Summary
Background. Landmine explosions cause most of the war injuries in the battlefield and pose a substantial public health risk. Although the lower limbs are usually affected, head injuries also occur. The aim of this study is to describe the types of head injuries caused by the explosion of landmines and the management of the victims.
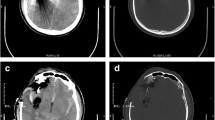
Patients and method. Fifteen patients who sustained a head injury due to a landmine explosion were treated in the Department of Neurosurgery between 2000 and 2006. The average age of the patients was 22.5 (range between 20 and 33). The Glasgow Coma Scale (GCS) score ranged between 3 and 15 and was 8 or less in 4. Shrapnel, stone and earth were the wounding agents. Four patients underwent neurosurgical treatment and 11, apart from simple scalp closure, had conservative treatment. Ten patients had associated lesions in the other parts of the body including thorax, upper and lower limbs, and the abdomen.
Findings. Two patients died. At the time of admission, one had a GCS score of 3 and the other a score of 4. Infection was observed among 4 patients and a cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) fistula in 1 patient.
Conclusion. Landmines occasionally cause head injuries. Surgical intervention is seldom required and survival is likely unless the patient is in deep coma. Multidisciplinary approaches are required in case there are associated lesions in the other parts of the body.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
OO Bilukha M Brennan BA Woodruff (2003) ArticleTitleDeath and injury from landmines and unexploded ordnance in Afghanistan JAMA 290 IssueID5 650–653 Occurrence Handle12902369 Occurrence Handle10.1001/jama.290.5.650
J Cobey B Ayotte (2000) ArticleTitleTools to measure landmine incidents and injuries Lancet 355 1549 Occurrence Handle10801190 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0140-6736(05)74597-9 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3c3lvFWhug%3D%3D
RM Coupland A Korver (1989) ArticleTitleInjuries from antipersonel landmines: the experience of the international committee of the Red Cross BMJ 303 1509–1512
E Erdogan E Gonul N Seber (2002) ArticleTitleCraniocerebral gunshot wounds Neurosurg Quart 12 1–18 Occurrence Handle10.1097/00013414-200203000-00001
InstitutionalAuthorNameFrom the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (1997) ArticleTitleLandmine-related injuries, 1993–1996 JAMA 278 621 Occurrence Handle10.1001/jama.278.8.621
K Hanevik G Kvale (2000) ArticleTitleLandmine injuries in Eritrea BMJ 321 1189 Occurrence Handle11073510 Occurrence Handle10.1136/bmj.321.7270.1189 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3M%2FltVWjtA%3D%3D
RH Hayda RM Harris CD Bass (2004) ArticleTitleBlast injury research: modeling injury effects of landmines, bullets and bombs Clin Orthop Relat Res 422 97–108 Occurrence Handle15187840 Occurrence Handle10.1097/01.blo.0000128295.28666.ee
Y Izci H Kayali M Daneyemez T Koksel K Cerrahoglu (2003) ArticleTitleThe clinical, radiological and surgical characteristics of supratentorial penetrating craniocerebral injuries: a retrospective clinical study Tohoku J Exp Med 201 39–46 Occurrence Handle14609259 Occurrence Handle10.1620/tjem.201.39
B Jennett M Bond (1975) ArticleTitleAssessment of outcome after severe brain damage Lancet 1 480–484 Occurrence Handle46957 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0140-6736(75)92830-5 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaE2M7hsl2jsw%3D%3D
MT Khan FN Husain A Ahmed (2002) ArticleTitleHindfoot injuries due to landmine blast accidents Int J Care Injured 33 167–171
S Kinra ME Black (2003) ArticleTitleLandmine related injuries in children of Bosnia and Herzegovina 1991–2000: comparisons with adults J Epidemiol Community Health 57 264–265 Occurrence Handle12646541 Occurrence Handle10.1136/jech.57.4.264 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3s7jt1ektw%3D%3D
Landmine Monitor: international campaign to ban Landmines, Landmine Monitor Reports 2001–2006: toward a mine-free World. (www.icbl.org/lm)
SA Papadakis EC Babourda TC Mitsitskas S Markakidis C Bachtis D Koukouvis AA Tentes (2006) ArticleTitleAnti-personel landmine injuries during peace: experience in a European country Prehosp Disast Med 21 237–240
J Pearn (1996) ArticleTitleLandmines: time for an international ban BMJ 312 990–991 Occurrence Handle8616381 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK287pvVehtA%3D%3D
BL Rish JD Dillon GH Weiss (1983) ArticleTitleMortality following penetrating craniocerebral injuries J Neurosurg 59 775–780 Occurrence Handle6619929 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaL2c%2FgvF2mug%3D%3D
KS Wolff AM Prusa A Wibmer P Rankl W Firbas H Teufelsbauer (2005) ArticleTitleEffect of body armor on simulated landmine blasts to cadaveric legs J Trauma 59 202–208 Occurrence Handle16096564 Occurrence Handle10.1097/01.TA.0000174512.57137.7E
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Secer, H., Gonul, E. & Izci, Y. Head injuries due to landmines. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 149, 777–782 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-007-1236-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-007-1236-8