Abstract
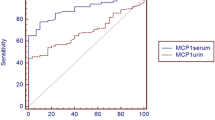
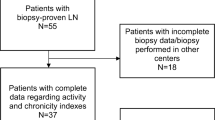
Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1) has a pathogenic role in murine lupus nephritis (LN). We recruited 25 pediatric and adolescent systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) patients from our lupus clinic [13 (52%) patients with LN and 12 (48%) lupus non-nephritis patients] and evaluated their urinary and plasma MCP-1 levels compared to adult and childhood controls. The median age and SLE disease duration of patients were 14.4 and 5.5 years, respectively. LN patients had a higher median renal (p = 0.01) British Isles Lupus Assessment Group (BILAG) index, with a tendency for higher total BILAG scores (p = 0.2). There were significantly increased urinary MCP-1 levels in the LN patients compared to healthy controls (p < 0.001) whose values were significantly higher than lupus non-nephritis children (p< 0.004). Urinary MCP-1 levels correlated well with total BILAG scores (r = 0.82, p = 0.04). There were no differences in plasma MCP-1 levels between SLE patient groups and pediatric controls, although the levels in the childhood controls were elevated compared to those of the adult controls (p < 0.04). These results provide evidence of increased urinary—but not plasma—MCP-1 levels in children with LN, which correlates well with SLE disease activity as measured by the BILAG index.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bernatsky S, Boivin JF, Joseph L, Manzi S, Ginzler E, Gladman DD, Urowitz M, Fortin PR, Petri M, Barr S, Gordon C, Bae SC, Isenberg D, Zoma A, Aranow C, Dooley MA, Nived O, Sturfelt G, Steinsson K, Alarcon G, Senecal JL, Zummer M, Hanly J, Ensworth S, Pope J, Edworthy S, Rahman A, Sibley J, El-Gabalawy H, McCarthy T, St Pierre Y, Clarke A, Ramsey-Goldman R (2006) Mortality in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 54:2550–2557
Cameron JS (1994) Lupus nephritis in childhood and adolescence. Pediatr Nephrol 8:230–249
Chambers SA, Allen E, Rahman A, Isenberg D (2009) Damage and mortality in a group of British patients with systemic lupus erythematosus followed up for over 10 years. Rheumatology (Oxford) 48:673–675
Walravens PA, Chase HP (1976) The prognosis of childhood systemic lupus erythematosus. Am J Dis Child 130:929–933
Baqi N, Moazami S, Singh A, Ahmad H, Balachandra S, Tejani A (1006) Lupus nephritis in children: a longitudinal study of prognostic factors and therapy. J Am Soc Nephrol 7:924–929
Brunner HI, Gladman DD, Ibanez D, Urowitz MD, Silverman ED (2008) Difference in disease features between childhood-onset and adult-onset systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 58:556–562
Emre S, Bilge I, Sirin A, Kilicaslan I, Nayir A, Oktem F, Uysal V (2001) Lupus nephritis in children: prognostic significance of clinicopathological findings. Nephron 87:118–126
Glidden RS, Mantzouranis EC, Borel Y (1983) Systemic lupus erythematosus in childhood: clinical manifestations and improved survival in fifty-five patients. Clin Immunol Immunopathol 29:196–210
Marini R, Costallat LT (1999) Young age at onset, renal involvement, and arterial hypertension are of adverse prognostic significance in juvenile systemic lupus erythematosus. Rev Rhum Engl Ed 66:303–309
Stichweh D, Arce E, Pascual V (2004) Update on pediatric systemic lupus erythematosus. Curr Opin Rheumatol 16:577–587
Weening JJ, D’Agati VD, Schwartz MM, Seshan SV, Alpers CE, Appel GB, Balow JE, Bruijn JA, Cook T, Ferrario F, Fogo AB, Ginzler EM, Hebert L, Hill G, Hill P, Jennette JC, Kong NC, Lesavre P, Lockshin M, Looi LM, Makino H, Moura LA, Nagata M (2004) The classification of glomerulonephritis in systemic lupus erythematosus revisited. J Am Soc Nephrol 15:241–250
Weening JJ, D’Agati VD, Schwartz MM, Seshan SV, Alpers CE, Appel GB, Balow JE, Bruijn JA, Cook T, Ferrario F, Fogo AB, Ginzler EM, Hebert L, Hill G, Hill P, Jennette JC, Kong NC, Lesavre P, Lockshin M, Looi LM, Makino H, Moura LA, Nagata M (2004) The classification of glomerulonephritis in systemic lupus erythematosus revisited. Kidney Int 65:521–530
Markowitz GS, D’Agati VD (2007) The ISN/RPS 2003 classification of lupus nephritis: an assessment at 3 years. Kidney Int 71:491–495
Marks SD, Sebire NJ, Pilkington C, Tullus K (2007) Clinicopathological correlations of paediatric lupus nephritis. Pediatr Nephrol 22:77–83
Yokoyama H, Wada T, Hara A, Yamahana J, Nakaya I, Kobayashi M, Kitagawa K, Kokubo S, Iwata Y, Yoshimoto K, Shimizu K, Sakai N, Furuichi K (2004) The outcome and a new ISN/RPS 2003 classification of lupus nephritis in Japanese. Kidney Int 66:2382–2388
Liu CC, Ahearn JM (2009) The search for lupus biomarkers. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol 23:507–523
Zhang X, Jin M, Wu H, Nadasdy T, Nadasdy G, Harris N, Green-Church K, Nagaraja H, Birmingham DJ, Yu CY, Hebert LA, Rovin BH (2008) Biomarkers of lupus nephritis determined by serial urine proteomics. Kidney Int 74:799–807
Rovin BH (2008) The chemokine network in systemic lupus erythematous nephritis. Front Biosci 13:904–922
Chan RW, Lai FM, Li EK, Tam LS, Chow KM, Lai KB, Li PK, Szeto CC (2007) Intrarenal cytokine gene expression in lupus nephritis. Ann Rheum Dis 66:886–892
Brown KS, Nackos E, Morthala S, Jensen LE, Whitehead AS, Von Feldt JM (2007) Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1: plasma concentrations and A(-2518)G promoter polymorphism of its gene in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Rheumatol 34:740–746
Marks SD, Williams SJ, Tullus K, Sebire NJ (2008) Glomerular expression of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 is predictive of poor renal prognosis in pediatric lupus nephritis. Nephrol Dial Transplant 23:3521–3526
Rovin BH, Song H, Birmingham DJ, Hebert LA, Yu CY, Nagaraja HN (2005) Urine chemokines as biomarkers of human systemic lupus erythematosus activity. J Am Soc Nephrol 16:467–473
Das L, Brunner HI (2009) Biomarkers for renal disease in childhood. Curr Rheumatol Rep 11:218–225
Hochberg MC (1997) Updating the American College of Rheumatology revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 40:1725
Tan EM, Cohen AS, Fries JF, Masi AT, McShane DJ, Rothfield NF, Schaller JG, Talal N, Winchester RJ (1982) The 1982 revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 25:1271–1277
Kim HL, Lee DS, Yang SH, Lim CS, Chung JH, Kim S, Lee JS, Kim YS (2002) The polymorphism of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 is associated with the renal disease of SLE. Am J Kidney Dis 40:1146–1152
Tucci M, Barnes EV, Sobel ES, Croker BP, Segal MS, Reeves WH, Richards HB (2004) Strong association of a functional polymorphism in the monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 promoter gene with lupus nephritis. Arthritis Rheum 50:1842–1849
Nakashima H, Akahoshi M, Shimizu S, Inoue Y, Miyake K, Ninomiya I, Igawa T, Sadanaga A, Otsuka T, Harada M (2004) Absence of association between the MCP-1 gene polymorphism and histological phenotype of lupus nephritis. Lupus 13:165–167
Wagrowska-Danilewicz M, Stasikowska O, Danilewicz M (2005) Correlative insights into immunoexpression of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1, transforming growth factor beta-1 and CD68+ cells in lupus nephritis. Pol J Pathol 56:115–120
Hasegawa H, Kohno M, Sasaki M, Inoue A, Ito MR, Terada M, Hieshima K, Maruyama H, Miyazaki J, Yoshie O, Nose M, Fujita S (2003) Antagonist of monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 ameliorates the initiation and progression of lupus nephritis and renal vasculitis in MRL/lpr mice. Arthritis Rheum 48:2555–2566
Shimizu S, Nakashima H, Masutani K, Inoue Y, Miyake K, Akahoshi M, Tanaka Y, Egashira K, Hirakata H, Otsuka T, Harada M (2004) Anti-monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 gene therapy attenuates nephritis in MRL/lpr mice. Rheumatology (Oxford) 43:1121–1128
Zoja C, Liu XH, Donadelli R, Abbate M, Testa D, Corna D, Taraboletti G, Vecchi A, Dong QG, Rollins BJ, Bertani T, Remuzzi G (1997) Renal expression of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 in lupus autoimmune mice. J Am Soc Nephrol 8:720–729
Dai C, Liu Z, Zhou H, Li L (2001) Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 expression in renal tissue is associated with monocyte recruitment and tubulo-interstitial lesions in patients with lupus nephritis. Chin Med J (Engl) 114:864–868
Tam FW, Sanders JS, George A, Hammad T, Miller C, Dougan T, Cook HT, Kallenberg CG, Gaskin G, Levy JB, Pusey CD (2004) Urinary monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1) is a marker of active renal vasculitis. Nephrol Dial Transplant 19:2761–2768
Wada T, Furuichi K, Segawa-Takaeda C, Shimizu M, Sakai N, Takeda SI, Takasawa K, Kida H, Kobayashi KI, Mukaida N, Ohmoto Y, Matsushima K, Yokoyama H (1999) MIP-1alpha and MCP-1 contribute to crescents and interstitial lesions in human crescentic glomerulonephritis. Kidney Int 56:995–1003
Murali NS, Ackerman AW, Croatt AJ, Cheng J, Grande JP, Sutor SL, Bram RJ, Bren GD, Badley AD, Alam J, Nath KA (2007) Renal upregulation of HO-1 reduces albumin-driven MCP-1 production: implications for chronic kidney disease. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 292:F837–F844
Rovin BH, Zhang X (2009) Biomarkers for lupus nephritis: the quest continues. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 4:1858–1865
Brunner HI, Mueller M, Rutherford C, Passo MH, Witte D, Grom A, Mishra J, Devarajan P (2006) Urinary neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin as a biomarker of nephritis in childhood-onset systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 54:2577–2584
Hinze CH, Suzuki M, Klein-Gitelman M, Passo MH, Olson J, Singer NG, Haines KA, Onel K, O’Neil K, Silverman ED, Tucker L, Ying J, Devarajan P, Brunner HI (2009) Neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin is a predictor of the course of global and renal childhood-onset systemic lupus erythematosus disease activity. Arthritis Rheum 60:2772–2781
Acknowledgments
SM received a grant from the Peel Medical Research Trust to carry out this research and would like to express his gratitude to them.
Conflicts of interest
None of the authors have any relationships with companies that may have a financial interest in the information contained in the manuscript. There are no financial interests or arrangements with a company whose product was used in a study or is referred to in a manuscript. There are no financial interests of arrangement with a competing company. There are no direct payments to an author(s) from any source for the purpose of writing the manuscript. There are no other financial connections, direct or indirect, or other situations that might raise the question of bias in the work reported or the conclusions, implications, or opinions stated including pertinent commercial or other sources of funding for the individual author(s) or for the associated department(s) or organization(s), personal relationships, or direct academic competition.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Marks, S.D., Shah, V., Pilkington, C. et al. Urinary monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 correlates with disease activity in lupus nephritis. Pediatr Nephrol 25, 2283–2288 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-010-1605-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-010-1605-z