Abstract
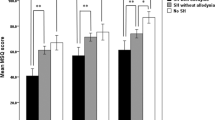
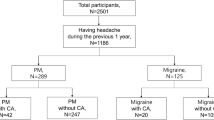
Cutaneous allodynia is a frequent complaint in migraine patients, possibly induced by central sensitisation of trigeminal nucleus. The objective of this study is to investigate if sleep quality is related to the presence of migraine-associated allodynia. A total of 175 consecutive migraineurs were included, 124 with episodic and 51 with chronic forms. As control group, 73 subjects free from any kind of headache were included (HC). The presence of allodynia and sleep disturbances was assessed by a set of semi-structured questions. Chi-square test was applied to compare frequencies among groups. Sleep quality was worse among migraineurs with respect to controls for each sleep item analysed. This difference was significant for all items but one (i.e. frequency in drug use to induce sleep). The frequency of sleep disturbances was higher than in controls in both allodynic and non-allodynic migraineurs, although statistical analysis showed that all these differences were still significant in allodynic migraineurs (also in this case for all the sleep items but one, i.e. frequency in drug use to induce sleep), whilst non-allodynic migraineurs were significantly different from controls only for one item (frequency of initial insomnia). These results suggest that allodynia is strongly related to sleep quality, in a bi-directional way: sleep disturbances may favour central sensitisation, and, in turn, allodynia may impair sleep.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lovati C et al (2009) Is allodynia influenced by psychological profile in headache patients? Neurol Sci 30(Suppl 1):S113–S115
Inamorato E, Minatti-Hannuch SN, Zukerman E (1993) The role of sleep in migraine attacks. Arq Neuropsiquiatr 51:429–432
Biondi DM (2001) Headaches and their relationship to sleep. Dent Clin N Am 45:685–700
Dodick DW, Eross EJ, Parish JM, Silber M (2003) Clinical, anatomical, and physiologic relationship between sleep and headache. Headache 43(3):282–292
Rains JC, Poceta JS (2006) Headache and sleep disorders: review and clinical implications for headache management. Headache 46(Suppl 3):S147–S148
Lovati C, D’Amico D, Raimondi E, Mariani C, Bertora P (2010) Sleep and headache: a bidirectional relationship. Expert Rev Neurother 10(1):105–117
Lovati C, D’Amico D, Bertora P, Rosa S, Suardelli M, Mailland E, Mariani C, Bussone G (2008) Acute and interictal allodynia in patients with different headache forms: an Italian pilot study. Headache 48(2):272–277
Lovati C, D’Amico D, Brambilla A, Mariani C, Bussone G (2008) Personality profile and allodynic migraine. Neurol Sci 29(Suppl 1):S152–S154
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest related to the publication of this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lovati, C., D’Amico, D., Bertora, P. et al. Correlation between presence of allodynia and sleep quality in migraineurs. Neurol Sci 31 (Suppl 1), 155–158 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-010-0317-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-010-0317-2