Summary
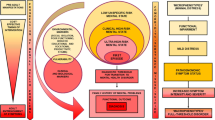
Using a longitudinal screening model, 772 mothers were screened for postnatal depression after delivery in Stuttgart (Germany). This model contained the Edinburgh Postnatal Depression Scale (EPDS) and the Hamilton Depression Scale (HAMD). The first screening was 6–8 weeks after delivery with the EPDS. Mothers with high scores in the first screening had a second screening 9–12 weeks after delivery with the EPDS at least three weeks after the first. Mothers with high scores in both screenings were investigated with the Hamilton Depression Scale (HAMD).
Classification was performed with the DSM-IV. After observation until the third month after delivery, 3.6% (N = 28) of the 772 mothers were diagnosed with postnatal depression. Various methods of therapy were offered to those mothers. 18% (N = 5) accepted one or more of these methods of treatment. The rest of the mothers with postnatal depression refused – mostly for attitudinal or practical reasons. 13.4% of the mothers showed high scores in the first screening but not in the second. For those mothers a longitudinal observation is currently being performed to distinguish between a depressive episode and a depression with oscillating symptoms.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
v. Ballestrem, CL., Strauß, M. & Kächele, H. Contribution to the epidemiology of postnatal depression in Germany – implications for the utilization of treatment. Arch Womens Ment Health 8, 29–35 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00737-005-0068-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00737-005-0068-x