Abstract
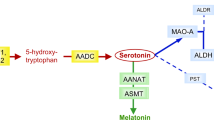
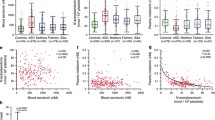
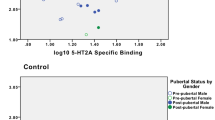
Disturbances in serotonin (5HT) neurotransmission have been indicated as biological substrates in several neuropsychiatric disorders including autism. Blood 5HT concentrations, elevated in about one-third of autistic subjects, are regulated through the action of peripheral 5HT-associated proteins. We have measured the activity of two platelet 5HT-associated proteins: 5HT transporter (5HTT) and monoamine oxidase B (MAOB), and indirectly studied the activity of 5HT2A receptor (5HT2Ar) in 15 hyperserotonemic (HS) and 17 normoserotonemic (NS) autistic subjects, and 15 healthy controls (C). While mean velocities of 5HTT kinetics did not significantly differ among the groups, significant elevation in the mean velocity of MAOB kinetics was observed in NS subjects and was even more pronounced in HS subjects in comparison to controls. Also, a decrease in adenosine 5′-diphosphate-induced platelet aggregation of borderline significance was observed in NS subjects, compared to C subjects. The results suggest a possibility of upregulation of monoaminergic synthesis/degradation and, probably consequential, downregulation of 5HT2Ar in autistic subjects.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson GM (1987) Monoamines in autism: an update of neurochemical research on a pervasive developmental disorder. Med Biol 65:67–74
Anderson GM, Minderaa RB, van Benthem PP, Volkmar FR, Cohen DJ (1984) Platelet imipramine binding in autistic subjects. Psychiatry Res 11:133–141
Anderson GM, Gutknecht L, Cohen DJ, Brailly-Tabard S, Cohen JH, Ferrari P et al (2002) Serotonin transporter promoter variants in autism: functional effects and relationship to platelet hyperserotonemia. Mol Psychiatry 7:831–836
Axelsson S, Hagg S, Eriksson AC, Lindahl TL, Whiss PA (2007) In vitro effects of antipsychotics on human platelet adhesion and aggregation and plasma coagulation. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 34:775–780
Barkan T, Peled A, Modai I, Weizman A, Rehavi M (2006) Characterization of the serotonin transporter in lymphocytes and platelets of schizophrenia patients treated with atypical or typical antipsychotics compared to healthy individuals. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 16:429–436
Billett EE (2004) Monoamine oxidase (MAO) in human peripheral tissues. Neurotoxicology 25:139–148
Boullin DJ, Bhagavan HN, Coleman M, O’Brien RA, Youdim MB (1975) Platelet monoamine oxidase in children with infantile autism. Med Biol 53:210–213
Carneiro AM, Cook EH, Murphy DL, Blakely RD (2008) Interactions between integrin alphaIIbbeta3 and the serotonin transporter regulate serotonin transport and platelet aggregation in mice and humans. J Clin Invest 118:1544–1552
Catalano M (2001) Functionally gene-linked polymorphic regions and genetically controlled neurotransmitters metabolism. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 11:431–439
Chen K, Wu HF, Shih JC (1993) The deduced amino acid sequences of human platelet and frontal cortex monoamine oxidase B are identical. J Neurochem 61:187–190
Chugani DC, Muzik O, Rothermel R, Behen M, Chakraborty P, Mangner T et al (1997) Altered serotonin synthesis in the dentatothalamocortical pathway in autistic boys. Ann Neurol 42:666–669
Chugani DC, Muzik O, Behen M, Rothermel R, Janisse JJ, Lee J, Chugani HT (1999) Developmental changes in brain serotonin synthesis capacity in autistic and nonautistic children. Ann Neurol 45:287–295
Cicin-Sain L, Mimica N, Hranilovic D, Balija M, Ljubin T, Makaric G et al (2000) Posttraumatic stress disorder and platelet serotonin measures. J Psychiatr Res 34:155–161
Cicin-Sain L, Froebe A, Bordukalo-Niksic T, Jernej B (2005) Serotonin transporter kinetics in rats selected for extreme values of platelet serotonin level. Life Sci 77:452–461
Coccini T, Randine G, Castoldi AF, Balloni L, Baiardi P, Manzo L (2005) Lymphocyte muscarinic receptors and platelet monoamine oxidase-B as biomarkers of CNS function: effects of age and gender in healthy humans. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 19:715–720
Cohen DJ, Young JG, Roth JA (1977) Platelet monoamine oxidase in early childhood autism. Arch Gen Psychiatry 34:534–537
Cook EH Jr, Leventhal BL (1996) The serotonin system in autism. Curr Opin Pediatr 8:348–354
Cook EH Jr, Arora RC, Anderson GM, Berry-Kravis EM, Yan SY, Yeoh HC et al (1993) Platelet serotonin studies in hyperserotonemic relatives of children with autistic disorder. Life Sci 52:2005–2015
Cook EH Jr, Fletcher KE, Wainwright M, Marks N, Yan SY, Leventhal BL (1994) Primary structure of the human platelet serotonin 5-HT2A receptor: identify with frontal cortex serotonin 5-HT2A receptor. J Neurochem 63:465–469
Croonenberghs J, Delmeire L, Verkerk R, Lin AH, Meskal A, Neels H et al (2000) Peripheral markers of serotonergic and noradrenergic function in post-pubertal, caucasian males with autistic disorder. Neuropsychopharmacol 22:275–283
Croonenberghs J, Verkerk R, Scharpe S, Deboutte D, Maes M (2005) Serotonergic disturbances in autistic disorder: L-5-hydroxytryptophan administration to autistic youngsters increases the blood concentrations of serotonin in patients but not in controls. Life Sci 76:2171–2183
De Berardis D, Campanella D, Matera V, Gambi F, La Rovere R, Sepede G et al (2003) Thrombocytopenia during valproic acid treatment in young patients with new-onset bipolar disorder. J Clin Psychopharmacol 23:451–458
Dwyer SD, Meyers KM (1986) Anesthetics and anticoagulants used in the preparation of rat platelet-rich-plasma alter rat platelet aggregation. Thromb Res 42:139–151
Emery JD, Leifer DW, Moura GL, Southern P, Morrissey JH, Lawrence JB (1995) Whole-blood platelet aggregation predicts in vitro and in vivo primary hemostatic function in the elderly. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc 15:748–753
Filinger EJ, Garcia-Cotto MA, Vila S, Gerbaldo H, Jerez D (1987) Possible relationship between prevasive developmental disorders and platelet monoamine oxidase activity. Braz J Med Biol Res 20:161–164
Gidal B, Spencer N, Maly M, Pitterle M, Williams E, Collins M, Jones J (1994) Valproate-mediated disturbances of hemostasis: relationship to dose and plasma concentration. Neurology 44:1418–1422
Gray JA, Roth BL (2001) Paradoxical trafficking and regulation of 5-HT(2A) receptors by agonists and antagonists. Brain Res Bull 56:441–451
Halbreich U, Rojansky N, Zander KJ, Barkai A (1991) Influence of age, sex and diurnal variability on imipramine receptor binding and serotonin uptake in platelets of normal subjects. J Psychiatr Res 25:7–18
Hollander E, Phillips A, Chaplin W, Zagursky K, Novotny S, Wasserman S, Iyengar R (2005) A placebo controlled crossover trial of liquid fluoxetine on repetitive behaviors in childhood and adolescent autism. Neuropsychopharmacology 30:582–589
Hoyer D, Hannon JP, Martin GR (2002) Molecular, pharmacological and functional diversity of 5-HT receptors. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 71:533–554
Hranilovic D, Bujas-Petkovic Z, Vragovic R, Vuk T, Hock K, Jernej B (2007) Hyperserotonemia in adults with autistic disorder. J Autism Dev Disord 37:1934–1940
Hranilovic D, Novak R, Babic M, Novokmet M, Bujas-Petkovic Z, Jernej B (2008) Hyperserotonemia in autism: the potential role of 5HT-related gene variants. Coll Antropol 32(Suppl 1):75–80
Janusonis S (2005) Serotonergic paradoxes of autism replicated in a simple mathematical model. Med Hypotheses 64:742–750
Jernej B, Cicin-Sain L, Froebe A, Hranilovic D, Banovic M, Iskric S et al (1996) Serotonin transporter: studies on platelet model in rats and humans. Period Biol 98:95–102
Jernej B, Banovic M, Cicin-Sain L, Hranilovic D, Balija M, Oreskovic D, Folnegovic-Smalc V (2000) Physiological characteristics of platelet/circulatory serotonin: study on a large human population. Psychiatry Res 94:153–162
Katsui T, Okuda M, Usuda S, Koizumi T (1986) Kinetics of 3H-serotonin uptake by platelets in infantile autism and developmental language disorder (including five pairs of twins). J Autism Dev Disord 16:69–76
Launay JM, Ferrari P, Haimart M, Bursztejn C, Tabuteau F, Braconnier A et al (1988) Serotonin metabolism and other biochemical parameters in infantile autism. A controlled study of 22 autistic children. Neuropsychobiology 20:1–11
Lesch KP (2001) Variation of serotonergic gene expression: neurodevelopment and the complexity of response to psychopharmacologic drugs. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 11:457–474
Lesch KP, Moessner R (1998) Genetically driven variation in serotonin uptake: is there a link to affective spectrum, neurodevelopmental, and neurodegenerative disorders? Biol Psychiatry 44:179–192
Lesch KP, Wolozin BL, Murphy DL, Reiderer P (1993) Primary structure of the human platelet serotonin uptake site: identity with the brain serotonin transporter. J Neurochem 60:2319–2322
Marcolin MA, Davis JM (1992) Platelet monoamine oxidase in schizophrenia: a meta-analysis. Schizophr Res 7:249–267
Marazziti D, Muratori F, Cesari A, Masala I, Baroni S, Giannaccini G et al (2000) Increased density of the platelet serotonin transporter in autism. Pharmacopsychiatry 33:165–168
McBride PA, Anderson GM, Hertzig ME, Sweeney JA, Kream J, Cohen DJ, Mann JJ (1989) Serotonergic responsivity in male young adults with autistic disorder. Results of a pilot study. Arch Gen Psychiatry 46:213–221
McDougle CJ, Naylor ST, Cohen DJ, Aghajanian GK, Heninger GR, Price LH (1996a) Effects of tryptophan depletion in drug-free adults with autistic disorder. Arch Gen Psychiatry 53:993–1000
McDougle CJ, Naylor ST, Cohen DJ, Volkmar FR, Heninger GR, Price LH (1996b) A double-blind, placebo-controlled study of fluvoxamine in adults with autistic disorder. Arch Gen Psychiatry 53:1001–1008
Mulder EJ, Anderson GM, Kema IP, de Bildt A, van Lang ND, den Boer JA, Minderaa RB (2004) Platelet serotonin levels in pervasive developmental disorders and mental retardation: diagnostic group differences, within-group distribution, and behavioral correlates. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 43:491–499
Murphy DL, Wright C, Buchsbaum M, Nichols A, Costa JL, Wyatt RJ (1976) Platelet and plasma amine oxidase activity in 680 normals: sex and age differences and stability over time. Biochem Med 16:264–265
Murphy DG, Daly E, Schmitz N, Toal F, Murphy K, Curran S et al (2006) Cortical serotonin 5-HT2A receptor binding and social communication in adults with Asperger’s syndrome: an in vivo SPECT study. Am J Psychiatry 163:934–936
Oreland L, Hallman J (1995) The correlation between platelet MAO activity and personality: short review of findings and discussion on possible mechanisms. Prog Brain Res 106:77–84
Puri RN, Colman RW (1997) ADP-induced platelet activation. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol 32:437–502
Rajtar G, Zolkowska D, Czechowska G, Kleinrok Z (2001) Effects of antiepileptic drugs on rat platelet aggregation: ex vivo and in vitro study. Epilepsy Res 43:59–66
Ritvo E, Yuwiler A, Geller E, Plotkin S, Mason A, Saeger K (1971) Maturational changes in blood serotonin levels and platelet counts. Biochem Med 5:90–96
Rohrer TF, Pfister B, Weber C, Imhof PR, Stucki P (1978) Quantitative changes in platelet aggregation due to physiological and pathological factors and medication. Blut 36:21–26
Rotman A, Caplan R, Szekely GA (1980) Platelet uptake of serotonin in psychotic children. Psychopharmacology 67:245–248
Safai-Kutti S, Denfors I, Kutti J, Wadenvik H (1988) In vitro platelet function in infantile autism. Folia Haematol (Leipz) 115:897–901
Salzman EW, Rosenberg RD, Smith MH, Lindon JN, Favreau L (1980) Effect of heparin and heparin fractions on platelet aggregation. J Clin Invest 65:64–73
Schopler E, Reichler RJ, DeVellis RF, Daly K (1980) Toward objective classification of childhood autism: Childhood Autism Rating Scale (CARS). J Autism Dev Disord 10:91–103
Shimizu M, Kanazawa K, Matsuda Y, Takai E, Iwai C, Miyamoto Y et al (2003) Serotonin-2A receptor gene polymorphisms are associated with serotonin-induced platelet aggregation. Thromb Res 112:137–142
Shojania AM, Turnbull G (1987) Effect of heparin on platelet count and platelet aggregation. Am J Hematol 26:255–262
Takahashi S, Kanai H, Miyamoto Y (1977) Monoamine oxidase activity in blood platelets from autistic children. Folia Psychiatr Neurol Jpn 31:597–603
Verrotti A, Greco R, Matera V, Altobelli E, Morgese G, Chiarelli F (1999) Platelet count and function in children receiving sodium valproate. Pediatr Neurol 21:611–614
Wallen NH, Ladjevardi M, Albert J, Broijersen A (1997) Influence of different anticoagulants on platelet aggregation in whole blood: a comparison between citrate, low molecular mass heparin and hirudin. Thromb Res 87:151–157
Weizman A, Gonen N, Tyano S, Szekely GA, Rehavi M (1987) Platelet [3H] imipramine binding in autism and schizophrenia. Psychopharmacology 91:101–103
Whitaker-Azmitia PM (2001) Serotonin and brain development: role in human developmental diseases. Brain Res Bull 56:479–485
Whitaker-Azmitia PM (2005) Behavioral and cellular consequences of increasing serotonergic activity during brain development: a role in autism? Int J Dev Neurosci 23:75–83
Acknowledgment
This study was supported by the grants “Neurobiological basis of autism: the role of serotonin system” (119-1081870-2396) and “Serotonergic neurotransmission: genes, proteins and behavior” (098-1081870-2395), both funded by the Ministry of Science Education and Sports of the Republic of Croatia. The authors wish to thank Mrs Drina Bagaric, a medical laboratory engineer, for her skillful, kind and gentle approach to the patients during blood sampling, and to Mrs Katarina Karlo, a senior technician, for her assistance in PSL and MAOB measurements.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hranilović, D., Bujas-Petković, Z., Tomičić, M. et al. Hyperserotonemia in autism: activity of 5HT-associated platelet proteins. J Neural Transm 116, 493–501 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-009-0192-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-009-0192-2