Summary
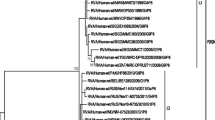
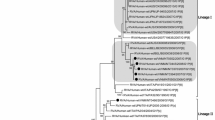
A rotavirus strain HMG89 from Nigeria with short electrophoretic pattern was typed G3 by PCR. A cDNA clone from the PCR product which hybridised in Northern blots to RNA segment 9 of the homologous Nigerian rotavirus strain HMG89 and laboratory reference strain 69M but not to other mammalian group A rotaviruses was sequenced. The VP7 gene 9 sequence is 1060 nucleotides long with two base deletions at positions 1034–1035. Sequence analysis of the primer (aAT8) used in the previous PCR serotyping assay revealed a mutation in one of the three nucleotide bases at the 3′ end of the primer binding site accounting for our inability to serotype G8 strains in our samples. These findings demonstrate that PCR analysis can, albeit infrequently, lead to error in typing of rotaviruses due to small numbers of mutations in the primer binding region.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received August 20, 1996 Accepted April 21, 1997
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Adah, M.I., Rohwedder, A., Olaleyle, O.D. et al. Nigerian rotavirus serotype G8 could not be typedby PCR due to nucleotide mutation at the 3′ endof the primer binding site. Arch. Virol. 142, 1881–1887 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/s007050050206
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s007050050206