL (1995) The zinc finger transcription factor Zif268/Egr-1 is essential for Schwann cell expression of the p75 NGF receptor. Mol Cell Neurosci 6(4):337–348
O’Donnell P, Grace AA (1997) Cortical afferents modulate striatal gap junction permeability via nitric oxide. Neuroscience 76(1):1–5
Olmstead MC, Franklin KB (1997) The development of a conditioned place preference to morphine: effects of microinjections into various CNS sites. Behav Neurosci 111(6):1324–1334
Paxinos G, Watson C (1998) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates. Academic Press, New York
Peters A, Palay SL, Webster HD (1991) The fine structure of the nervous system: neurons and their supporting cells. Oxford University Press, New York
Pinard R, Benfares J, Lanoir J (1991) Electron microscopic study of GABA-immunoreactive neuronal processes in the superficial gray layer of the rat superior colliculus: their relationships with degenerating retinal nerve endings. J Neurocytol 20(4):262–276
Pinard CR, Muller JF, Mascagni F, McDonald AJ (2008) Dopaminergic innervation of interneurons in the rat basolateral amygdala. Neuroscience 157(4):850–863
Pintchovski SA, Peebles CL, Kim HJ, Verdin E, Finkbeiner S (2009) The serum response factor and a putative novel transcription factor regulate expression of the immediate-early gene Arc/Arg3.1 in neurons. J Neurosci 29(5):1525–1537
Plath N, Ohana O, Dammermann B, Errington ML, Schmitz D, Gross C, Mao X, Engelsberg A, Mahlke C, Welzl H, Kobalz U, Strawrakakis A, Fernandez E, Waltereit R, Bick-Sander A, Therstappen E, Cooke SF, Blanquet V, Wurst W, Salmen B, Bösl MR, Lipp HP, Grant SG, Bliss TV, Wolfer DP, Kuhl D (2006) Arc/Arg3.1 is essential for the consolidation of synaptic plasticity and memories. Neuron 52(3):437–444
Rademacher DJ, Kovacs B, Shen F, Napier TC, Meredith GE (2006) The neural substrates of amphetamine conditioned place preference: implications for the formation of conditioned stimulus-reward associations. Eur J Neurosci 24(7):2089–2097
Rademacher DJ, Napier TC, Meredith GE (2007) Context modulates the expression of conditioned motor sensitization, cellular activation and synaptophysin immunoreactivity. Eur J Neurosci 26(9):2661–2668
Rademacher DJ, Rosenkranz JA, Morshedi MM, Sullivan EM, Meredith GE (2010) Amphetamine-associated contextual learning is accompanied by structural and functional plasticity in the basolateral amygdala. J Neurosci 30(13):4676–4686
Ramírez-Amaya V, Vazdarjanova A, Mikhael D, Rosi S, Worley PF, Barnes CA (2005) Spatial exploration-induced Arc mRNA and protein expression: evidence for selective, network-specific reactivation. J Neurosci 25(7):1761–1768
Robinson TE, Berridge KC (2000) The psychology and neurobiology of addiction: an incentive-sensitization view. Addiction 95(Suppl 2):S91–S117
Rudy JW, Sutherland RJ (1995) Configural association theory and the hippocampal formation: an appraisal and reconfiguration. Hippocampus 5(5):375–389
Sadler R, Herzig V, Schmidt WJ (2007) Repeated treatment with the NMDA antagonist MK-801 disrupts reconsolidation of memory for amphetamine-conditioned place preference. Behav Pharmacol 18(7):699–703
Schiltz CA, Kelley AE, Landry CF (2005) Contextual cues associated with nicotine administration increase arc mRNA expression in corticolimbic areas of the rat brain. Eur J Neurosci 21(6):1703–1711
Schroeder JP, Packard MG (2003) Systemic or intra-amygdala injections of glucose facilitate memory consolidation for extinction of drug-induced conditioned reward. Eur J Neurosci 17(7):1482–1488
Shen F, Meredith GE, Napier TC (2006) Amphetamine-induced place preference and conditioned motor sensitization requires activation of tyrosine kinase receptors in the hippocampus. J Neurosci 26(43):11041–11051
Shepherd JD, Bear MF (2011) New views of Arc, a master regulator of synaptic plasticity. Nat Neurosci 14(3):279–284
Small JV (1968) Measurement of section thickness, In: Fourth European regional conference on electron microscopy, Rome, Italy
Somogyi P, Soltész I (1986) Immunogold demonstration of GABA in synaptic terminals of intracellularly recorded, horseradish peroxidase-filled basket cells and clutch cells in the cat’s visual cortex. Neuroscience 19(4):1051–1065
Sterio DC (1984) The unbiased estimation of number and sizes of arbitrary particles using the disector. J Microsc 134(Pt 2):127–136
Steward O (1995) Targeting of mRNAs to subsynaptic microdomains in dendrites. Curr Opin Neurobiol 5(1):55–61
Steward O, Worley PF (2001) A cellular mechanism for targeting newly synthesized mRNAs to synaptic sites on dendrites. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98(13):7062–7068
Steward O, Wallace CS, Lyford GL, Worley PF (1998) Synaptic activation causes the mRNA for the IEG Arc to localize selectively near activated postsynaptic sites on dendrites. Neuron 21(4):741–751
Tan A, Moratalla R, Lyford GL, Worley P, Graybiel AM (2000) The activity-regulated cytoskeletal-associated protein arc is expressed in different striosome-matrix patterns following exposure to amphetamine and cocaine. J Neurochem 74(5):2074–2078
Teber I, Köhling R, Speckmann EJ, Barnekow A, Kremerskothen J (2004) Muscarinic acetylcholine receptor stimulation induces expression of the activity-regulated cytoskeleton-associated gene (ARC). Brain Res Mol Brain Res 121(1–2):131–136
Toni N, Buchs PA, Nikonenko I, Bron CR, Muller D (1999) LTP promotes formation of multiple spine synapses between a single axon terminal and a dendrite. Nature 402(6760):421–425
Toni N, Buchs PA, Nikonenko I, Povilaitite P, Parisi L, Muller D (2001) Remodeling of synaptic membranes after induction of long-term potentiation. J Neurosci 21(16):6245–6251
van den Pol AN (1991) Glutamate and aspartate immunoreactivity in hypothalamic presynaptic axons. J Neurosci 11(7):2087–2101
Vazdarjanova A, Ramírez-Amaya V, Insel N, Plummer TK, Rosi S, Chowdhury S, Mikhael D, Worley PF, Guzowski JF, Barnes CA (2006) Spatial exploration induces ARC, a plasticity-related immediate-early gene, only in calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II-positive principal excitatory and inhibitory neurons of the rat forebrain. J Comp Neurol 498(3):317–329
Wallace CS, Lyford GL, Worley PF, Steward O (1998) Differential intracellular sorting of immediate early gene mRNAs depends on signals in the mRNA sequence. J Neurosci 18(1):26–35
Wang JQ, McGinty JF (1995) Alterations in striatal zif/268, preprodynorphin and preproenkephalin mRNA expression induced by repeated amphetamine administration in rats. Brain Res 673(2):262–274
Wang H, Pickel VM (2004) Activity-regulated cytoskeleton-associated protein Arc is targeted to dendrites and coexpressed with mu-opioid receptors in postnatal rat caudate-putamen nucleus. J Neurosci Res 77(3):323–333
White NM (1996) Addictive drugs as reinforcers: multiple partial actions on memory systems. Addiction 91(7):921–949 (Discussion 951–965)
Woodruff AR, Monyer H, Sah P (2006) GABAergic excitation in the basolateral amygdala. J Neurosci 26(46):11881–11887
Waung MW, Pfeiffer BE, Nosyreva ED, Ronesi JA, Huber KM (2008) Rapid translation of Arc/Arc3.1 selectively mediates mGluR-dependent LTD through persistent increases in AMPAR endocytosis rate. Neuron 59(1):84–97
Zhang WP, Guzowski JF, Thomas SA (2005) Mapping neuronal activation and the influence of adrenergic signaling during contextual memory retrieval. Learn Mem 12(3):239–247
Zhou W, Mailloux AW, Jung BJ, Edmunds HS Jr, McGinty JF (2004) GABAB receptor stimulation decreases amphetamine-induced behavior and neuropeptide gene expression in the striatum. Brain Res 1004(1–2):18–28
Acknowledgments
These studies were funded by Grant DA024790 to D.J.R. from the National Institute on Drug Abuse and summer research fellowships to P.J.D. and I.R. We thank Figen Seiler of the Electron Microscopy Center at Rosalind Franklin University of Medicine and Science for her careful and diligent technical assistance.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Figge, D.A., Rahman, I., Dougherty, P.J. et al. Retrieval of contextual memories increases activity-regulated cytoskeleton-associated protein in the amygdala and hippocampus. Brain Struct Funct 218, 1177–1196 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-012-0453-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00429-012-0453-y