Abstract
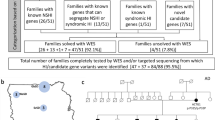
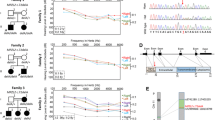
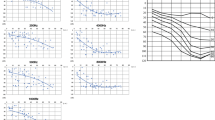
A missense mutation of Gipc3 was previously reported to cause age-related hearing loss in mice. Point mutations of human GIPC3 were found in two small families, but association with hearing loss was not statistically significant. Here, we describe one frameshift and six missense mutations in GIPC3 cosegregating with DFNB72 hearing loss in six large families that support statistically significant evidence for genetic linkage. However, GIPC3 is not the only nonsyndromic hearing impairment gene in this region; no GIPC3 mutations were found in a family cosegregating hearing loss with markers of chromosome 19p. Haplotype analysis excluded GIPC3 from the obligate linkage interval in this family and defined a novel locus spanning 4.08 Mb and 104 genes. This closely linked but distinct nonsyndromic hearing loss locus was designated DFNB81.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed ZM, Morell RJ, Riazuddin S, Gropman A, Shaukat S, Ahmad MM, Mohiddin SA, Fananapazir L, Caruso RC, Husnain T, Khan SN, Griffith AJ, Friedman TB, Wilcox ER (2003) Mutations of MYO6 are associated with recessive deafness, DFNB37. Am J Hum Genet 72(5):1315–1322
Ain Q, Nazli S, Riazuddin S, Jaleel AU, Riazuddin SA, Zafar AU, Khan SN, Husnain T, Griffith AJ, Ahmed ZM, Friedman TB (2007) The autosomal recessive nonsyndromic deafness locus DFNB72 is located on chromosome 19p13.3. Hum Genet 122(5):445–450
Avraham KB, Hasson T, Steel KP, Kingsley DM, Russell LB, Mooseker MS, Copeland NG, Jenkins NA (1995) The mouse Snell’s waltzer deafness gene encodes an unconventional myosin required for structural integrity of inner ear hair cells. Nat Genet 11(4):369–375
Cavalli-Sforza LL, King MC (1986) Detecting linkage for genetically heterogeneous diseases and detecting heterogeneity with linkage data. Am J Hum Genet 38(5):599–616
Charizopoulou N, Lelli A, Schraders M, Ray K, Hildebrand MS, Ramesh A, Srisailapathy CR, Oostrik J, Admiraal RJ, Neely HR, Latoche JR, Smith RJ, Northup JK, Kremer H, Holt JR, Noben-Trauth K (2011) Gipc3 mutations associated with audiogenic seizures and sensorineural hearing loss in mouse and human. Nat Commun 2:201
Chen A, Wayne S, Bell A, Ramesh A, Srisailapathy CR, Scott DA, Sheffield VC, Van Hauwe P, Zbar RI, Ashley J, Lovett M, Van Camp G, Smith RJ (1997) New gene for autosomal recessive non-syndromic hearing loss maps to either chromosome 3q or 19p. Am J Med Genet 71(4):467–471
Dror AA, Avraham KB (2009) Hearing loss: mechanisms revealed by genetics and cell biology. Annu Rev Genet 43:411–437
Friedman TB, Griffith AJ (2003) Human nonsyndromic sensorineural deafness. Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet 4:341–402
Grimwood J, Gordon LA, Olsen A, Terry A, Schmutz J, Lamerdin J, Hellsten U, Goodstein D, Couronne O, Tran-Gyamfi M, Aerts A, Altherr M, Ashworth L, Bajorek E, Black S, Branscomb E, Caenepeel S, Carrano A, Caoile C, Chan YM, Christensen M, Cleland CA, Copeland A, Dalin E, Dehal P, Denys M, Detter JC, Escobar J, Flowers D, Fotopulos D, Garcia C, Georgescu AM, Glavina T, Gomez M, Gonzales E, Groza M, Hammon N, Hawkins T, Haydu L, Ho I, Huang W, Israni S, Jett J, Kadner K, Kimball H, Kobayashi A, Larionov V, Leem SH, Lopez F, Lou Y, Lowry S, Malfatti S, Martinez D, McCready P, Medina C, Morgan J, Nelson K, Nolan M, Ovcharenko I, Pitluck S, Pollard M, Popkie AP, Predki P, Quan G, Ramirez L, Rash S, Retterer J, Rodriguez A, Rogers S, Salamov A, Salazar A, She X, Smith D, Slezak T, Solovyev V, Thayer N, Tice H, Tsai M, Ustaszewska A, Vo N, Wagner M, Wheeler J, Wu K, Xie G, Yang J, Dubchak I, Furey TS, DeJong P, Dickson M, Gordon D, Eichler EE, Pennacchio LA, Richardson P, Stubbs L, Rokhsar DS, Myers RM, Rubin EM, Lucas SM (2004) The DNA sequence and biology of human chromosome 19. Nature 428(6982):529–535
Hilgert N, Smith RJ, Van Camp G (2009) Function and expression pattern of nonsyndromic deafness genes. Curr Mol Med 9(5):546–564
Katoh M (2002) GIPC gene family. Int J Mol Med 9(6):585–589
Li Y, Vinckenbosch N, Tian G, Huerta-Sanchez E, Jiang T, Jiang H, Albrechtsen A, Andersen G, Cao H, Korneliussen T, Grarup N, Guo Y, Hellman I, Jin X, Li Q, Liu J, Liu X, Sparso T, Tang M, Wu H, Wu R, Yu C, Zheng H, Astrup A, Bolund L, Holmkvist J, Jorgensen T, Kristiansen K, Schmitz O, Schwartz TW, Zhang X, Li R, Yang H, Wang J, Hansen T, Pedersen O, Nielsen R (2010) Resequencing of 200 human exomes identifies an excess of low-frequency non-synonymous coding variants. Nat Genet 42(11):969–972
MacArthur DG, Tyler-Smith C (2010) Loss-of-function variants in the genomes of healthy humans. Hum Mol Genet 19(R2):R125–R130
Morton CC, Nance WE (2006) Newborn hearing screening—a silent revolution. N Engl J Med 354(20):2151–2164
Muller HJ (1950) Our load of mutations. Am J Hum Genet 2(2):111–176
Nicholson P, Yepiskoposyan H, Metze S, Zamudio Orozco R, Kleinschmidt N, Muhlemann O (2010) Nonsense-mediated mRNA decay in human cells: mechanistic insights, functions beyond quality control and the double-life of NMD factors. Cell Mol Life Sci 67(5):677–700
Rehman AU, Morell RJ, Belyantseva IA, Khan SY, Boger ET, Shahzad M, Ahmed ZM, Riazuddin S, Khan SN, Friedman TB (2010) Targeted capture and next-generation sequencing identifies C9orf75, encoding taperin, as the mutated gene in nonsyndromic deafness DFNB79. Am J Hum Genet 86(3):378–388
Saitoh T, Mine T, Katoh M (2002) Molecular cloning and characterization of human GIPC3, a novel gene homologous to human GIPC1 and GIPC2. Int J Oncol 20(3):577–582
Santos RL, Hassan MJ, Sikandar S, Lee K, Ali G, Martin PE Jr, Wambangco MA, Ahmad W, Leal SM (2006) DFNB68, a novel autosomal recessive non-syndromic hearing impairment locus at chromosomal region 19p13.2. Hum Genet 120(1):85–92
Walsh T, Shahin H, Elkan-Miller T, Lee MK, Thornton AM, Roeb W, Abu Rayyan A, Loulus S, Avraham KB, King MC, Kanaan M (2010) Whole exome sequencing and homozygosity mapping identify mutation in the cell polarity protein GPSM2 as the cause of nonsyndromic hearing loss DFNB82. Am J Hum Genet 87(1):90–94
Yngvadottir B, Xue Y, Searle S, Hunt S, Delgado M, Morrison J, Whittaker P, Deloukas P, Tyler-Smith C (2009) A genome-wide survey of the prevalence and evolutionary forces acting on human nonsense SNPs. Am J Hum Genet 84(2):224–234
Acknowledgements
We thank the families who participated in this study and Andrew J. Griffith, Dennis Drayna, and Julie M. Schultz for valuable suggestions. This work was supported by grants from the National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders (NIDCD/NIH) R00-DC009287-03 to Z.M.A, from the Higher Education Commission, Islamabad to W.A., and from NIDCD/NIH DC03594 to S.M.L. Genotyping services were provided to S.M.L. by the Center for Inherited Disease Research through a fully funded federal contract from the NIH to The Johns Hopkins University, Contract Number N01-HG-65403. Work in Pakistan was also supported by the Higher Education Commission, EMRO/WHO23 COMSTECH and Ministry of Science and Technology (MoST, Lahore), and the International Center for Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology, Trieste, Italy under project CRP/PAK08-01 Contract no. 08/009 to Sh.R. Work at NIDCD/NIH was supported by intramural funds DC00039-14 to T.B.F.
Ethical standards
Experiments for this study were performed in Pakistan and in the United States, and comply with the current laws of the country in which they were performed.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rehman, A.U., Gul, K., Morell, R.J. et al. Mutations of GIPC3 cause nonsyndromic hearing loss DFNB72 but not DFNB81 that also maps to chromosome 19p. Hum Genet 130, 759–765 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-011-1018-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-011-1018-5