Abstract
Background
The severity of childhood gastroenteritis is generally believed to be age-related rather than aetiology-related. Rotavirus-induced gastroenteritis is more severe than gastroenteritis caused by other enteric pathogens and is also age-related. We thus addressed the question of whether the increased severity of rotavirus-induced gastroenteritis is related to age or to features intrinsic to the agent.
Study design
In this multicentre, hospital-based, prospective survey, we evaluated the severity of diarrhoea in rotavirus-positive and rotavirus-negative children up to 4 years of age. Severity was assessed with a score in four groups of age-matched children.
Results
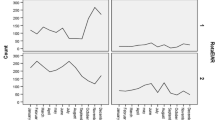
Rotavirus was detected in 381 of 911 children. Disease severity was evaluated in 589 cases for which clinical data were complete. The rotavirus-positive and rotavirus-negative groups differed with regards to diarrhoea duration, hospital stay, degree of dehydration and the number of episodes of vomiting. Gastroenteritis was more severe in rotavirus-positive than in rotavirus-negative children. In contrast, none of the main severity parameters differed in the four age groups, irrespective of the presence of rotavirus.
Conclusions
These data provide the evidence that aetiology and not age determines diarrhoeal severity. The demonstration that diarrhoea was more severe in rotavirus-positive children supports the need for a rotavirus vaccine and for studies that address the duration of vaccine protection.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- EIA:
-
enzyme immunoassay
- PCR:
-
polymerase chain reaction
References
Avendano P, Matson DO, Long J, Whitney S, Matson CC, Pickering LK (1993) Costs associated with office visits for diarrhea in infants and toddlers. Pediatric Infect Dis J 12(11):897–902
Bern C, Unicomb L, Gentsch JR, Banul N, Yunus M, Sack RB, Glass RI (1992) Rotavirus diarrhea in Bangladeshi children: correlation of disease severity with serotypes. J Clin Microbiol 30(12):3234–3238
Cascio A, Vizzi E, Alaimo C, Arista S (2001) Rotavirus gastroenteritis in Italian children: can severity of symptoms be related to the infecting virus? Clin Infect Dis 32(8):1126–1132
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) (1998) Rotavirus vaccine for the prevention of rotavirus gastroenteritis among children: recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP). MMWR Recomm Rep 48(RR-2):1–20
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) (1999) Intussusceptions among recipients of rotavirus vaccine—United States, 1998–1999. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 48(27):577–581
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) (1999) Withdrawal of rotavirus vaccine recommendation. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep 48(43):1007
Clark HF, Lawley DA, Schaffer A, Patacsil JM, Marcello AE, Glass RI, Jain V, Gentsch J (2004) Assessment of the epidemic potential of a new strain of rotavirus associated with the novel G9 the epidemic potential of a new strain of rotavirus associated with the novel G9 serotype which caused an outbreak in the United States for the first time in the 1995–1996 season. J Clin Microbiol 42(4):1434–1438
Cohen MB (1991) Etiology and mechanisms of acute infectious diarrhea in infants in the United States. J Pediatric 118(4 Pt 2):S34–S39
Coulson BS, Unicomb LE, Pitson GA, Bishop RF (1987) Simple and specific enzyme immunoassay using monoclonal antibodies for serotyping human rotaviruses. J Clin Microbiol 25(3):509–515
Ehlken B, Laubereau B, Karmaus W, Petersen G, Rohwedder A, Forster J; RoMoD Study Group (2002) Prospective population-based study on rotavirus disease in Germany. Acta Paediatric 91(7):769–775
Fruhwirth M, Heininger U, Ehlken B, Petersen G, Laubereau B, Moll-Schuler I, Mutz I, Forster J (2001) International variation in disease burden of rotavirus gastroenteritis in children with community- and nosocomially acquired infection. Pediatric Infect Dis J 20(8):784–791
Fruhwirth M, Karmaus W, Moll-Schuler I, Brosl S, Mutz I (2001) A prospective evaluation of community acquired gastroenteritis in paediatric practices: impact and disease burden of rotavirus infection. Arch Dis Child 84(5):393–397
Gonzales-Adriano SR, Valdes-Garza HE, Garcia-Valdes LC (1988) Hidratacion oral versus hidratacion endovenosa en pacientes con diarrea aguda. Bol Med Hosp Infant Mex 45(3):165–172
Gorelick MH, Shaw KN, Murphy KO (1997) Validity and reliability of clinical signs in the diagnosis of dehydration in children. Pediatrics 99(5):e6
Gouvea V, Glass RI, Woods P, Taniguchi K, Clark HF, Forrester B, Fang ZY (1990) Polymerase chain reaction amplification and typing of rotavirus nucleic acid from stool specimens. J Clin Microbiol 28(2):276–282
Guarino A, Albano F (2004) Viral diarrhea. In: Guandalini S (ed) Textbook of pediatric gastroenterology and nutrition. Taylor and Francis, London, UK, pp 127–144
Hsu VP, Staat MA, Roberts N, Thieman C, Bernstein DI, Bresee J, Glass RI, Parashar UD (2005) Use of active surveillance to validate International Classification of Diseases code estimates of rotavirus hospitalizations in children. Pediatrics 115(1):78–82
Johansen K, Bennet R, Bondesson K, Eriksson M, Hedlund KO, De Verdier Klingenberg K, Uhnoo I, Svensson L (1999) Incidence and estimates of the disease burden of rotavirus in Sweden. Acta Paediatric Suppl 88(426):20–23
Kapikian AZ (1996) Overview of viral gastroenteritis. Arch Virol Suppl 12:7–19
Matson DO, Estes MK (1990) Impact of rotavirus infection at a large pediatric hospital. J Infect Dis 162(3):598–604
Mrukowicz JZ, Krobicka B, Duplaga M, Kowalska-Duplaga K, Domanski J, Szajewska H, Kantecki M, Iwanczak F, Pytrus T (1999) Epidemiology and impact of rotavirus diarrhoea in Poland. Acta Paediatric Suppl 88(426):53–60
Murphy TV, Gargiullo PM, Massoudi MS, Nelson DB, Jumaan AO, Okoro CA, Zanardi LR, Setia S, Fair E, LeBaron CW, Wharton M, Livengood JR; Rotavirus Intussusception Investigation Team (2001) Intussusceptions among infants given an oral rotavirus vaccine. N Engl J Med 344(8):564–572
Parashar UD, Hummelman EG, Bresee JS, Miller MA, Glass RI (2003) Global illness and deaths caused by rotavirus disease in children. Emerg Infect Dis 9(5):565–572
Rivest P, Proulx M, Lonergan G, Lebel MH, Bedard L (2004) Hospitalizations for gastroenteritis: the role of rotavirus. Vaccine 22(15–16):2013–2017
Ruiz-Palacios GM, Perez-Schael I, Velazquez FR, Abate H, Breuer T, Clemens SC, Cheuvart B, Espinoza F, Gillard P, Innis BL, Cervantes Y, Linhares AC, Lopez P, Macias-Parra M, Ortega-Barria E, Richardson V, Rivera-Medina DM, Rivera L, Salinas B, Pavia-Ruz N, Salmeron J, Ruttimann R, Tinoco JC, Rubio P, Nunez E, Guerrero ML, Yarzabal JP, Damaso S, Tornieporth N, Saez-Llorens X, Vergara RF, Vesikari T, Bouckenooghe A, Clemens R, De Vos B, O’Ryan M; Human Rotavirus Vaccine Study Group (2006) Safety and efficacy of an attenuated vaccine against severe rotavirus gastroenteritis. N Engl J Med 354(1):11–22
Ruuska T, Vesikari T (1990) Rotavirus disease in Finnish children: use of numerical scores for clinical severity of diarrhoeal episodes. Scand J Infect Dis 22(3):259–267
Ruuska T, Vesikari T (1991) A prospective study of acute diarrhea in Finnish children from birth to 2.5 years of age: clinical severity, etiology and risk factors. Acta Paediatric Scand 80(5):500–507
Santos N, Hoshino Y (2005) Global distribution of rotavirus serotypes/genotypes and its implication for the development and implementation of an effective rotavirus vaccine. Rev Med Virol 15(1):29–56
Velazquez FR, Matson DO, Calva JJ, Guerrero L, Morrow AL, Carter-Campbell S, Glass RI, Estes MK, Pickering LK, Ruiz-Palacios GM (1996) Rotavirus infection in infants as protection against subsequent infections. N Engl J Med 335(14):1022–1028
Velazquez FR, Matson DO, Guerrero ML, Shults J, Calva JJ, Morrow AL, Glass RI, Pickering LK, Ruiz-Palacios GM (2000) Serum antibody as a marker of protection against natural rotavirus infection and disease. J Infect Dis 182(6):1602–1609
Vesikari T, Matson DO, Dennehy P, Van Damme P, Santosham M, Rodriguez Z, Dallas MJ, Heyse JF, Goveia MG, Black SB, Shinefield HR, Christie CD, Ylitalo S, Itzler RF, Coia ML, Onorato MT, Adeyi BA, Marshall GS, Gothefors L, Campens D, Karvonen A, Watt JP, O’Brien KL, DiNubile MJ, Clark HF, Boslego JW, Offit PA, Heaton PM; Rotavirus Efficacy and Safety Trial (REST) Study Team (2006) Safety and efficacy of a pentavalent human-bovine (WC3) reassortant rotavirus vaccine. N Engl J Med 354(1):23–33
Widdowson MA, Bresee JS, Gentsch JR, Glass RI (2005) Rotavirus disease and its prevention. Curr Opin Gastroenterol 21(1):26–31
Yolken RH, Wyatt RG, Zissis G, Brandt CD, Rodriguez WJ, Kim HW, Parrott RH, Urrutia JJ, Mata L, Greenberg HB, Kapikian AZ, Chanock RM (1978) Epidemiology of human rotavirus Types 1 and 2 as studied by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. N Engl J Med 299(21):1156–1161
Acknowledgement
This work was financially supported by a grant from the Italian Ministry of Health, 4th AIDS Research Project, Program 50 D.28.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Albano, F., Bruzzese, E., Bella, A. et al. Rotavirus and not age determines gastroenteritis severity in children: a hospital-based study. Eur J Pediatr 166, 241–247 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00431-006-0237-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00431-006-0237-6