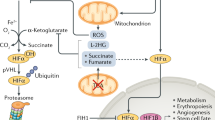
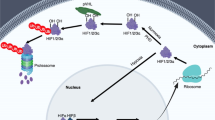
Abstract
To avoid localised problems resulting from excess or inadequate oxygen, all cells and tissues have the ability to sense and respond to changes in oxygen levels. Despite their rich blood supply, the kidneys have unique properties with respect to oxygen that enable them to act as specialised organs, sensing oxygen delivery as well as rendering them prone to hypoxic injury. Essential to normal growth and development, as well as the control of energy metabolism, angiogenesis and erythropoiesis, cellular oxygen homoeostasis is central to the pathophysiology of anaemia, ischaemia, inflammation and cancer, both within the kidney and more generally. A major transcriptional pathway, predominantly regulated by hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF), controls many hundreds of genes, either directly or indirectly, that serve to modulate both the supply and consumption of oxygen. Recent advances have illuminated the mechanisms underlying the regulation of HIF by oxygen and have defined novel therapeutic targets. The challenge now is for us to understand the complexities generated by multiple isoforms of the various components of oxygen sensing, the identification of additional levels of control, and the tissue specific responses to activation of the HIF pathway.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bauer C, Kurtz A (1989) Oxygen sensing in the kidney and its relation to erythropoietin production. Annu Rev Physiol 51:845–856
Koury ST, Koury MJ, Bondurant MC, Caro J, Graber SE (1989) Quantitation of erythropoietin-producing cells in kidneys of mice by in situ hybridization: correlation with hematocrit, renal erythropoietin mRNA, and serum erythropoietin concentration. Blood 74:645–651
Eckardt KU, Koury ST, Tan CC, Schuster SJ, Kaissling B, Ratcliffe PJ, Kurtz A (1993) Distribution of erythropoietin producing cells in rat kidneys during hypoxic hypoxia. Kidney Int 43:815–823
Jelkmann W (1992) Erythropoietin: structure, control of production, and function. Physiol Rev 72:449–489
Semenza GL, Wang GL (1992) A nuclear factor induced by hypoxia via de novo protein synthesis binds to the human erythropoietin gene enhancer at a site required for transcriptional activation. Mol Cell Biol 12:5447–5454
Imagawa S, Goldberg MA, Doweiko J, Bunn HF (1991) Regulatory elements of the erythropoietin gene. Blood 77:278–285
Semenza GL, Nejfelt MK, Chi SM, Antonarakis SE (1991) Hypoxia-inducible nuclear factors bind to an enhancer element located 3′ to the human erythropoietin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:5680–5684
Beck I, Ramirez S, Weinmann R, Caro J (1991) Enhancer element at the 3′-flanking region controls transcriptional response to hypoxia in the human erythropoietin gene. J Biol Chem 266:15563–15566
Pugh CW, Tan CC, Jones RW, Ratcliffe PJ (1991) Functional analysis of an oxygen-regulated transcriptional enhancer lying 3′ to the mouse erythropoietin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:10553–10557
Wang GL, Jiang BH, Rue EA, Semenza GL (1995) Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 is a basic-helix-loop-helix-PAS heterodimer regulated by cellular O2 tension. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92:5510–5514
Reyes H, Reisz-Porszasz S, Hankinson O (1992) Identification of the Ah receptor nuclear translocator protein (Arnt) as a component of the DNA binding form of the Ah receptor. Science 256:1193–1195
Maxwell PH, Pugh CW, Ratcliffe PJ (1993) Inducible operation of the erythropoietin 3′ enhancer in multiple cell lines: evidence for a widespread oxygen-sensing mechanism. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:2423–2427
Schofield CJ, Ratcliffe PJ (2004) Oxygen sensing by HIF hydroxylases. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 5:343–354
Kim JW, Tchernyshyov I, Semenza GL, Dang CV (2006) HIF-1-mediated expression of pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase: a metabolic switch required for cellular adaptation to hypoxia. Cell Metab 3:177–185
Papandreou I, Cairns RA, Fontana L, Lim AL, Denko NC (2006) HIF-1 mediates adaptation to hypoxia by actively downregulating mitochondrial oxygen consumption. Cell Metab 3:187–197
Forsythe JA, Jiang BH, Iyer NV, Agani F, Leung SW, Koos RD, Semenza GL (1996) Activation of vascular endothelial growth factor gene transcription by hypoxia-inducible factor 1. Mol Cell Biol 16:4604–4613
Gerber HP, Condorelli F, Park J, Ferrara N (1997) Differential transcriptional regulation of the two vascular endothelial growth factor receptor genes. Flt-1, but not Flk-1/KDR, is up-regulated by hypoxia. J Biol Chem 272:23659–23667
Pugh CW, Ratcliffe PJ (2003) Regulation of angiogenesis by hypoxia: role of the HIF system. Nat Med 9:677–684
Walmsley SR, Cadwallader KA, Chilvers ER (2005) The role of HIF-1alpha in myeloid cell inflammation. Trends Immunol 26:434–439
Cramer T, Yamanishi Y, Clausen BE, Forster I, Pawlinski R, Mackman N, Haase VH, Jaenisch R, Corr M, Nizet V, Firestein GS, Gerber HP, Ferrara N, Johnson RS (2003) HIF-1alpha is essential for myeloid cell-mediated inflammation. Cell 112:645–657
Kong T, Eltzschig HK, Karhausen J, Colgan SP, Shelley CS (2004) Leukocyte adhesion during hypoxia is mediated by HIF-1-dependent induction of beta2 integrin gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:10440–10445
Makino Y, Kanopka A, Wilson WJ, Tanaka H, Poellinger L (2002) Inhibitory PAS domain protein (IPAS) is a hypoxia-inducible splicing variant of the hypoxia-inducible factor-3alpha locus. J Biol Chem 277:32405–32408
Wiesener MS, Jurgensen JS, Rosenberger C, Scholze CK, Horstrup JH, Warnecke C, Mandriota S, Bechmann I, Frei UA, Pugh CW, Ratcliffe PJ, Bachmann S, Maxwell PH, Eckardt KU (2003) Widespread hypoxia-inducible expression of HIF-2alpha in distinct cell populations of different organs. FASEB J 17:271–273
Rosenberger C, Mandriota S, Jurgensen JS, Wiesener MS, Horstrup JH, Frei U, Ratcliffe PJ, Maxwell PH, Bachmann S, Eckardt KU (2002) Expression of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha and -2alpha in hypoxic and ischemic rat kidneys. J Am Soc Nephrol 13:1721–1732
Iyer NV, Kotch LE, Agani F, Leung SW, Laughner E, Wenger RH, Gassmann M, Gearhart JD, Lawler AM, Yu AY, Semenza GL (1998) Cellular and developmental control of O2 homeostasis by hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha. Genes Dev 12:149–162
Carmeliet P, Dor Y, Herbert JM, Fukumura D, Brusselmans K, Dewerchin M, Neeman M, Bono F, Abramovitch R, Maxwell P, Koch CJ, Ratcliffe P, Moons L, Jain RK, Collen D, Keshert E (1998) Role of HIF-1alpha in hypoxia-mediated apoptosis, cell proliferation and tumour angiogenesis. Nature 394:485–490
Scortegagna M, Ding K, Oktay Y, Gaur A, Thurmond F, Yan LJ, Marck BT, Matsumoto AM, Shelton JM, Richardson JA, Bennett MJ, Garcia JA (2003) Multiple organ pathology, metabolic abnormalities and impaired homeostasis of reactive oxygen species in Epas1−/− mice. Nat Genet 35:331–340
Tian H, Hammer RE, Matsumoto AM, Russell DW, McKnight SL (1998) The hypoxia-responsive transcription factor EPAS1 is essential for catecholamine homeostasis and protection against heart failure during embryonic development. Genes Dev 12:3320–3324
Peng J, Zhang L, Drysdale L, Fong GH (2000) The transcription factor EPAS-1/hypoxia-inducible factor 2alpha plays an important role in vascular remodeling. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:8386–8391
Compernolle V, Brusselmans K, Acker T, Hoet P, Tjwa M, Beck H, Plaisance S, Dor Y, Keshet E, Lupu F, Nemery B, Dewerchin M, Van Veldhoven P, Plate K, Moons L, Collen D, Carmeliet P (2002) Loss of HIF-2alpha and inhibition of VEGF impair fetal lung maturation, whereas treatment with VEGF prevents fatal respiratory distress in premature mice. Nat Med 8:702–710
Lee YM, Jeong CH, Koo SY, Son MJ, Song HS, Bae SK, Raleigh JA, Chung HY, Yoo MA, Kim KW (2001) Determination of hypoxic region by hypoxia marker in developing mouse embryos in vivo: a possible signal for vessel development. Dev Dyn 220:175–186
Krogh A (1919) The number and distribution of capillaries in muscles with calculations of the oxygen pressure head necessary for supplying the tissue. J Physiol 52:409–415
Kitamoto Y, Tokunaga H, Tomita K (1997) Vascular endothelial growth factor is an essential molecule for mouse kidney development: glomerulogenesis and nephrogenesis. J Clin Invest 99:2351–2357
Bernhardt WM, Schmitt R, Rosenberger C, Munchenhagen PM, Grone HJ, Frei U, Warnecke C, Bachmann S, Wiesener MS, Willam C, Eckardt KU (2006) Expression of hypoxia-inducible transcription factors in developing human and rat kidneys. Kidney Int 69:114–122
Sanchez-Elsner T, Botella LM, Velasco B, Langa C, Bernabeu C (2002) Endoglin expression is regulated by transcriptional cooperation between the hypoxia and transforming growth factor-beta pathways. J Biol Chem 277:43799–43808
Freeburg PB, Abrahamson DR (2003) Hypoxia-inducible factors and kidney vascular development. J Am Soc Nephrol 14:2723–2730
Bates CM (2007) Role of fibroblast growth factor receptor signaling in kidney development. Pediatr Nephrol 22:343–349
Li J, Shworak NW, Simons M (2002) Increased responsiveness of hypoxic endothelial cells to FGF2 is mediated by HIF-1alpha-dependent regulation of enzymes involved in synthesis of heparan sulfate FGF2-binding sites. J Cell Sci 115:1951–1959
Elvidge GP, Glenny L, Appelhoff RJ, Ratcliffe PJ, Ragoussis J, Gleadle JM (2006) Concordant regulation of gene expression by hypoxia and 2-oxoglutarate-dependent dioxygenase inhibition: the role of HIF-1alpha, HIF-2alpha, and other pathways. J Biol Chem 281:15215–15226
Sowter HM, Raval RR, Moore JW, Ratcliffe PJ, Harris AL (2003) Predominant role of hypoxia-inducible transcription factor (Hif)-1alpha versus Hif-2alpha in regulation of the transcriptional response to hypoxia. Cancer Res 63:6130–6134
Warnecke C, Zaborowska Z, Kurreck J, Erdmann VA, Frei U, Wiesener M, Eckardt KU (2004) Differentiating the functional role of hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1alpha and HIF-2alpha (EPAS-1) by the use of RNA interference: erythropoietin is a HIF-2alpha target gene in Hep3B and Kelly cells. FASEB J 18:1462–1464
O’Rourke JF, Tian YM, Ratcliffe PJ, Pugh CW (1999) Oxygen-regulated and transactivating domains in endothelial PAS protein 1: comparison with hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha. J Biol Chem 274:2060–2071
Pugh CW, O’Rourke JF, Nagao M, Gleadle JM, Ratcliffe PJ (1997) Activation of hypoxia-inducible factor-1; definition of regulatory domains within the alpha subunit. J Biol Chem 272:11205–11214
Wiesener MS, Turley H, Allen WE, Willam C, Eckardt KU, Talks KL, Wood SM, Gatter KC, Harris AL, Pugh CW, Ratcliffe PJ, Maxwell PH (1998) Induction of endothelial PAS domain protein-1 by hypoxia: characterization and comparison with hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha. Blood 92:2260–2268
Salceda S, Caro J (1997) Hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha (HIF-1alpha) protein is rapidly degraded by the ubiquitin-proteasome system under normoxic conditions. Its stabilization by hypoxia depends on redox-induced changes. J Biol Chem 272:22642–22647
Huang LE, Gu J, Schau M, Bunn HF (1998) Regulation of hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha is mediated by an O2-dependent degradation domain via the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:7987–7992
Arany Z, Huang LE, Eckner R, Bhattacharya S, Jiang C, Goldberg MA, Bunn HF, Livingston DM (1996) An essential role for p300/CBP in the cellular response to hypoxia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:12969–12973
Jaakkola P, Mole DR, Tian YM, Wilson MI, Gielbert J, Gaskell SJ, Kriegsheim A, Hebestreit HF, Mukherji M, Schofield CJ, Maxwell PH, Pugh CW, Ratcliffe PJ (2001) Targeting of HIF-alpha to the von Hippel-Lindau ubiquitylation complex by O2-regulated prolyl hydroxylation. Science 292:468–472
Ivan M, Kondo K, Yang H, Kim W, Valiando J, Ohh M, Salic A, Asara JM, Lane WS, Kaelin WG Jr (2001) HIFalpha targeted for VHL-mediated destruction by proline hydroxylation: implications for O2 sensing. Science 292:464–468
Masson N, Willam C, Maxwell PH, Pugh CW, Ratcliffe PJ (2001) Independent function of two destruction domains in hypoxia-inducible factor-alpha chains activated by prolyl hydroxylation. EMBO J 20:5197–5206
Hirsila M, Koivunen P, Gunzler V, Kivirikko KI, Myllyharju J (2003) Characterization of the human prolyl 4-hydroxylases that modify the hypoxia-inducible factor HIF. J Biol Chem 278:30772–30780
Lando D, Peet DJ, Whelan DA, Gorman JJ, Whitelaw ML (2002) Asparagine hydroxylation of the HIF transactivation domain: a hypoxic switch. Science 295:858–861
Kallio PJ, Okamoto K, O’Brien S, Carrero P, Makino Y, Tanaka H, Poellinger L (1998) Signal transduction in hypoxic cells: inducible nuclear translocation and recruitment of the CBP/p300 coactivator by the hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha. EMBO J 17:6573–6586
Groulx I, Lee S (2002) Oxygen-dependent ubiquitination and degradation of hypoxia-inducible factor requires nuclear-cytoplasmic trafficking of the von Hippel-Lindau tumor suppressor protein. Mol Cell Biol 22:5319–5336
Maynard MA, Qi H, Chung J, Lee EH, Kondo Y, Hara S, Conaway RC, Conaway JW, Ohh M (2003) Multiple splice variants of the human HIF-3 alpha locus are targets of the von Hippel-Lindau E3 ubiquitin ligase complex. J Biol Chem 278:11032–11040
Hara S, Hamada J, Kobayashi C, Kondo Y, Imura N (2001) Expression and characterization of hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-3alpha in human kidney: suppression of HIF-mediated gene expression by HIF-3alpha. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 287:808–813
Myllyharju J (2003) Prolyl 4-hydroxylases, the key enzymes of collagen biosynthesis. Matrix Biol 22:15–24
Schofield CJ, Zhang Z (1999) Structural and mechanistic studies on 2-oxoglutarate-dependent oxygenases and related enzymes. Curr Opin Struct Biol 9:722–731
Knowles HJ, Mole DR, Ratcliffe PJ, Harris AL (2006) Normoxic stabilization of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha by modulation of the labile iron pool in differentiating U937 macrophages: effect of natural resistance-associated macrophage protein 1. Cancer Res 66:2600–2607
Knowles HJ, Raval RR, Harris AL, Ratcliffe PJ (2003) Effect of ascorbate on the activity of hypoxia-inducible factor in cancer cells. Cancer Res 63:1764–1768
Epstein AC, Gleadle JM, McNeill LA, Hewitson KS, O’Rourke J, Mole DR, Mukherji M, Metzen E, Wilson MI, Dhanda A, Tian YM, Masson N, Hamilton DL, Jaakkola P, Barstead R, Hodgkin J, Maxwell PH, Pugh CW, Schofield CJ, Ratcliffe PJ (2001) C. elegans EGL-9 and mammalian homologs define a family of dioxygenases that regulate HIF by prolyl hydroxylation. Cell 107:43–54
Bruick RK, McKnight SL (2001) A conserved family of prolyl-4-hydroxylases that modify HIF. Science 294:1337–1340
Lando D, Peet DJ, Gorman JJ, Whelan DA, Whitelaw ML, Bruick RK (2002) FIH-1 is an asparaginyl hydroxylase enzyme that regulates the transcriptional activity of hypoxia-inducible factor. Genes Dev 16:1466–1471
Berra E, Benizri E, Ginouves A, Volmat V, Roux D, Pouyssegur J (2003) HIF prolyl-hydroxylase 2 is the key oxygen sensor setting low steady-state levels of HIF-1α in normoxia. EMBO J 22:4082–4090
Takeda K, Ho VC, Takeda H, Duan LJ, Nagy A, Fong GH (2006) Placental but not heart defects are associated with elevated hypoxia-inducible factor alpha levels in mice lacking prolyl hydroxylase domain protein 2. Mol Cell Biol 26:8336–8346
Metzen E, Berchner-Pfannschmidt U, Stengel P, Marxsen JH, Stolze I, Klinger M, Huang WQ, Wotzlaw C, Hellwig-Burgel T, Jelkmann W, Acker H, Fandrey J (2003) Intracellular localisation of human HIF-1alpha hydroxylases: implications for oxygen sensing. J Cell Sci 116:1319–1326
Appelhoff RJ, Tian Y-M, Raval RR, Turley H, Harris AL, Pugh CW, Ratcliffe PJ, Gleadle JM (2004) Differential function of the prolyl hydroxylases, PHD1, 2 and 3 in the regulation of hypoxia inducible factor (HIF). J Biol Chem 279:38458–38465
Cioffi CL, Qin Liu X, Kosinski PA, Garay M, Bowen BR (2003) Differential regulation of HIF-1alpha prolyl-4-hydroxylase genes by hypoxia in human cardiovascular cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 303:947–953
Nakayama K, Frew IJ, Hagensen M, Skals M, Habelhah H, Bhoumik A, Kadoya T, Erdjument-Bromage H, Tempst P, Frappell PB, Bowtell DD, Ronai Z (2004) Siah2 regulates stability of prolyl-hydroxylases, controls HIF1alpha abundance, and modulates physiological responses to hypoxia. Cell 117:941–952
Hopfer U, Hopfer H, Jablonski K, Stahl RA, Wolf G (2006) The novel WD-repeat protein Morg1 acts as a molecular scaffold for hypoxia-inducible factor prolyl hydroxylase 3 (PHD3). J Biol Chem 281:8645–8655
Lieb ME, Menzies K, Moschella MC, Ni R, Taubman MB (2002) Mammalian EGLN genes have distinct patterns of mRNA expression and regulation. Biochem Cell Biol 80:421–426
Dupuy D, Aubert I, Duperat VG, Petit J, Taine L, Stef M, Bloch B, Arveiler B (2000) Mapping, characterization, and expression analysis of the SM-20 human homologue, c1orf12, and identification of a novel related gene, SCAND2. Genomics 69:348–354
Lee S, Nakamura E, Yang H, Wei W, Linggi MS, Sajan MP, Farese RV, Freeman RS, Carter BD, Kaelin WG Jr, Schlisio S (2005) Neuronal apoptosis linked to EglN3 prolyl hydroxylase and familial pheochromocytoma genes: developmental culling and cancer. Cancer Cell 8:155–167
Cockman ME, Lancaster DE, Stolze IP, Hewitson KS, McDonough MA, Coleman ML, Coles CH, Yu X, Hay RT, Ley SC, Pugh CW, Oldham NJ, Masson N, Schofield CJ, Ratcliffe PJ (2006) Posttranslational hydroxylation of ankyrin repeats in IkappaB proteins by the hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) asparaginyl hydroxylase, factor inhibiting HIF (FIH). Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:14767–14772
Kuznetsova AV, Meller J, Schnell PO, Nash JA, Ignacak ML, Sanchez Y, Conaway JW, Conaway RC, Czyzyk-Krzeska MF (2003) von Hippel-Lindau protein binds hyperphosphorylated large subunit of RNA polymerase II through a proline hydroxylation motif and targets it for ubiquitination. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:2706–2711
Hanson ES, Rawlins ML, Leibold EA (2003) Oxygen and iron regulation of iron regulatory protein 2. J Biol Chem 278:40337–40342
Wang J, Chen G, Muckenthaler M, Galy B, Hentze MW, Pantopoulos K (2004) Iron-mediated degradation of IRP2, an unexpected pathway involving a 2-oxoglutarate-dependent oxygenase activity. Mol Cell Biol 24:954–965
Selak MA, Armour SM, MacKenzie ED, Boulahbel H, Watson DG, Mansfield KD, Pan Y, Simon MC, Thompson CB, Gottlieb E (2005) Succinate links TCA cycle dysfunction to oncogenesis by inhibiting HIF-alpha prolyl hydroxylase. Cancer Cell 7:77–85
Isaacs JS, Jung YJ, Mole DR, Lee S, Torres-Cabala C, Chung Y-L, Merino M, Trepel J, Zbar B, Toro J, Ratcliffe PJ, Linehan WM, Neckers L (2005) HIF overexpression correlates with biallelic loss of fumarate hydratase in renal cancer: Novel role of fumarate in regulation of HIF stability. Cancer Cell 8:143–153
D’Angelo G, Duplan E, Boyer N, Vigne P, Frelin C (2003) Hypoxia up regulates prolyl hydroxylase. A feedback mechanism that limits HIF-1 responses during reoxygenation. J Biol Chem 278:38183–38187
Aprelikova O, Chandramouli GV, Wood M, Vasselli JR, Riss J, Maranchie JK, Linehan WM, Barrett JC (2004) Regulation of HIF prolyl hydroxylases by hypoxia-inducible factors. J Cell Biochem 92:491–501
Harris AL (2002) Hypoxia—a key regulatory factor in tumour growth. Nat Rev Cancer 2:38–47
Maxwell PH, Wiesener MS, Chang GW, Clifford SC, Vaux EC, Cockman ME, Wykoff CC, Pugh CW, Maher ER, Ratcliffe PJ (1999) The tumour suppressor protein VHL targets hypoxia-inducible factors for oxygen-dependent proteolysis. Nature 399:271–275
Cockman ME, Masson N, Mole DR, Jaakkola P, Chang GW, Clifford SC, Maher ER, Pugh CW, Ratcliffe PJ, Maxwell PH (2000) Hypoxia inducible factor-alpha binding and ubiquitylation by the von Hippel-Lindau tumor suppressor protein. J Biol Chem 275:25733–25741
Kamura T, Sato S, Iwai K, Czyzyk-Krzeska M, Conaway RC, Conaway JW (2000) Activation of HIF1alpha ubiquitination by a reconstituted von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) tumor suppressor complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:10430–10435
Ohh M, Park CW, Ivan M, Hoffman MA, Kim TY, Huang LE, Pavletich N, Chau V, Kaelin WG (2000) Ubiquitination of hypoxia-inducible factor requires direct binding to the beta-domain of the von Hippel-Lindau protein. Nat Cell Biol 2:423–427
Tanimoto K, Makino Y, Pereira T, Poellinger L (2000) Mechanism of regulation of the hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha by the von Hippel-Lindau tumor suppressor protein. EMBO J 19:4298–4309
Hon WC, Wilson MI, Harlos K, Claridge TD, Schofield CJ, Pugh CW, Maxwell PH, Ratcliffe PJ, Stuart DI, Jones EY (2002) Structural basis for the recognition of hydroxyproline in HIF-1 alpha by pVHL. Nature 417:975–978
Min JH, Yang H, Ivan M, Gertler F, Kaelin WG Jr, Pavletich NP (2002) Structure of an HIF-1alpha -pVHL complex: hydroxyproline recognition in signaling. Science 296:1886–1889
Mandriota SJ, Turner KJ, Davies DR, Murray PG, Morgan NV, Sowter HM, Wykoff CC, Maher ER, Harris AL, Ratcliffe PJ, Maxwell PH (2002) HIF activation identifies early lesions in VHL kidneys: evidence for site-specific tumor suppressor function in the nephron. Cancer Cell 1:459–468
Raval RR, Lau KW, Tran MG, Sowter HM, Mandriota SJ, Li JL, Pugh CW, Maxwell PH, Harris AL, Ratcliffe PJ (2005) Contrasting properties of hypoxia-inducible factor 1 (HIF-1) and HIF-2 in von Hippel–Lindau-associated renal cell carcinoma. Mol Cell Biol 25:5675–5686
Kondo K, Kim WY, Lechpammer M, Kaelin WG Jr (2003) Inhibition of HIF2alpha is sufficient to suppress pVHL-defective tumor growth. PLoS Biol 1:E83
Kondo K, Klco J, Nakamura E, Lechpammer M, Kaelin WG Jr (2002) Inhibition of HIF is necessary for tumor suppression by the von Hippel-Lindau protein. Cancer Cell 1:237–246
Maranchie JK, Vasselli JR, Riss J, Bonifacino JS, Linehan WM, Klausner RD (2002) The contribution of VHL substrate binding and HIF1-alpha to the phenotype of VHL loss in renal cell carcinoma. Cancer Cell 1:247–255
Eng C, Kiuru M, Fernandez MJ, Aaltonen LA (2003) A role for mitochondrial enzymes in inherited neoplasia and beyond. Nat Rev Cancer 3:193–202
Vanharanta S, Buchta M, McWhinney SR, Virta SK, Peczkowska M, Morrison CD, Lehtonen R, Januszewicz A, Jarvinen H, Juhola M, Mecklin JP, Pukkala E, Herva R, Kiuru M, Nupponen NN, Aaltonen LA, Neumann HP, Eng C (2004) Early-onset renal cell carcinoma as a novel extraparaganglial component of SDHB-associated heritable paraganglioma. Am J Hum Genet 74:153–159
Gimenez-Roqueplo AP, Favier J, Rustin P, Mourad JJ, Plouin PF, Corvol P, Rotig A, Jeunemaitre X (2001) The R22X mutation of the SDHD gene in hereditary paraganglioma abolishes the enzymatic activity of complex II in the mitochondrial respiratory chain and activates the hypoxia pathway. Am J Hum Genet 69:1186–1197
Tomlinson IP, Alam NA, Rowan AJ, Barclay E, Jaeger EE, Kelsell D, Leigh I, Gorman P, Lamlum H, Rahman S, Roylance RR, Olpin S, Bevan S, Barker K, Hearle N, Houlston RS, Kiuru M, Lehtonen R, Karhu A, Vilkki S, Laiho P, Eklund C, Vierimaa O, Aittomaki K, Hietala M, Sistonen P, Paetau A, Salovaara R, Herva R, Launonen V, Aaltonen LA (2002) Germline mutations in FH predispose to dominantly inherited uterine fibroids, skin leiomyomata and papillary renal cell cancer. Nat Genet 30:406–410
Pollard PJ, Spencer-Dene B, Shukla D, Howarth K, Nye E, El-Bahrawy M, Deheragoda M, Joannou M, McDonald S, Martin A, Igarashi P, Varsani-Brown S, Rosewell I, Poulsom R, Maxwell P, Stamp GW, Tomlinson IP (2007) Targeted inactivation of fh1 causes proliferative renal cyst development and activation of the hypoxia pathway. Cancer Cell 11:311–319
Brugarolas J, Kaelin WG Jr (2004) Dysregulation of HIF and VEGF is a unifying feature of the familial hamartoma syndromes. Cancer Cell 6:7–10
Maxwell PH, Pugh CW, Ratcliffe PJ (2001) Activation of the HIF pathway in cancer. Curr Opin Genet Dev 11:293–299
Dery MA, Michaud MD, Richard DE (2005) Hypoxia-inducible factor 1: regulation by hypoxic and non-hypoxic activators. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 37:535–540
Elson DA, Thurston G, Huang LE, Ginzinger DG, McDonald DM, Johnson RS, Arbeit JM (2001) Induction of hypervascularity without leakage or inflammation in transgenic mice overexpressing hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha. Genes Dev 15:2520–2532
Rosenberger C, Heyman SN, Rosen S, Shina A, Goldfarb M, Griethe W, Frei U, Reinke P, Bachmann S, Eckardt KU (2005) Up-regulation of HIF in experimental acute renal failure: evidence for a protective transcriptional response to hypoxia. Kidney Int 67:531–542
Rosenberger C, Rosen S, Shina A, Bernhardt W, Wiesener MS, Frei U, Eckardt KU, Heyman SN (2006) Hypoxia-inducible factors and tubular cell survival in isolated perfused kidneys. Kidney Int 70:60–70
Jiang BH, Semenza GL, Bauer C, Marti HH (1996) Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 levels vary exponentially over a physiologically relevant range of O2 tension. Am J Physiol 271:C1172–C1180
Rosenberger C, Pratschke J, Rudolph B, Heyman SN, Schindler R, Babel N, Eckardt KU, Frei U, Rosen S, Reinke P (2007) Immunohistochemical detection of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha in human renal allograft biopsies. J Am Soc Nephrol 18:343–351
Cai Z, Manalo DJ, Wei G, Rodriguez ER, Fox-Talbot K, Lu H, Zweier JL, Semenza GL (2003) Hearts from rodents exposed to intermittent hypoxia or erythropoietin are protected against ischemia-reperfusion injury. Circulation 108:79–85
Kido M, Du L, Sullivan CC, Li X, Deutsch R, Jamieson SW, Thistlethwaite PA (2005) Hypoxia-inducible factor 1-alpha reduces infarction and attenuates progression of cardiac dysfunction after myocardial infarction in the mouse. J Am Coll Cardiol 46:2116–2124
Bernhardt WM, Campean V, Kany S, Jurgensen JS, Weidemann A, Warnecke C, Arend M, Klaus S, Gunzler V, Amann K, Willam C, Wiesener MS, Eckardt KU (2006) Preconditional activation of hypoxia-inducible factors ameliorates ischemic acute renal failure. J Am Soc Nephrol 17:1970–1978
Helton R, Cui J, Scheel JR, Ellison JA, Ames C, Gibson C, Blouw B, Ouyang L, Dragatsis I, Zeitlin S, Johnson RS, Lipton SA, Barlow C (2005) Brain-specific knock-out of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha reduces rather than increases hypoxic-ischemic damage. J Neurosci 25:4099–4107
Nangaku M (2006) Chronic hypoxia and tubulointerstitial injury: a final common pathway to end-stage renal failure. J Am Soc Nephrol 17:17–25
Goldfarb M, Rosenberger C, Abassi Z, Shina A, Zilbersat F, Eckardt KU, Rosen S, Heyman SN (2006) Acute-on-chronic renal failure in the rat: functional compensation and hypoxia tolerance. Am J Nephrol 26:22–33
Matsumoto M, Tanaka T, Yamamoto T, Noiri E, Miyata T, Inagi R, Fujita T, Nangaku M (2004) Hypoperfusion of peritubular capillaries induces chronic hypoxia before progression of tubulointerstitial injury in a progressive model of rat glomerulonephritis. J Am Soc Nephrol 15:1574–1581
Mole DR, Schlemminger I, McNeill LA, Hewitson KS, Pugh CW, Ratcliffe PJ, Schofield CJ (2003) 2-Oxoglutarate analogue inhibitors of hif prolyl hydroxylase. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 13:2677–2680
Schlemminger I, Mole DR, McNeill LA, Dhanda A, Hewitson KS, Tian YM, Ratcliffe PJ, Pugh CW, Schofield CJ (2003) Analogues of dealanylalahopcin are inhibitors of human HIF prolyl hydroxylases. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 13:1451–1454
Koivunen P, Hirsila M, Gunzler V, Kivirikko KI, Myllyharju J (2004) Catalytic properties of the asparaginyl hydroxylase (FIH) in the oxygen sensing pathway are distinct from those of its prolyl 4-hydroxylases. J Biol Chem 279:9899–9904
Warnecke C, Griethe W, Weidemann A, Jurgensen JS, Willam C, Bachmann S, Ivashchenko Y, Wagner I, Frei U, Wiesener M, Eckardt KU (2003) Activation of the hypoxia-inducible factor-pathway and stimulation of angiogenesis by application of prolyl hydroxylase inhibitors. FASEB J 17:1186–1188
Ivan M, Haberberger T, Gervasi DC, Michelson KS, Gunzler V, Kondo K, Yang H, Sorokina I, Conaway RC, Conaway JW, Kaelin WG Jr (2002) Biochemical purification and pharmacological inhibition of a mammalian prolyl hydroxylase acting on hypoxia-inducible factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:13459–13464
Linden T, Katschinski DM, Eckhardt K, Scheid A, Pagel H, Wenger RH (2003) The antimycotic ciclopirox olamine induces HIF-1alpha stability, VEGF expression, and angiogenesis. FASEB J 17:761–763
Warshakoon NC, Wu S, Boyer A, Kawamoto R, Renock S, Xu K, Pokross M, Evdokimov AG, Zhou S, Winter C, Walter R, Mekel M (2006) Design and synthesis of a series of novel pyrazolopyridines as HIF-1alpha prolyl hydroxylase inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 16:5687–5690
Warshakoon NC, Wu S, Boyer A, Kawamoto R, Sheville J, Bhatt RT, Renock S, Xu K, Pokross M, Zhou S, Walter R, Mekel M, Evdokimov AG, East S (2006) Design and synthesis of substituted pyridine derivatives as HIF-1alpha prolyl hydroxylase inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 16:5616–5620
Warshakoon NC, Wu S, Boyer A, Kawamoto R, Sheville J, Renock S, Xu K, Pokross M, Evdokimov AG, Walter R, Mekel M (2006) A novel series of imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine derivatives as HIF-1alpha prolyl hydroxylase inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 16:5598–5601
Warshakoon NC, Wu S, Boyer A, Kawamoto R, Sheville J, Renock S, Xu K, Pokross M, Zhou S, Winter C, Walter R, Mekel M, Evdokimov AG (2006) Structure-based design, synthesis, and SAR evaluation of a new series of 8-hydroxyquinolines as HIF-1alpha prolyl hydroxylase inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 16:5517–5522
Cunliffe CJ, Franklin TJ, Hales NJ, Hill GB (1992) Novel inhibitors of prolyl 4-hydroxylase. 3. Inhibition by the substrate analogue N-oxaloglycine and its derivatives. J Med Chem 35:2652–2658
Hewitson KS, Schofield CJ (2004) The HIF pathway as a therapeutic target. Drug Discov Today 9:704–711
Elkins JM, Hewitson KS, McNeill LA, Seibel JF, Schlemminger I, Pugh CW, Ratcliffe PJ, Schofield CJ (2003) Structure of factor-inhibiting hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) reveals mechanism of oxidative modification of HIF-1 alpha. J Biol Chem 278:1802–1806
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mole, D.R., Ratcliffe, P.J. Cellular oxygen sensing in health and disease. Pediatr Nephrol 23, 681–694 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-007-0632-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-007-0632-x