Abstract
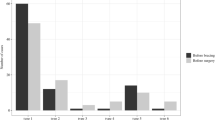
Telemeterized internal spinal fixation devices were implanted in ten patients. The loads acting on the fixators were compared for different body positions, including standing, sitting, and lying in a supine, prone, and lateral position. Implant loads differed considerably from patient to patient depending, for example, on the indication for surgery and the surgical procedure. They were altered by anterior interbody fusion. Mostly, only small differences in implant loads were found for the various lying positions. Flexion bending moments were significantly higher in upright than in lying body positions. Loads on the fixators were not higher for sitting than for standing. Patients who have undergone mono- or bisegmental spine stabilization should therefore be allowed to sit as soon as they can leave the bed.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 16 July 1999 Accepted: 20 July 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rohlmann, A., Bergmann, G. & Graichen, F. Loads on internal spinal fixators measured in different body positions. E Spine J 8, 354–359 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s005860050187
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s005860050187