Abstract
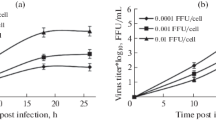
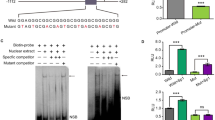
The development of new antiviral molecules to fight the possible emergence of influenza viruses with pandemic potential is needed. In this study, phosphorothioate oligonucleotides (S-ONs) derived from the packaging signals in the 3′ and 5′ ends of the viral PB2 RNA were associated with liposomes and tested against influenza virus in vitro. A 15-mer S-ON derived from the 5′ end of the viral PB2 RNA, complementary to the 3′ end of its coding region (nucleotides 2279–2293) and designated 5-15b, proved markedly inhibitory. The antiviral activity of 5-15b was dose- and time-dependent but was independent of the cell substrate and multiplicity of infection used. Importantly, inhibition of influenza A and B viruses required S-ONs reproducing the respective packaging signals. Furthermore, 5-15b and its antisense derivative S-ON activity did not affect intracellular accumulation of viral RNA. Confocal microscopy showed that 5-15b is clearly nucleophilic. These findings indicate that the packaging signal at the 5′ end of the PB2 RNA is an interesting target for the design of new anti-influenza-virus compounds.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abe T, Mizuta T, Hatta T, Miyano-Kurosaki N, Fujiwara M, Takai K, Shigeta S, Yokota T, Takaku H (2001) Antisense therapy of influenza. Eur J Pharm Sci 13:61–69
Abe T, Mizuta T, Suzuki S, Hatta T, Takai K, Yokota T, Takaku H (1999) In vitro and in vivo anti-influenza A virus activity of antisense oligonucleotides. Nucleosides Nucleotides 18:1685–1688
Bancroft CT, Parslow TG (2002) Evidence for segment-nonspecific packaging of the influenza a virus genome. J Virol 76:7133–7139
Brown DE, Arzumanov A, Syed S, Gait MJ, Lever AM (2006) Inhibition of HIV-1 replication by oligonucleotide analogues directed to the packaging signal and trans-activating response region. Antivir Chem Chemother 17:1–9
Chadwick DR, Lever AM (2000) Antisense RNA sequences targeting the 5′ leader packaging signal region of human immunodeficiency virus type-1 inhibits viral replication at post-transcriptional stages of the life cycle. Gene Ther 7:1362–1368
De Clercq E (2006) Antiviral agents active against influenza A viruses. Nat Rev Drug Discov 5:1015–1025
De Clercq E, Neyts J (2007) Avian influenza A (H5N1) infection: targets and strategies for chemotherapeutic intervention. Trends Pharmacol Sci 28:280–285
de Wit E, Spronken MI, Rimmelzwaan GF, Osterhaus ADME, Fouchier RAM (2006) Evidence for specific packaging of the influenza A virus genome from conditionally defective virus particles lacking a polymerase gene. Vaccine 24:6647–6650
Dimmock NJ, Rainsford EW, Scott PD, Marriott AC (2008) Influenza virus protecting RNA: an effective prophylactic and therapeutic antiviral. J Virol 82:8570–8578
Dos Santos Afonso E, Escriou N, Leclercq I, van der Werf S, Naffakh N (2005) The generation of recombinant influenza A viruses expressing a PB2 fusion protein requires the conservation of a packaging signal overlapping the coding and noncoding regions at the 5′ end of the PB2 segment. Virology 341:34–46
Duan M, Zhou Z, Lin R-X, Yang J, Xia X-Z, Wang S-Q (2008) In vitro and in vivo protection against the highly pathogenic H5N1 influenza virus by an antisense phosphorothioate oligonucleotide. Antivir Ther 13:109–114
Duhaut S, Dimmock NJ (2000) Approximately 150 nucleotides from the 5′ end of an influenza A segment 1 defective virion RNA are needed for genome stability during passage of defective virus in infected cells. Virology 275:278–285
Duhaut S, Dimmock NJ (2002) Defective segment 1 RNAs that interfere with production of infectious influenza A virus require at least 150 nucleotides of 5′ sequence: evidence from a plasmid-driven system. J Gen Virol 83:403–411
Duhaut SD, McCauley JW (1996) Defective RNAs inhibit the assembly of influenza virus genome segments in a segment-specific manner. Virology 216:326–337
Enami M, Sharma G, Benham C, Palese P (1991) An influenza virus containing nine different RNA segments. Virology 18:5291–5298
Fosmire JA, Hwang K, Makino S (1992) Identification and characterization of a coronavirus packaging signal. J Virol 66:3522–3530
Fujii K, Fujii Y, Noda T, Muramoto Y, Watanabe T, Takada A, Goto H, Horimoto T, Kawaoka Y (2005) Importance of both the coding and the segment-specific noncoding regions of the influenza A virus NS segment for its efficient incorporation into virions. J Virol 79:3766–3774
Fujii Y, Goto H, Watanabe T, Yoshida T, Kawaoka Y (2003) Selective incorporation of influenza virus RNA segments into virions. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:2002–2007
Gabriel G, Nordmann A, Stein DA, Iversen PL, Klenk H-D (2008) Morpholino oligomers targeting the PB1 and NP genes enhance the survival of mice infected with highly pathogenic influenza A H7N7 virus. J Gen Virol 89:939–948
Ge Q, McManus MT, Nguyen T, Shen CH, Sharp PA, Eisen HN, Chen J (2003) RNA interference of influenza virus production by directly targeting mRNA for degradation and indirectly inhibiting all viral RNA transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:2718–2723
Ge Q, Pastey M, Kobasa D, Puthavathana P, Lupfer C, Bestwick RK, Iversen PL, Chen J, Stein DA (2006) Inhibition of multiple subtypes of influenza A virus in cell cultures with morpholino oligomers. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 50:3724–3733
Ghanem A, Mayer D, Chase G, Tegge W, Frank R, Kochs G, García-Sastre A, Schwemmle M (2007) Peptide-mediated interference with influenza A virus polymerase. J Virol 81:7801–7804
Giannecchini S, Campitelli L, Calzoletti L, De Marco MA, Azzi A, Donatelli I (2006) Comparison of in vitro replication features of H7N3 influenza viruses from wild ducks and turkeys: potential implications for interspecies transmission. J Gen Virol 87:171–175
Gitlin L, Andino R (2003) Nucleic acid-based immune system: the antiviral potential of mammalian RNA silencing. J Virol 77:7159–7165
Gog JR, Afonso Edos S, Dalton RM, Leclercq I, Tiley L, Elton D, von Kirchbach JC, Naffakh N, Escriou N, Digard P (2007) Codon conservation in the influenza A virus genome defines RNA packaging signals. Nucl Acids Res 35:1897–1907
Greatorex J (2004) The retroviral RNA dimer linkage: different structures may reflect different roles. Retrovirology 22:1–10
Gu S, Ji J, Kim JD, Yee JK, Rossi JJ (2006) Inhibition of infectious human immunodeficiency virus type 1 virions via lentiviral vector encoded short antisense RNAs. Oligonucleotides 16:287–295
Haasnoot J, Westerhout EM, Berkhout B (2007) RNA interference against viruses: strike and counterstrike. Nat Biotechnol 25:1435–1443
Harris A, Cardone G, Winkler DC, Heymann JB, Brecher M, White JM, Steven AC (2006) Influenza virus pleiomorphy characterized by cryoelectron tomography. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:19123–19127
Hutchinson EC, Curran MD, Read EK, Gog JR, Digard P (2008) Mutational analysis of cis-acting RNA signals in segment 7 of influenza A virus. J Virol 82:11869–11879
Liang Y, Hong Y, Parslow TG (2005) cis-Acting packaging signals in the influenza virus PB1, PB2, and PA genomic RNA segments. J Virol 79:10348–10355
Liang Y, Huang T, Ly H, Parslow TG, Liang Y (2008) Mutational analyses of packaging signals in influenza virus PA, PB1, and PB2 genomic RNA segments. J Virol 82:229–236
Lipatov AS, Govorkova EA, Webby RJ, Ozaki H, Peiris M, Guan Y, Poon L, Webster RG (2004) Influenza: emergence and control. J Virol 78:8951–8959
Marsh GA, Hatami R, Palese P (2007) Specific residues of the influenza A virus hemagglutinin viral RNA are important for efficient packaging into budding virions. J Virol 81:9727–9736
Marsh GA, Rabadán R, Levine AJ, Palese P (2008) Highly conserved regions of the influenza A virus polymerase gene segments are critical for efficient vRNA packaging. J Virol 82:2295–2304
McKimm-Breschkin JL, Trivedi T, Hampson A, Hay A, Klimov A, Tashiro M, Hayden F, Zambon M (2003) Neuraminidase sequence analysis and susceptibilities of influenza virus clinical isolates to zanamivir and oseltamivir. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 47:2264–2272
Mizuta T, Fujiwara M, Hatta T, Abe T, Miyano-Kurosaki N, Shigeta S, Yokota T, Takaku H (1999) Antisense oligonucleotides directed against the viral RNA polymerase gene enhance survival of mice infected with influenza A. Nat Biotechnol 17:583–587
Monto AS, McKimm-Breschkin JL, Macken C, Hampson AW, Hay A, Klimov A, Tashiro M, Webster RG, Aymard M, Hayden FG, Zambon M (2006) Detection of influenza viruses resistant to neuraminidase inhibitors in global surveillance during the first 3 years of their use. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 50:2395–2402
Muramoto Y, Takada A, Fujii K, Noda T, Iwatsuki-Horimoto K, Watanabe S, Horimoto T, Kida H, Kawaoka Y (2006) Hierarchy among viral RNA (vRNA) segments in their role in vRNA incorporation into influenza A virions. J Virol 80:2318–2325
Nayak DP, Hui EK, Barman S (2004) Assembly and budding of influenza virus. Virus Res 106:147–165
Nasser EH, Judd AK, Sanchez A, Anastasiou D, Bucher DJ (1996) Antiviral activity of influenza virus M1 zinc finger peptides. J Virol 70:8639–8644
Nicholson KG, Wood JM, Zambon M (2003) Influenza. Lancet 362:1733–1745
Noda T, Sagara H, Yen A, Takada A, Kida H, Cheng RH, Kawaoka Y (2006) Architecture of ribonucleoprotein complexes in influenza A virus particles. Nature 439:490–492
Ozawa M, Fujii K, Muramoto Y, Yamada S, Yamayoshi S, Takada A, Goto H, Horimoto T, Kawaoka Y (2007) Contributions of two nuclear localization signals of influenza A virus nucleoprotein to viral replication. J Virol 81:30–41
Ozawa M, Maeda J, Iwatsuki-Horimoto K, Watanabe S, Goto H, Horimoto T, Kawaoka Y (2009) Nucleotide sequence requirements at the 5′ end of the influenza A virus M RNA segment for efficient virus replication. J Virol 83:3384–3388
Palese P, Shaw ML (2007) Orthomyxoviridae: the viruses and their replication. In: Knipe DM, Howley PM (eds) Field Virology, 5th edn. Lippincott-Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia, pp 1647–1690
Portela A, Digard P (2002) The influenza virus nucleoprotein: a multifunctional RNA-binding protein pivotal to virus replication. J Gen Virol 83:723–734
Reed LJ, Müench HA (1938) A simple method for estimating fifty percent end points. Am J Hyg 27:493–497
Rimmelzwaan GF, Baars M, Claas ECJ, Osterhaus ADME (1998) Comparison of RNA hybridization, hemagglutination assay, titration of infectious virus and immunofluorescence as methods for monitoring influenza virus replication in vitro. J Virol Methods 74:57–66
Schreier E, Petzold DR, Michel S, Dittmann S (1988) Evolution of influenza polymerase: nucleotide sequence of the PB2 gene of A/Chile/1/83 (H1N1). Arch Virol 103:179–187
Suzuki Y (2005) Sialobiology of influenza: molecular mechanism of host range variation of influenza viruses. Biol Pharm Bull 28:399–408
Twu KY, Noah DL, Rao P, Kuo RL, Krug RM (2006) The CPSF30 binding site on the NS1A protein of influenza A virus is a potential antiviral target. J Virol 80:3957–3965
Van Aerschot A (2006) Oligonucleotides as antivirals: dream or realistic perspective? Antiviral Res 71:307–316
Watanabe T, Watanabe S, Noda T, Fujii Y, Kawaoka Y (2003) Exploitation of nucleic acid packaging signals to generate a novel influenza virus-based vector stably expressing two foreign genes. J Virol 77:10575–10583
Wong JP, Christopher ME, Salazar AM, Dale RM, Sun LQ, Wang M (2007) Nucleic acid-based antiviral drugs against seasonal and avian influenza viruses. Vaccine 25:3175–3178
Wu Y, Zhang G, Li Y, Jin Y, Dale R, Sun LQ, Wang M (2008) Inhibition of highly pathogenic avian H5N1 influenza virus replication by RNA oligonucleotides targeting NS1 gene. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 365:369–374
Acknowledgments
We thank Prof. Mauro Bendinelli, Department of Experimental Pathology, University of Pisa, Italy, for the critical review of the manuscript. This study was supported in part by grants from the Fondazione “Istituto di Ricerca Virologica Oretta Bartolomei Corsi” and from the Ente “Cassa di Risparmio di Firenze”, Florence, Italy.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Giannecchini, S., Clausi, V., Nosi, D. et al. Oligonucleotides derived from the packaging signal at the 5′ end of the viral PB2 segment specifically inhibit influenza virus in vitro. Arch Virol 154, 821–832 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-009-0380-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00705-009-0380-2