Abstract
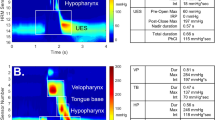
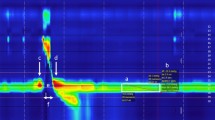
We present an algorithm developed in MATLAB that can be applied to both normal and disordered swallowing to automatically extract a wide array of measurements from the spatiotemporal plots produced by high-resolution manometry (HRM) of the pharyngeal swallow. The algorithm was developed from data from 12 normal and 3 disordered subjects swallowing 5-ml water boluses. Automated extraction was compared to manual extraction for a subset of seven normal and the three disordered subjects to evaluate algorithm accuracy. Area and line integrals, pressure wave velocity, and pressure gradients during upper esophageal sphincter opening were also measured. Automated extraction showed strong correlations with manual extraction, producing high correlation coefficients in both normal and disordered subjects for maximum velopharyngeal pressure and maximum tongue base pressure. Timing data were also strongly correlated for all variables, including velopharyngeal pressure duration, tongue base pressure duration, and total swallow duration. Preliminary descriptive data on area and line integrals are presented. Our results indicate that the algorithm can effectively extract data automatically from HRM spatiotemporal plots. The efficiency of the algorithm makes it a valuable tool to supplement clinical and research use of HRM.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kim SM, McCulloch TM, Rim K. Pharyngeal pressure analysis by the finite element method during liquid bolus swallow. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 2000;109:585–9.
McConnel FM. Analysis of pressure generation and bolus transit during pharyngeal swallowing. Laryngoscope. 1988;98:71–8.
Cook IJ. Normal and disordered swallowing: new insights. Baillieres Clin Gastroenterol. 1991;5:245–67.
McConnel FM, Hood D, Jackson K, O’Connor A. Analysis of intrabolus forces in patients with Zenker’s diverticulum. Laryngoscope. 1994;104:571–81.
Olsson R, Kjellin O, Ekberg O. Videomanometric aspects of pharyngeal constrictor activity. Dysphagia. 1996;11:83–6.
Xue S, Katz PO, Castell JA, et al. Upper esophageal sphincter and pharyngeal manometry: which patients? Gastroenterology. 2000;118:A410 (Abstract).
Logemann JA, Kahrilas PJ, Kobara M, Vakil NB. The benefit of head rotation on pharyngoesophageal dysphagia. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1989;70:767–71.
Lazarus C, Logemann JA, Song CW, Rademaker AW, Kahrilas PJ. Effects of voluntary maneuvers on tongue base function for swallowing. Folia Phoniatr Logop. 2002;54:171–6.
Boden K, Hallgren A, Witt Hedstrom H. Effects of three different swallow maneuvers analyzed by videomanometry. Acta Radiol. 2006;47:628–33.
Hind JA, Nicosia MA, Roecker EB, Carnes ML, Robbins J. Comparison of effortful and noneffortful swallows in healthy middle-aged and older adults. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2001;82:1661–5.
Bulow M, Olsson R, Ekkberg O. Supraglottic swallow, effortful swallow, and chin tuck did not alter hypopharyngeal intrabolus pressure in patients with pharyngeal dysfunction. Dysphagia. 2002;17:197–201.
Bulow M, Olsson R, Ekberg O. Videomanometric analysis of supraglottic swallow, effortful swallow, and chin tuck in healthy volunteers. Dysphagia. 1999;14:67–72.
Isberg A, Nilsson ME, Schiratzki H. The upper esophageal sphincter during normal deglutition. A simultaneous cineradiographic and manometric investigation. Acta Radiol Diagn (Stockh). 1985;26:563–8.
Fox MR, Bredenoord AJ. Oesophageal high-resolution manometry: moving from research into clinical practice. Gut. 2008;57:405–23.
Takasaki K, Umeki H, Enatsu K, Tanaka F, Sakihama N, Kumagami H, Takahashi H. Investigation of pharyngeal swallowing function using high-resolution manometry. Laryngoscope. 2008;118:1729–32.
McCulloch T, Hoffman MR, Ciucci MR. High resolution manometry of pharyngeal swallow pressure events associated with head turn and chin tuck. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 2010;119(6):369–76.
Umeki H, Takasaki K, Enatsu K, Tanaka F, Kumagami H, Takahashi H. Effects of a tongue-holding maneuver during swallowing evaluated by high-resolution manometry. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2009;141:119–22.
Takasaki K, Umeki H, Kumagami H, Takahashi H. Influence of head rotation on upper esophageal sphincter pressure evaluated by high-resolution manometry system. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2010;142:214–7.
Hoffman MR, Ciucci MR, Mielens JD, Jiang JJ, McCulloch TM. Pharyngeal swallow adaptations to bolus volume measured with high resolution manometry. Laryngoscope. 2010;120(12):2367–73.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by a grant from the Department of Surgery, University of Wisconsin School of Medicine and Public Health. The authors thank Dr. Glen Leverson for his assistance with the statistical analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mielens, J.D., Hoffman, M.R., Ciucci, M.R. et al. Automated Analysis of Pharyngeal Pressure Data Obtained with High-Resolution Manometry. Dysphagia 26, 3–12 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-010-9320-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00455-010-9320-2