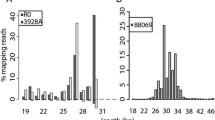
Abstract
Microsporidia are a group of intracellular parasites characterized by highly reduced and compact genomes. The presence of a high gene density had several consequences for microsporidian genomes, including a high frequency of overlap between transcripts of adjacent genes. This phenomenon is apparently widespread in microsporidia, and strongly correlated with gene density. However, all analyses to date have focused on one or a few transcripts from many loci, so it is unclear how diverse the pool of transcripts at a given locus may be. To address this question, we characterized initiation and termination points from 62 transcripts in gene-dense regions in Antonospora locustae spores using both conventional and fluorescence-based RACE-PCR procedures. In parallel, we investigated the abundance and nature of transcripts along a 6 kb region surrounding the actin locus of A. locustae using northern blotting, RACE-PCR and previously characterised EST sequences. Overall, we confirmed previous suggestions that most transcripts in A. locustae spores overlap with the downstream gene, but that at the 5′ end untranslated regions are very short and overlap is rare. From fluorescence-based RACE-PCR we show that transcription of most genes (31 out of 34) initiates at a single position, whereas 35% of loci analyzed with 3′ RACE polyadenylate mRNA at several sites. Finally, we identified the presence of previously unsuspected and very large transcripts in A. locustae spores. Those transcripts were found to overlap up to four open reading frames in different strands, adding a novel layer of complexity in the mRNA transcription of this microsporidian species.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Becnel JJ, Andreadis TG (1999) Microsporidia in insects. In: Witter M, WLM (ed) The microsporidia and microsporidiosis. American Society of Microbiology Press, pp 447–501
Biderre C, Pages M, Metenier G, David D, Bata J, Prensier G, Vivares CP (1994) On small genomes in eukaryotic organisms: molecular karyotypes of two microsporidian species (Protozoa) parasites of vertebrates. C R Acad Sci III 317(5):399–404
Blumenthal T (1998) Gene clusters and polycistronic transcription in eukaryotes. Bioessays 20(6):480–487
Blumenthal T (2004) Operons in eukaryotes. Brief Funct Genomic Proteomic 3(3):199–211
Blumenthal T, Gleason KS (2003) Caenorhabditis elegans operons: form and function. Nat Rev Genet 4(2):112–120
Corradi N, Akiyoshi DE, Morrison HG, Feng X, Weiss LM, Tzipori S, Keeling PJ (2007) Patterns of genome evolution among the microsporidian parasites Encephalitozoon cuniculi, Antonospora locustae and Enterocytozoon bieneusi. PLoS ONE 2(12):e1277
Corradi N, Gangaeva A, Keeling PJ (2008) Comparative profiling of overlapping transcription in the compacted genomes of microsporidia Antonospora locustae and Encephalitozoon cuniculi. Genomics 91(4):388–393
Gerads M, Ernst JF (1998) Overlapping coding regions and trancriptional units of two essential chromosomal genes (CCT8, TRP1) in the fungal pathogen Candida albicans. Nucleic Acids Res 26(22):5061–50616
Gilson PR, Maier UG, McFadden GI (1997) Size isn’t everything: lessons in genetic miniaturisation from nucleomorphs. Curr Opin Genet Dev 7(6):800–806
Gilson PR, McFadden GI (2002) Jam packed genomes–a preliminary, comparative analysis of nucleomorphs. Genetica 115(1):13–28
Goldberg AV, Molik S, Tsaousis AD, Neumann K, Kuhnke G, Delbac F, Vivares CP, Hirt RP, Lill R, Embley TM (2008) Localization and functionality of microsporidian iron-sulphur cluster assembly proteins. Nature 452(7187):624–628
Hansen K, Birse CE, Proudfoot NJ (1998) Nascent transcription from the nmt1 and nmt2 genes of Schizosaccharomyces pombe overlaps neighbouring genes. Embo J 17(11):3066–3077
James TY, Kauff F, Schoch CL, Matheny PB, Hofstetter V, Cox CJ, Celio G, Gueidan C, Fraker E, Miadlikowska J and others (2006) Reconstructing the early evolution of Fungi using a six-gene phylogeny. Nature 443(7113):818–822
Katinka MD, Duprat S, Cornillot E, Metenier G, Thomarat F, Prensier G, Barbe V, Peyretaillade E, Brottier P, Wincker P, Others (2001) Genome sequence and gene compaction of the eukaryote parasite Encephalitozoon cuniculi. Nature 414(6862):450–453
Keeling PJ (2003) Congruent evidence from alpha-tubulin and beta-tubulin gene phylogenies for a zygomycete origin of microsporidia. Fungal Genet Biol 38(3):298–309
Keeling PJ, Doolittle WF (1996) Alpha-tubulin from early-diverging eukaryotic lineages and the evolution of the tubulin family. Mol Biol Evol 13(10):1297–1305
Keeling PJ, Luker MA, Palmer JD (2000) Evidence from beta-tubulin phylogeny that microsporidia evolved from within the fungi. Mol Biol Evol 17(1):23–31
Larsson JIR (1999) Identification of microsporidia. Acta Protozoologica 38(3):161–197
Mignone F, Gissi C, Liuni S, Pesole G (2002) Untranslated regions of mRNAs. Genome Biol 3(3):REVIEWS0004
Peyretaillade E, Biderre C, Peyret P, Duffieux F, Metenier G, Gouy M, Michot B, Vivares CP (1998) Microsporidian encephalitozoon cuniculi, a unicellular eukaryote with an unusual chromosomal dispersion of ribosomal genes and a LSU rRNA reduced to the universal core. Nucleic Acids Res 26(15):3513–3520
Prescott EM, Proudfoot NJ (2002) Transcriptional collision between convergent genes in budding yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99(13):8796–8801
Slamovits CH, Fast NM, Law JS, Keeling PJ (2004) Genome compaction and stability in microsporidian intracellular parasites. Curr Biol 14(10):891–896
Slamovits CH, Keeling PJ (2004) Class II photolyase in a microsporidian intracellular parasite. J Mol Biol 341(3):713–721
Spieth J, Brooke G, Kuersten S, Lea K, Blumenthal T (1993) Operons in C. elegans polycistronic mRNA precursors are processed by trans-splicing of SL2 to downstream coding regions. Cell 73(3):521–532
Thomarat F, Vivares CP, Gouy M (2004) Phylogenetic analysis of the complete genome sequence of Encephalitozoon cuniculi supports the fungal origin of microsporidia and reveals a high frequency of fast-evolving genes. J Mol Evol 59(6):780–791
Tsaousis AD, Kunji ER, Goldberg AV, Lucocq JM, Hirt RP, Embley TM (2008) A novel route for ATP acquisition by the remnant mitochondria of Encephalitozoon cuniculi. Nature
Van de Peer Y, Ben Ali A, Meyer A (2000) Microsporidia: accumulating molecular evidence that a group of amitochondriate and suspectedly primitive eukaryotes are just curious fungi. Gene 246(1/2):1–8
Vivares CP, Metenier G (2000) Towards the minimal eukaryotic parasitic genome. Curr Opin Microbiol 3(5):463–467
Williams BA, Slamovits CH, Patron NJ, Fast NM, Keeling PJ (2005) A high frequency of overlapping gene expression in compacted eukaryotic genomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102(31):10936–10941
Zorio DA, Cheng NN, Blumenthal T, Spieth J (1994) Operons as a common form of chromosomal organization in C. elegans. Nature 372(6503):270–272
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a grant from the Canadian Institutes for Health Research (MOP-84265). PJK is a Fellow of the Canadian Institute for Advanced Research and a Senior Scholar of the Michael Smith Foundation for Health Research. NC was partly supported by a fellowship from the Swiss National Science Foundation (PBLAA - 114238). L.B. was supported by fellowships from MSFHR and CIHR. We thank Todd Harper for critically reading of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by S. Hohmann.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Corradi, N., Burri, L. & Keeling, P.J. mRNA processing in Antonospora locustae spores. Mol Genet Genomics 280, 565–574 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-008-0387-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-008-0387-5