Abstract.
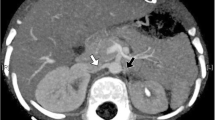
We report a hypertensive child with renal artery stenosis who exhibited increased urinary excretion of norepinephrine (NE) and normetanephrine (NMN), while vanillylmandelic acid (VMA) excretion was within the normal range. The NMN values prompted us to investigate the patient for pheochromocytoma; for this purpose, NE was determined by plasma catecholamine assays in venous samples obtained by catheterization. The moderately increased NE levels could not be localized to any particular sampling site. Arteriography demonstrated right renal artery abnormalities. Following right nephrectomy with preservation of the right adrenal gland, arterial blood pressure returned to normal. The cause of increased NMN excretion without a concomitant rise in VMA during hypertension is discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received May 23, 1995; received in revised form and accepted February 6, 1996
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Berard, E., Candito, M., Diaine, B. et al. Increased urinary catecholamines in a hypertensive child with renal artery stenosis. Pediatr Nephrol 10, 761–763 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004670050212
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004670050212