Abstract
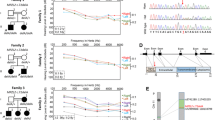
A genome wide linkage analysis of nonsyndromic deafness segregating in a consanguineous Pakistani family (PKDF537) was used to identify DFNB63, a new locus for congenital profound sensorineural hearing loss. A maximum two-point lod score of 6.98 at θ = 0 was obtained for marker D11S1337 (68.55 cM). Genotyping of 550 families revealed three additional families (PKDF295, PKDF702 and PKDF817) segregating hearing loss linked to chromosome 11q13.2-q13.3. Meiotic recombination events in these four families define a critical interval of 4.81 cM bounded by markers D11S4113 (68.01 cM) and D11S4162 (72.82 cM), and SHANK2, FGF-3, TPCN2 and CTTN are among the candidate genes in this interval. Positional identification of this deafness gene should reveal a protein necessary for normal development and/or function of the auditory system.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed ZM, Smith TN, Riazuddin S, Makishima T, Ghosh M, Bokhari S, Menon PSN, Deshmukh D, Griffith AJ, Riazuddin S, Friedman TB, Wilcox ER (2002) Nonsyndromic recessive deafness DFNB18 and Usher syndrome type IC are allelic mutations of USHIC. Hum Genet 110:527–531
Friedman TB, Griffith AJ (2003) Human nonsyndromic sensorineural deafness. Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet 4:341–402
Grimberg J, Nawoschik S, Belluscio L, McKee R, Turck A, Eisenberg A (1989) A simple and efficient non-organic procedure for the isolation of genomic DNA from blood. Nucleic Acids Res 17:8390
Han W, Kim KH, Jo MJ, Lee JH, Yang J, Doctor RB, Moe OW, Lee J, Kim E, Lee MG (2006) Shank2 associates with and regulates Na+/H+ exchanger 3. J Biol Chem 281:1461–1469
Huang X, Godfrey TE, Gooding WE, McCarty KS Jr, Gollin SM (2006) Comprehensive genome and transcriptome analysis of the 11q13 amplicon in human oral cancer and synteny to the 7F5 amplicon in murine oral carcinoma. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 45:1058–1069
Kharkovets T, Hardelin JP, Safieddine S, Schweizer M, El-Amraoui A, Petit C, Jentsch Tj (2000) KCNQ4, a K+ channel mutated in a form of dominant deafness, is exoressed in the inner ear and central auditory pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:4333–4338
Kubisch C, Schroeder BC, Friedrich T, Lutjohann B, El-Amraoui A, Marlin S, Petit C, Jentsch TJ (1999) KCNQ4, a novel potassium channel expressed in sensory outer hair cells, is mutated in dominant deafness. Cell 96:437–446
Mansour SL, Goddard JM, Capecchi MR (1993) Mice homozygous for a targeted disruption of the proto-oncogene int-2 have developmental defects in the tail and inner ear. Development 117:13–28
Marazita ML, Ploughman LM, Rawlings B, Remington E, Arnos KS, Nance WE (1993) Genetic Epedimiological studies of early onset deafness in U. S. School-age population. Am J Med Genet 46:486–491
Marcus DC, Wu T, Wangemann P, Kofuji P (2002) KCNJ10 (Kir4.1) potassium channel knockout abolishes endocochlear potential. Am J Physiol 282:C403–C407
Morton CC, Nance WE (2006) Newborn hearing screening—a silent revolution. N Engl J Med 18:2151–2164
Moynihan L, Houseman M, Newton V, Mueller R, Lench N (1999) DFNB20, a novel locus for autosomal recessive, non-syndromal sensorineural hearing loss maps to chromosome 11q25-qter. Eur J Hum Genet 7:243–246
Mustapha M, Weil D, Chardenoux S, Elias S, El-Zir E, Beckmann JS, Loiselet J, Petit C (1999) An alpha-tectorin gene defect causes a newly identified autosomal recessive form of sensorineural pre-lingual non-syndromic deafness, DFNB21. Hum Mol Genet 8:409–412
Neyroud N, Tesson F, Denjoy I, Leibovici M, Donger C, Barhanin J, Faure S, Gary F, Coumel P, Petit C, Schwartz K, Guicheney P (1997) A novel mutation in the potassium channel gene KVLQT1 causes the Jervell and Lange-Nielsen cardioauditory syndrome. Nat Genet 15:186–189
Petersen MB, Willems PJ (2006) Nonsyndromic, autosomal-recessive deafness. Clin Genet 69:371–392
Schaffer AA (1996) Faster linkage analysis computations for pedigrees with loops or unused alleles. Hum Hered 46:226–235
Shabbir MI, Ahmed ZM, Khan SY, Riazuddin S, Waryah AM, Khan SN, Camps RD, Gosh M, Kabra M, Belyantseva IA, Friedman TB, Riazuddin S (2006) Mutations of human TMHS cause recessively inherited non-syndromic hearing loss. J Med Genet 43(8):634–640
Shaikh RS, Ramzan K, Nazli S, Sattar S, Khan SN, Riazuddin S, Ahmed ZM, Friedman TB, Riazuddin S (2005) A new locus for nonsyndromic deafness DFNB51 maps to chromosome 11p13-p12. Am J Med Genet 138(4):392–395
Wangemann P, Liu J, Marcus DC (1995) Ion transport mechanisms responsible for K+ secretion and the transepithelial voltage across marginal cells of stria vascularis in vitro. Hear Res 84:19–29
Weil D, Kussel P, Blanchard S, Levy G, Levi-Acobas F, Drira M, Ayadi H, Petit C (1997) The autosomal recessive isolated deafness, DFNB2, and the Usher 1B syndrome are allelic defects of the myosin-VIIA gene. Nat Genet 16:191–193
Wilkinson DG, Bhatt S, McMahon AP (1989) Expression pattern of the FGF-related proto-oncogene int-2 suggest multiple roles in fetal development. Development 105:131–136
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the families who made this research possible. We are also thankful to Julie Schultz, Linda Peters, Byung-Yoon Choi, Rob Morell and Dennis Drayna for their suggestions regarding this manuscript. This study was supported by the Higher Education Commission, Islamabad, Pakistan; Ministry of Science and Technology, Islamabad, Pakistan and by the International Center for Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology, Trieste, Italy under project CRP/PAK02-01 (contract no. 02/013) and by intramural funds from the National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders, NIH (1 ZO1 DC000039-09).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khan, S.Y., Riazuddin, S., Tariq, M. et al. Autosomal recessive nonsyndromic deafness locus DFNB63 at chromosome 11q13.2–q13.3. Hum Genet 120, 789–793 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-006-0275-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-006-0275-1