Abstract
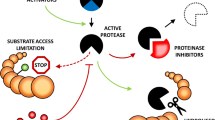
Control of proteolysis is important for plant growth, development, responses to stress, and defence against insects and pathogens. Members of the serpin protein family are likely to play a critical role in this control through irreversible inhibition of endogenous and exogenous target proteinases. Serpins have been found in diverse species of the plant kingdom and represent a distinct clade among serpins in multicellular organisms. Serpins are also found in green algae, but the evolutionary relationship between these serpins and those of plants remains unknown. Plant serpins are potent inhibitors of mammalian serine proteinases of the chymotrypsin family in vitro but, intriguingly, plants and green algae lack endogenous members of this proteinase family, the most common targets for animal serpins. An Arabidopsis serpin with a conserved reactive centre is now known to be capable of inhibiting an endogenous cysteine proteinase. Here, knowledge of plant serpins in terms of sequence diversity, inhibitory specificity, gene expression and function is reviewed. This was advanced through a phylogenetic analysis of amino acid sequences of expressed plant serpins, delineation of plant serpin gene structures and prediction of inhibitory specificities based on identification of reactive centres. The review is intended to encourage elucidation of plant serpin functions.


Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
AGI is an acronym for the author of this article, “The Arabidopsis Genome Initiative”.
Chapters within Silverman and Lomas (eds) (2007) Molecular and Cellular Aspects of the Serpinopathies and Disorders in Serpin Activity, World Scientific (ISBN-10 981–256–963–4) are recommended reading, but many are not cited in this review because of lack of easy access for most readers.
In the cellulosome, dockerin domains are conserved noncatalytic subdomains borne by catalytic subunits. The dockerins bind to cohesion (receptor) domains of the protein CipA (Beguin and Lemaire 1996).
All numbers of this type in the review (including tables) are accession numbers.
There are many errors in the sequencing and only a few clear overlaps here, but at least two serpins appear to be expressed.
Serpins in Populus will not be considered here as annotation of the genome is at only a preliminary stage.
“IRGSP” is an acronym for the author of this article, “International Rice Genome Sequencing Project”.
TAIR7, released April 2007
The pox virus serpin crmA lacks D helix and has shortened versions of helix A and helix E (Simonovic et al. 2000).
Among these three loci, only the gene at At1g64030 can encode a true serpin (the others encode proteins with 185 and 121 amino acid residues).
The current dataset used to train WoLF PSORT contains over 12,000 animal sequences and more than 2,000 plant and fungi sequences, respectively. It was gathered mainly from Uniprot, but several hundred Arabidopsis sequences from the Gene Ontology database were also included.
Prediction scores obtained with values 8 only are mentioned here.
Location: Chlre3/scaffold_28:1327628–1332277; Protein ID: 149241
This is the subject of experiments currently underway in Roberts’ laboratory.
See http://www.tigr.org/tdb/e2k1/osa1/; May 2007
In the TIGR annotation, Os03g41419 contains four introns, and Os03g41438, Os11g12410 and Os11g12420 contain two introns, but these annotations have errors (see footnotes for Table 3). Interestingly, for Os03g41419, the TIGR-annotated exons 4 and 5 appear to be possible alternative splicing variants, each encoding the C-terminal approximately two-thirds of the protein sequence starting at identical positions; however, there is no EST evidence to suggest that alternative splicing occurs with this gene.
The alignment was performed using the Gonnet series for the substitution matrix, a gap opening penalty=10 and a gap extension penalty=0.2.
Attempts to generate a “branch and bound” tree failed due to insufficient computing power available.
In the latter clustering, reference is not to conservation of reactive centres, but rather to the whole protein; SoltuZ1a and LycesZ1 have P2-P1′ PLS and TTS, respectively, and thus would not be expected to inhibit proteinases of similar specificity.
An 8% acrylamide gel and a buffer at pH ~8 are normally used.
This layer is not present in wheat grain.
The nucellus is located between the testa and the endosperm.
Plant Expression DataBase; see http://www.plexdb.org
Matches Exemplar Sequence Barley1_01878
Matches Exemplar Sequence Barley1_01877
DAP = days after pollination
The Arabidopsis Information Resource; see http://www.arabidopsis.org
Personal communication
Using individual a priori statistical tests at the 5% level
A herbacious perennial from the family Asteraceae
In contrast to the fixed length of the N-terminal region of the RCL (P17 to P1), the length of the C-terminal region (ending at the conserved sequence DFVAD) ranges from 6 to 18 residues among the plant serpins.
The MEROPS webpage used was created 23 April 2007.
Peptidase clans found in Arabidopsis are AA, AD, CA, CD, CE, CF, MA, MC, ME, MF, MG, MH, MJ, MK, MM, MP, PA, PB, PC, SB, SC, SE, SF, SJ, SK, SP, ST, T- and U-.
The legumains are asparagine-specific cysteine proteinases that cleave peptide bonds at the carboxyl group of asparagines, or in some cases, at relatively low pH (4.0) and with reduced activity at the carbonyl group of aspartic acid. Legumain, from jackbean (Canavalia ensiformis), is the type identifier for the family (Trobacher et al. 2006).
The pH at which a protein has no net charge.
Predicted using the program ProtParam available at http://www.expasy.org
References
Aleshkov SB, Fa M, Karolin J, Strandberg L, Johansson LB, Wilczynska M, Ny T (1996) Biochemical and biophysical studies of reactive center cleaved plasminogen activator inhibitor type 1. The distance between P3 and P1’ determined by donor–donor fluorescence energy transfer. J Biol Chem 271:21231–21238
Annand RR, Dahlen JR, Sprecher CA, De Dreu P, Foster DC, Mankovich JA, Talanian RV, Kisiel W, Giegel DA (1999) Caspase-1 (interleukin-1beta-converting enzyme) is inhibited by the human serpin analogue proteinase inhibitor 9. Biochem J 342:655–665
Arabidopsis Genome Initiative (2000) Analysis of the genome sequence of the flowering plant Arabidopsis thaliana. Nature 408:796–815
Atchley WR, Lokot T, Wollenberg K, Dress A, Ragg H (2001) Phylogenetic analyses of amino acid variation in the serpin proteins. Mol Biol Evol 18:1502–1511
Baglin TP, Carrell RW, Church FC, Esmon CT, Huntington JA (2002) Crystal structures of native and thrombin-complexed heparin cofactor II reveal a multistep allosteric mechanism. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:11079–11084
Barbour KW, Goodwin RL, Guillonneau F, Wang YP, Baumann H, Berger FG (2002) Functional diversification during evolution of the murine alpha(1)-proteinase inhibitor family: role of the hypervariable reactive center loop. Mol Biol Evol 19:718–727
Becerra SP, Sagasti A, Spinella P, Notario V (1995) Pigment epithelium-derived factor behaves like a noninhibitory serpin. Neurotrophic activity does not require the serpin reactive loop. J Biol Chem 270:25992–25999
Beguin P, Lemaire M (1996) The cellulosome: an exocellular, multiprotein complex specialized in cellulose degradation. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol 31:201–236
Benarafa C, Remold-O’Donnell E (2005) The ovalbumin serpins revisited: perspective from the chicken genome of clade B serpin evolution in vertebrates. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:11367–11372
Brandt A, Svendsen I, Hejgaard J (1990) A plant serpin gene. Structure, organization and expression of the gene encoding barley protein Z4. Eur J Biochem 194:499–505
Bruch M, Weiss V, Engel J (1988) Plasma serine proteinase inhibitors (serpins) exhibit major conformational changes and a large increase in conformational stability upon cleavage at their reactive sites. J Biol Chem 263:16626–16630
Buck MJ, Atchley WR (2005) Networks of coevolving sites in structural and functional domains of serpin proteins. Mol Biol Evol 22:1627–1634
Carrell RW, Evan DLI (1992) Serpins: mobile conformations in a family of proteinase inhibitors. Curr Opin Struct Biol 2:438–446
Carrell RW, Owen MC (1985) Plakalbumin, alpha 1-antitrypsin, antithrombin and the mechanism of inflammatory thrombosis. Nature 317:730–732
Carrell R, Travis J (1985) Alpha1-antitrypsin and the serpins: variation and countervariation. Trends Biochem Sci 10:20–24
Chauhan RS, Farman ML, Zhang HB, Leong SA (2002) Genetic and physical mapping of a rice blast resistance locus, Pi-CO39(t), that corresponds to the avirulence gene AVR1-CO39 of Magnaporthe grisea. Mol Genet Genom 267:603–612
Chen WQJ, Chang SH, Hudson ME, Kwan WK, Li JQ, Estes B, Knoll D, Shi L, Zhu T (2005) Contribution of transcriptional regulation to natural variations in Arabidopsis. Genome Biol 6:R32
Christeller JT, Farley PC, Ramsay RJ, Sullivan PA, Laing WA (1998) Purification, characterization and cloning of an aspartic proteinase inhibitor from squash phloem exudate. Eur J Biochem 254:160–167
Creighton TE, Darby NJ (1989) Functional evolutionary divergence of proteolytic enzymes and their inhibitors. Trends Biochem Sci 14:319–324
Curioni A, Pressi G, Furegon L, Peruffo ADB (1995) Major proteins of beer and their precursors in barley: electrophoretic and immunological studies. J Agric Food Chem 43:2620–2626
Dahl SW, Rasmussen SK, Hejgaard J (1996a) Heterologous expression of three plant serpins with distinct inhibitory specificities. J Biol Chem 271:25083–25088
Dahl SW, Rasmussen SK, Petersen LC, Hejgaard J (1996b) Inhibition of coagulation factors by recombinant barley serpin BSZx. FEBS Lett 394:165–168
Dahlen JR, Foster DC, Kisiel W (1997) Human proteinase inhibitor 9 (PI9) is a potent inhibitor of subtilisin A. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 238:329–333
Dahlen JR, Jean F, Thomas G, Foster DC, Kisiel W (1998) Inhibition of soluble recombinant furin by human proteinase inhibitor 8. J Biol Chem 273:1851–1854
Dementiev A, Simonovic M, Volz K, Gettins PG (2003) Canonical inhibitor-like interactions explain reactivity of alpha1-proteinase inhibitor Pittsburgh and antithrombin with proteinases. J Biol Chem 278:37881–37887
Dementiev A, Petitou M, Herbert JM, Gettins PGW (2004) The ternary complex of antithrombin-anhydrothrombin heparin reveals the basis of inhibitor specificity. Nat Struct Mol Biol 11:863–867
Druka A, Muehlbauer G, Druka I, Caldo R, Baumann U, Rostoks N, Schreiber A, Wise R, Close T, Kleinhofs A, Graner A, Schulman A, Langridge P, Sato K, Hayes P, McNicol J, Marshall D, Waugh R (2006) An atlas of gene expression from seed to seed through barley development. Funct Integr Genomics 6:202–211
Evans DE, Hejgaard J (1999) The impact of malt derived proteins on beer foam quality. Part 1. The effect of germination and kilning on the level of protein Z4, protein Z7 and LTP1. J Inst Brew 105:159–169
Evans DE, Sheehan MC (2002) Don’t be fobbed off: the substance of beer foam - A review. J Am Soc Brew Chem 60:47–57
Finer-Moore JS, Kossiakoff AA, Hurley JH, Earnest T, Stroud RM (1992) Solvent structure in crystals of trypsin determined by X-ray and neutron diffraction. Proteins 12:203–222
Finnie C, Svensson B (2003) Feasibility study of a tissue-specific approach to barley proteome analysis: aleurone layer, endosperm, embryo and single seeds. J Cer Sci 38:217–227
Finnie C, Melchior S, Roepstorff P, Svensson B (2002) Proteome analysis of grain filling and seed maturation in barley. Plant Physiol 129:1308–1319
Finnie C, Maeda K, Ostergaard O, Bak-Jensen KS, Larsen J, Svensson B (2004a) Aspects of the barley seed proteome during development and germination. Biochem Soc Trans 32:517–519
Finnie C, Steenholdt T, Roda Noguera O, Knudsen S, Larsen J, Brinch-Pedersen H, Bach Holm P, Olsen O, Svensson B (2004b) Environmental and transgene expression effects on the barley seed proteome. Phytochemistry 65:1619–1627
Fowler S, Thomashow MF (2002) Arabidopsis transcriptome profiling indicates that multiple regulatory pathways are activated during cold acclimation in addition to the CBF cold response pathway. Plant Cell 14:1675–1690
Fulton KF, Buckle AM, Cabrita LD, Irving JA, Butcher RE, Smith I, Reeve S, Lesk AM, Bottomley SP, Rossjohn J, Whisstock JC (2005) The high resolution crystal structure of a native thermostable serpin reveals the complex mechanism underpinning the stressed to relaxed transition. J Biol Chem 280:8435–8442
Gan H, Wang Y, Jiang HB, Mita K, Kanost MR (2001) A bacteria-induced, intracellular serpin in granular hemocytes of Manduca sexta. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 31:887–898
Gettins PGW (2002) Serpin structure, mechanism, and function. Chem Rev 102:4751–4803
Gettins PGW (2007) Mechanisms of serpin inhibition. In: Silverman GA, Lomas DA (eds) Molecular and cellular aspects of the serpinopathies and disorders in serpin activity. World Scientific, New Jersey, pp 67–100
Giavalisco P, Nordhoff E, Kreitler T, Kloppel KD, Lehrach H, Klose J, Gobom J (2005) Proteome analysis of Arabidopsis thaliana by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis and matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionisation-time of flight mass spectrometry. Proteomics 5:1902–1913
Giese H, Hejgaard J (1984) Synthesis of salt-soluble proteins in barley. Pulse-labeling study of grain filling in liquid-cultured detached spikes. Planta 161:172–177
Gorinstein S, Zemser M, Vargas-Albores F, Ochoa JL, Paredes-Lopez O, Scheler C, Salnikow J, Martin-Belloso O, Trakhtenberg S (1999) Proteins and amino acids in beers, their contents and relationships with other analytical data. Food Chem 67:71–78
Grigoryev SA, Bednar J, Woodcock CL (1999) MENT, a heterochromatin protein that mediates higher order chromatin folding, is a new serpin family member. J Biol Chem 274:5626–5636
Grossman AR (2005) Paths toward algal genomics. Plant Physiol 137:410–427
Guex N, Peitsch MC (1997) SWISS-MODEL and the Swiss-PdbViewer: an environment for comparative protein modeling. Electrophoresis 18:2714–2723
Han J, Zhang H, Min G, Kemler D, Hashimoto C (2000) A novel Drosophila serpin that inhibits serine proteases. FEBS Lett 468:194–198
Hannah MA, Heyer AG, Hincha DK (2005) A global survey of gene regulation during cold acclimation in Arabidopsis thaliana. PloS Genet 1: e26
Harris EH (2001) Chlamydomonas as a model organism. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 52:363–406
Haubrick LL, Assmann SM (2006) Brassinosteroids and plant function: some clues, more puzzles. Plant Cell Environ 29:446–457
Hejgaard J (1976) Free and protein-bound beta-amylases of barley grain: characterization by two-dimensional immunoelectrophoresis. Physiol Plant 38:293–299
Hejgaard J (1977) Origin of a dominant beer protein: immunochemical identity with a beta-amylase-associated protein from barley. J Inst Brew 83:94–96
Hejgaard J (1978) ‘Free’ and ‘bound’ beta-amylases during malting of barley, characterization by two-dimensional immunoelectrophoresis. J Inst Brew 84:43–46
Hejgaard J (1982) Purification and properties of protein Z—a major albumin of barley endosperm. Physiol Plant 54:174–182
Hejgaard J (2001) Inhibitory serpins from rye grain with glutamine as P-1 and P-2 residues in the reactive center. FEBS Lett 488:149–153
Hejgaard J (2005) Inhibitory plant serpins with a sequence of three glutamine residues in the reactive center. Biol Chem 386:1319–1323
Hejgaard J, Bog-Hansen TC (1974) Quantitative immunoelectrophoresis of barley and malt proteins. J Inst Brew 80:436–442
Hejgaard J, Boisen S (1980) High-lysine proteins in Hiproly barley breeding: identification, nutritional significance and new screening methods. Hereditas 93:311–320
Hejgaard J, Carlsen S (1977) Immunoelectrophoretic identification of a heterodimer beta-amylase in extracts of barley grain. J Sci Food Agric 28:900–904
Hejgaard J, Hauge S (2002) Serpins of oat (Avena sativa) grain with distinct reactive centres and inhibitory specificity. Physiol Plant 116:155–163
Hejgaard J, Kaersgaard P (1983) Purification and properties of the major antigenic beer protein of barley origin. J Inst Brew 89:402–410
Hejgaard J, Roberts TH (2007) Plant serpins. In: Silverman GA Lomas DA (eds) Molecular and cellular aspects of the serpinopathies and disorders in serpin activity. World Scientific, New Jersey, pp 279–300
Hejgaard J, Sorensen SB (1975) Characterization of a protein-rich beer fraction by two-dimensional immunoelectrophoretic techniques. Comptes Rendus des Travaux du Laboratoire Carlsberg 40:187–203
Hejgaard J, Rasmussen SK, Brandt A, Svendsen I (1985) Sequence homology between barley endosperm protein Z and protease inhibitors of the alpha-1-antitrypsin family. FEBS Lett 180:89–94
Hejgaard J, Laing WA, Marttila S, Gleave AP, Roberts TH (2005) Serpins in fruit and vegetative tissues of apple (Malus domestica): expression of four serpins with distinct reactive centres and characterisation of a major inhibitory seed form, MdZ1b. Funct Plant Biol 32:517–527
Hill RE, Hastie ND (1987) Accelerated evolution in the reactive centre regions of serine protease inhibitors. Nature 326:96–99
Hook VYH, Purviance RT, Azaryan AV, Hubbard G, Krieger TJ (1993) Purification and characterization of alpha 1-antichymotrypsin-like protease inhibitor that regulates prohormone thiol protease involved in enkephalin precursor processing. J Biol Chem 268:20570–20577
Hunt LT, Dayhoff MO (1980) A surprising new protein superfamily containing ovalbumin, antithrombin- III, and alpha 1-proteinase inhibitor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 95:864–871
Huntington JA, Read RJ, Carrell RW (2000) Structure of a serpin–protease complex shows inhibition by deformation. Nature 407:923–926
Ibarra CA, Blouse GE, Christian TD, Shore JD (2004) The contribution of the exosite residues of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 to proteinase inhibition. J Biol Chem 279:3643–3650
Inglis JD, Hill RE (1991) The murine Spi-2 proteinase inhibitor locus: a multigene family with a hypervariable reactive site domain. EMBO J 10:255–261
International Rice Genome Sequencing Project (2005) The map-based sequence of the rice genome. Nature 436:793–800
Irving JA, Pike RN, Lesk AM, Whisstock JC (2000) Phylogeny of the serpin superfamily. Implications of amino acid conservation for structure and function. Genome Res 10:1845–1864
Irving JA, Shushanov SS, Pike RN, Popova EY, Bromme D, Coetzer THT, Bottomley SP, Boulynko IA, Grigoryev SA, Whisstock JC (2002a) Inhibitory activity of a heterochromatin-associated serpin (MENT) against papain-like cysteine proteinases affects chromatin structure and blocks cell proliferation. J Biol Chem 277:13192–13201
Irving JA, Steenbakkers PJM, Lesk AM, den Camp HJMO, Pike RN, Whisstock JC (2002b) Serpins in prokaryotes. Mol Biol Evol 19:1881–1890
Irving JA, Cabrita LD, Rossjohn J, Pike RN, Bottomley SP, Whisstock JC (2003) The 1.5 angstrom crystal structure of a prokaryote serpin: controlling conformational change in a heated environment. Structure 11:387–397
Irving JA, Askew DJ, Whisstock JC (2004) Computational analysis of evolution and conservation in a protein superfamily. Methods 32:73–92
Ivanov D, Emonet C, Foata F, Affolter M, Delley M, Fisseha M, Blum-Sperisen S, Kochhar S, Arigoni F (2006) A serpin from the gut bacterium Bifidobacterium longum inhibits eukaryotic elastase-like serine proteases. J Biol Chem 281:17246–17252
Jiang H, Kanost MR (1997) Characterization and functional analysis of 12 naturally occurring reactive site variants of serpin-1 from Manduca sexta. J Biol Chem 272:1082–1087
Jiang H, Mulnix AB, Kanost MR (1995) Expression and characterization of recombinant Manduca sexta serpin-1B and site-directed mutants that change its inhibitory selectivity. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 25:1093–1100
Jiang H, Wang Y, Huang Y, Mulnix AB, Kadel J, Cole K, Kanost MR (1996) Organization of serpin gene-1 from Manduca sexta. Evolution of a family of alternate exons encoding the reactive site loop. J Biol Chem 271:28017–28023
Johnson DJ, Li W, Adams TE, Huntington JA (2006) Antithrombin-S195A factor Xa-heparin structure reveals the allosteric mechanism of antithrombin activation. EMBO J 25:2029–2037
Jongsma MA, Bolter C (1997) The adaption of insects to plant protease inhibitors. J Insect Physiol 43:885–895
Kaersgaard P, Hejgaard J (1979) Antigenic beer macromolecules: an experimental survey of purification methods. J Inst Brew 85:103–111
Kaiserman D, Bird PI (2005) Analysis of vertebrate genomes suggests a new model for clade B serpin evolution. BMC Genomics 6:167
Kang SH, Barak Y, Lamed R, Bayer EA, Morrison M (2006) The functional repertoire of prokaryote cellulosomes includes the serpin superfamily of serine proteinase inhibitors. Mol Microbiol 60:1344–1354
Kanost MR, Prasad SV, Wells MA (1989) Primary structure of a member of the serpin superfamily of proteinase inhibitors from an insect, Manduca sexta. J Biol Chem 264:965–972
Ke SH, Coombs GS, Tachias K, Navre M, Corey DR, Madison EL (1997) Distinguishing the specificities of closely related proteases. Role of P3 in substrate and inhibitor discrimination between tissue-type plasminogen activator and urokinase. J Biol Chem 272:16603–16609
Keates SE, Kostman TA, Anderson JD, Bailey BA (2003) Altered gene expression in three plant species in response to treatment with Nep1, a fungal protein that causes necrosis. Plant Physiol 132:1610–1622
Koller A, Washburn MP, Lange BM, Andon NL, Deciu C, Haynes PA, Hays L, Schieltz D, Ulaszek R, Wei J, Wolters D, Yates JR (2002) Proteomic survey of metabolic pathways in rice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:11969–11974
Komiyama T, Ray CA, Pickup DJ, Howard AD, Thornberry NA, Peterson EP, Salvesen G (1994) Inhibition of interleukin-1 beta converting enzyme by the cowpox virus serpin CrmA. An example of cross-class inhibition. J Biol Chem 269:19331–19337
Kreis M, Williamson M, Buxton B, Pywell J, Hejgaard J, Svendsen I (1987) Primary structure and differential expression of beta-amylase in normal and mutant barleys. Eur J Biochem 169:517–525
Krem MM, Di Cera E (2003) Conserved ser residues, the shutter region, and speciation in serpin evolution. J Biol Chem 278:37810–37814
Kreps JA, Wu YJ, Chang HS, Zhu T, Wang X, Harper JF (2002) Transcriptome changes for Arabidopsis in response to salt, osmotic, and cold stress. Plant Physiol 130:2129–2141
la Cour Petersen M, Hejgaard J, Thompson GA, Schulz A (2005) Cucurbit phloem serpins are graft-transmissible and appear to be resistant to turnover in the sieve element–companion cell complex. J Exp Bot 56:3111–120
Law RHP, Zhang QW, McGowan S, Buckle AM, Silverman GA, Wong W, Rosado CJ, Langendorf CG, Pike RN, Bird PI, Whisstock JC (2006) An overview of the serpin superfamily. Genome Biol 7:216
Lawrence DA, Ginsburg D, Day DE, Berkenpas MB, Verhamme IM, Kvassman JO, Shore JD (1995) Serpin-protease complexes are trapped as stable acyl-enzyme intermediates. J Biol Chem 270:25309–25312
Leicht M, Long GL, Chandra T, Kurachi K, Kidd VJ, Mace M Jr., Davie EW, Woo SL (1982) Sequence homology and structural comparison between the chromosomal human alpha 1-antitrypsin and chicken ovalbumin genes. Nature 297:655–659
Li J, Wang Z, Canagarajah B, Jiang H, Kanost M, Goldsmith EJ (1999) The structure of active serpin 1K from Manduca sexta. Struct Fold Des 7:103–109
Li W, Johnson DJ, Esmon CT, Huntington JA (2004) Structure of the antithrombin–thrombin–heparin ternary complex reveals the antithrombotic mechanism of heparin. Nat Struct Mol Biol 11:857–862
Ligoxygakis P, Roth S, Reichhart JM (2003) A serpin regulates dorsal–ventral axis formation in the Drosophila embryo. Curr Biol 13:2097–2102
Lough TJ, Lucas WJ (2006) Integrative plant biology: role of phloem long-distance macromolecular trafficking. Annu Rev Plant Biol 57:203–232
Luke CJ, Pak SC, Askew DJ, Askew YS, Smith JE, Silverman GA (2006) Selective conservation of the RSL-encoding, proteinase inhibitory-type, clade L serpins in Caenorhabditis species. Front Biosci 11:581–594
Lusk LT, Goldstein H, Ryder D (1995) Independent role of beer proteins, melanoidins and polysaccharides in foam formation. J Am Soc Brew Chem 53:93–103
Marshall CJ (1993) Evolutionary relationships among the serpins. Philos Trans Royal Soc London B Biol Sci 342:101–119
Matheson NR, van Halbeek H, Travis J (1991) Evidence for a tetrahedral intermediate complex during serpin–proteinase interactions. J Biol Chem 266:13489–13491
McGowan S, Buckle AM, Irving JA, Ong PC, Bashtannyk-Puhalovich TA, Kan WT, Henderson KN, Bulynko YA, Popova EY, Smith AI, Bottomley SP, Rossjohn J, Grigoryev SA, Pike RN, Whisstock JC (2006) X-ray crystal structure of MENT: evidence for functional loop-sheet polymers in chromatin condensation. EMBO J 25:3144–3155
Mellet P, Boudier C, Mely Y, Bieth JG (1998) Stopped flow fluorescence energy transfer measurement of the rate constants describing the reversible formation and the irreversible rearrangement of the elastase-alpha1-proteinase inhibitor complex. J Biol Chem 273:9119–9123
Mills ENC, Kauffman JA, Morgan MRA, Field JM, Hejgaard J, Proudlove MO, Onishi A (1998) Immunological study of hydrophobic polypeptides in beer. J Agric Food Chem 46:4475–4483
Murray C, Christeller JT (1995) Purification of a trypsin inhibitor (PFTI) from pumpkin fruit phloem exudate and isolation of putative trypsin and chymotrypsin inhibitor cDNA clones. Biol Chem 376:281–287
Nielsen G, Johansen H, Jensen J, Hejgaard J (1983) Localization on barley chromosome 4 of genes coding for β-amylase (Bmy1) and protein Z (Paz1). Barley Genet Newslett 13:55–57
Nixon JE, Wang A, Field J, Morrison HG, McArthur AG, Sogin ML, Loftus BJ, Samuelson J (2002) Evidence for lateral transfer of genes encoding ferredoxins, nitroreductases, NADH oxidase, and alcohol dehydrogenase 3 from anaerobic prokaryotes to Giardia lamblia and Entamoeba histolytica. Eukaryot Cell 1:181–190
O’Malley KM, Nair SA, Rubin H, Cooperman BS (1997) The kinetic mechanism of serpin-proteinase complex formation. An intermediate between the Michaelis complex and the inhibited complex. J Biol Chem 272:5354–5359
Oley M, Letzel MC, Ragg H (2004) Inhibition of furin by serpin Spn4A from Drosophila melanogaster. FEBS Lett 577:165–169
Olson ST, Swanson R, Day D, Verhamme I, Kvassman J, Shore JD (2001) Resolution of Michaelis complex, acylation, and conformational change steps in the reactions of the serpin, plasminogen activator inhibitor-1, with tissue plasminogen activator and trypsin. Biochemistry 40:11742–11756
Ostergaard H, Rasmussen SK, Roberts TH, Hejgaard J (2000) Inhibitory serpins from wheat grain with reactive centers resembling glutamine-rich repeats of prolamin storage proteins—cloning and characterization of five major molecular forms. J Biol Chem 275:33272–33279
Ostergaard O, Melchior S, Roepstorff P, Svensson B (2002) Initial proteome analysis of mature barley seeds and malt. Proteomics 2:733–739
Ostergaard O, Finnie C, Laugesen S, Roepstorff P, Svensson B (2004) Proteome analysis of barley seeds: identification of major proteins from two-dimensional gels (pl 4–7). Proteomics 4:2437–2447
Pak SC, Kumar V, Tsu C, Luke CJ, Askew YS, Askew DJ, Mills DR, Bromme D, Silverman GA (2004) SRP-2 is a cross-class inhibitor that participates in postembryonic development of the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans: initial characterization of the clade L serpins. J Biol Chem 279:15448–15459
Pak SC, Tsu C, Luke CJ, Askew YS, Silverman GA (2006) The Caenorhabditis elegans muscle specific serpin, SRP-3, neutralizes chymotrypsin-like serine peptidases. Biochemistry 45:4474–4480
Patston PA, Gettins P, Beechem J, Schapira M (1991) Mechanism of serpin action: evidence that C1 inhibitor functions as a suicide substrate. Biochemistry 30:8876–8882
Pearce MC, Pike RN, Lesk AM, Bottomley SP (2007) Serpin conformations molecular and cellular aspects of the serpinopathies and disorders in serpin activity. Molecular and cellular aspects of the serpinopathies and disorder in serpin activity. World Scientific, New Jersey, pp 35–66
Perrocheau L, Rogniaux H, Boivin P, Marion D (2005) Probing heat-stable water-soluble proteins from barley to malt and beer. Proteomics 5:2849–2858
Perron MJ, Blouse GE, Shore JD (2003) Distortion of the catalytic domain of tissue-type plasminogen activator by plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 coincides with the formation of stable serpin–proteinase complexes. J Biol Chem 278:48197–48203
Peterson FC, Gordon NC, Gettins PG (2000) Formation of a noncovalent serpin–proteinase complex involves no conformational change in the serpin. Use of 1H-15N HSQC NMR as a sensitive nonperturbing monitor of conformation. Biochemistry 39:11884–11892
Plotnick MI, Schechter NM, Wang ZM, Liu X, Rubin H (1997) Role of the P6-P3 region of the serpin reactive loop in the formation and breakdown of the inhibitory complex. Biochemistry 36:14601–14608
Potempa J, Shieh BH, Travis J (1988) Alpha-2-antiplasmin: a serpin with two separate but overlapping reactive sites. Science 241:699–700
Rasmussen SK (1993) A gene coding for a new plant serpin. Biochim Biophys Acta 1172:151–154
Rasmussen SK, Dahl SW, Norgard A, Hejgaard J (1996) A recombinant wheat serpin with inhibitory activity. Plant Mol Biol 30:673–677
Raven PH, Evert RF, Eichhorn SE (2005) Biology of plants. W.H. Freeman and Company, New York
Rawlings ND, Tolle DP, Barrett AJ (2004) Evolutionary families of peptidase inhibitors. Biochem J 378:705–716
Ray CA, Black RA, Kronheim SR, Greenstreet TA, Sleath PR, Salvesen GS, Pickup DJ (1992) Viral inhibition of inflammation: cowpox virus encodes an inhibitor of the interleukin-1 beta converting enzyme. Cell 69:597–604
Reichhart JM (2005) Tip of another iceberg: Drosophila serpins. Trends Cell Biol 15:659–665
Rezaie AR (2006) Pentasaccharide enhances the inactivation of factor xa by antithrombin by promoting the assembly of a Michaelis-type intermediate complex. Demonstration by rapid kinetic, surface plasmon resonance, and competitive binding studies. Biochemistry 45:5324–5329
Riahi Y, Siman-Tov R, Ankri S (2004) Molecular cloning, expression and characterization of a serine proteinase inhibitor gene from Entamoeba histolytica. Mol Biochem Parasitol 133:153–162
Roberts TH, Marttila S, Rasmussen SK, Hejgaard J (2003) Differential gene expression for suicide-substrate serine proteinase inhibitors (serpins) in vegetative and grain tissues of barley. J Exp Bot 54:2251–2263
Roberts TH, Hejgaard J, Saunders NFW, Cavicchioli R, Curmi PMG (2004) Serpins in unicellular Eukarya, Archaea, and Bacteria: sequence analysis and evolution. J Mol Evol 59:437–447
Robertson AS, Belorgey D, Lilley KS, Lomas DA, Gubb D, Dafforn TR (2003) Characterization of the necrotic protein that regulates the Toll-mediated immune response in Drosophila. J Biol Chem 278:6175–6180
Rollini P, Fournier RE (1997) A 370-kb cosmid contig of the serpin gene cluster on human chromosome 14q32.1: molecular linkage of the genes encoding alpha 1-antichymotrypsin, protein C inhibitor, kallistatin, alpha 1-antitrypsin, and corticosteroid-binding globulin. Genomics 46:409–415
Rosenkrands I, Hejgaard J, Rasmussen SK, Bjorn SE (1994) Serpins from wheat grain. FEBS Lett 343:75–80
Ruuska SA, Girke T, Benning C, Ohlrogge JB (2002) Contrapuntal networks of gene expression during Arabidopsis seed filling. Plant Cell 14:1191–1206
Schechter NM, Plotnick MI (2004) Measurement of the kinetic parameters mediating protease-serpin inhibition. Methods 32:159–168
Schick C, Pemberton PA, Shi GP, Kamachi Y, Cataltepe S, Bartuski AJ, Gornstein ER, Bromme D, Chapman HA, Silverman GA (1998) Cross-class inhibition of the cysteine proteinases cathepsins K, L, and S by the serpin squamous cell carcinoma antigen 1: a kinetic analysis. Biochemistry 37:5258–5266
Schwartz BS, Espana F (1999) Two distinct urokinase-serpin interactions regulate the initiation of cell surface-associated plasminogen activation. J Biol Chem 274:15278–15283
Scott FL, Eyre HJ, Lioumi M, Ragoussis J, Irving JA, Sutherland GA, Bird PI (1999) Human ovalbumin serpin evolution: phylogenic analysis, gene organization, and identification of new PI8-related genes suggest that two interchromosomal and several intrachromosomal duplications generated the gene clusters at 18q21-q23 and 6p25. Genomics 62:490–499
Shieh BH, Potempa J, Travis J (1989) The use of alpha 2-antiplasmin as a model for the demonstration of complex reversibility in serpins. J Biol Chem 264:13420–13423
Silverman GA, Lomas DA (eds) (2007) Molecular and cellular aspects of the serpinopathies and disorders in serpin activity. World Scientific, New Jersey
Silverman GA, Bird PI, Carrell RW, Church FC, Coughlin PB, Gettins PGW, Irving JA, Lomas DA, Luke CJ, Moyer RW, Pemberton PA, Remold-O'Donnell E, Salvesen GS, Travis J, Whisstock JC (2001) The serpins are an expanding superfamily of structurally similar but functionally diverse proteins—evolution, mechanism of inhibition, novel functions, and a revised nomenclature. J Biol Chem 276:33293–33296
Silverman GA, Whisstock JC, Askew DJ, Pak SC, Luke CJ, Cataltepe S, Irving JA, Bird PI (2004) Human clade B serpins (ov-serpins) belong to a cohort of evolutionarily dispersed intracellular proteinase inhibitor clades that protect cells from promiscuous proteolysis. Cell Mol Life Sci 61:301–325
Simonovic M, Gettins PGW, Volz K (2000) Crystal structure of viral serpin crmA provides insights into its mechanism of cysteine proteinase inhibition. Protein Sci 9:1423–1427
Sorensen MB, Cameron-Mills V, Brandt A (1989) Transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulation of gene expression in developing barley endosperm. Mol Gen Genet 217:195–201
Sprecher CA, Morgenstern KA, Mathewes S, Dahlen JR, Schrader SK, Foster DC, Kisiel W (1995) Molecular cloning, expression, and partial characterization of two novel members of the ovalbumin family of serine proteinase inhibitors. J Biol Chem 270:29854–29861
Springhetti EM, Istomina NE, Whisstock JC, Nikitina T, Woodcock CL, Grigoryev SA (2003) Role of the M-loop and reactive center loop domains in the folding and bridging of nucleosome arrays by MENT. J Biol Chem 278:43384–43393
Stein PE, Tewkesbury DA, Carrell RW (1989) Ovalbumin and angiotensinogen lack serpin S-R conformational change. Biochem J 262:103–107
Stratikos E, Gettins PG (1997) Major proteinase movement upon stable serpin–proteinase complex formation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:453–458
Sun J, Ooms L, Bird CH, Sutton VR, Trapani JA, Bird PI (1997) A new family of 10 murine ovalbumin serpins includes two homologs of proteinase inhibitor 8 and two homologs of the granzyme B inhibitor (proteinase inhibitor 9). J Biol Chem 272:15434–15441
Sun J, Stephens R, Mirza G, Kanai H, Ragoussis J, Bird PI (1998) A serpin gene cluster on human chromosome 6p25 contains PI6, PI9 and ELANH2 which have a common structure almost identical to the 18q21 ovalbumin serpin genes. Cytogenet Cell Genet 82:273–277
Sun J, Whisstock JC, Harriott P, Walker B, Novak A, Thompson PE, Smith AI, Bird PI (2001) Importance of the P4′ residue in human granzyme B inhibitors and substrates revealed by scanning mutagenesis of the proteinase inhibitor 9 reactive center loop. J Biol Chem 276:15177–15184
Swofford DL (2002) PAUP. Phylogenetic analysis using parsimony (and other methods). Sinauer and Associates, Sunderland, Massachusetts
Tanaka N, Fujita M, Handa H, Murayama S, Uemura M, Kawamura Y, Mitsui T, Mikami S, Tozawa Y, Yoshinaga T, Komatsu S (2004) Proteomics of the rice cell: systematic identification of the protein populations in subcellular compartments. Mol Gen Genet 271:566–576
Thomas JC, Wasmann CC, Echt C, Dunn RL, Bohnert HJ, McCoy TJ (1994) Introduction and expression of an insect proteinase inhibitor in alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.). Plant Cell Rep 14:31–36
Thomas JC, Adams DG, Keppenne VD, Wasmann CC, Brown JK, Kanost MR, Bohnert HJ (1995a) Manduca sexta encoded protease inhibitors expressed in Nicotiana tabacum provide protection against insects. Plant Physiol Biochem 33:611–614
Thomas JC, Adams DG, Keppenne VD, Wasmann CC, Brown JK, Kanost MR, Bohnert HJ (1995b) Protease inhibitors of Manduca sexta expressed in transgenic cotton. Plant Cell Rep 14:758–762
Thomas L, Moore NR, Miller S, Booth NA (2007) The C-terminus of alpha2-antiplasmin interacts with endothelial cells. Br J Haematol 136:472–479
Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F, Jeanmougin F, Higgins DG (1997) The CLUSTAL_X windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucl Acids Res 25:4876–4882
Trobacher CP, Senatore A, Greenwood JS (2006) Masterminds or minions? Cysteine proteinases in plant programmed cell death. Can J Bot 84:651–667
Tsutsui Y, Liu L, Gershenson A, Wintrode PL (2006) The conformational dynamics of a metastable serpin studied by hydrogen exchange and mass spectrometry. Biochemistry 45:6561–6569
Tuskan GA, Difazio S, Jansson S, Bohlmann J, Grigoriev I, Hellsten U, Putnam N, Ralph S, Rombauts S, Salamov A, Schein J, Sterck L, Aerts A, Bhalerao RR, Bhalerao RP, Blaudez D, Boerjan W, Brun A, Brunner A, Busov V, Campbell M, Carlson J, Chalot M, Chapman J, Chen GL, Cooper D, Coutinho PM, Couturier J, Covert S, Cronk Q, Cunningham R, Davis J, Degroeve S, Dejardin A, Depamphilis C, Detter J, Dirks B, Dubchak I, Duplessis S, Ehlting J, Ellis B, Gendler K, Goodstein D, Gribskov M, Grimwood J, Groover A, Gunter L, Hamberger B, Heinze B, Helariutta Y, Henrissat B, Holligan D, Holt R, Huang W, Islam-Faridi N, Jones S, Jones-Rhoades M, Jorgensen R, Joshi C, Kangasjarvi J, Karlsson J, Kelleher C, Kirkpatrick R, Kirst M, Kohler A, Kalluri U, Larimer F, Leebens-Mack J, Leple JC, Locascio P, Lou Y, Lucas S, Martin F, Montanini B, Napoli C, Nelson DR, Nelson C, Nieminen K, Nilsson O, Pereda V, Peter G, Philippe R, Pilate G, Poliakov A, Razumovskaya J, Richardson P, Rinaldi C, Ritland K, Rouze P, Ryaboy D, Schmutz J, Schrader J, Segerman B, Shin H, Siddiqui A, Sterky F, Terry A, Tsai CJ, Uberbacher E, Unneberg P, Vahala J, Wall K, Wessler S, Yang G, Yin T, Douglas C, Marra M, Sandberg G, Van de Peer Y, Rokhsar D (2006) The genome of black cottonwood, Populus trichocarpa (Torr. & Gray). Science 313:1596–1604
Vercammen D, Belenghi B, van de Cotte B, Beunens T, Gavigan JA, De Rycke R, Brackenier A, Inze D, Harris JL, Van Breusegem F (2006) Serpin1 of Arabidopsis thaliana is a suicide inhibitor for Metacaspase 9. J Mol Biol 364:625–636
Walz C, Giavalisco P, Schad M, Juenger M, Klose J, Kehr J (2004) Proteomics of curcurbit phloem exudate reveals a network of defence proteins. Phytochemistry 65:1795–1804
Whisstock JC, Bottomley SP (2006) Molecular gymnastics: serpin structure, folding and misfolding. Curr Opin Struct Biol 16:761–768
Whisstock J, Skinner R, Lesk AM (1998) An atlas of serpin conformations. Trends Biochem Sci 23:63–67
Whisstock JC, Irving JA, Bottomley SP, Pike RN, Lesk AM (1999) Serpins in the Caenorhabditis elegans genome. Proteins 36:31–41
Wilczynska M, Fa M, Ohlsson PI, Ny T (1995) The inhibition mechanism of serpins. Evidence that the mobile reactive center loop is cleaved in the native protease–inhibitor complex. J Biol Chem 270:29652–29655
Xu X, Zhang SS, Barnstable CJ, Tombran-Tink J (2006) Molecular phylogeny of the antiangiogenic and neurotrophic serpin, pigment epithelium derived factor in vertebrates. BMC Genomics 7:248
Ye S, Cech AL, Belmares R, Bergstrom RC, Tong YR, Corey DR, Kanost MR, Goldsmith EJ (2001) The structure of a Michaelis serpin–protease complex. Nat Struct Biol 8:979–983
Yokoi S, Yamashiro K, Kunitake N, Koshino S (1994) Hydrophobic beer proteins and their function in beer foam. J Am Soc Brew Chem 52:123–126
Yoo BC, Aoki K, Xiang Y, Campbell LR, Hull RJ, Xoconostle-Cazares B, Monzer J, Lee JY, Ullman DE, Lucas WJ (2000) Characterization of Cucurbita maxima phloem serpin-1 (CmPS-1)—a developmentally regulated elastase inhibitor. J Biol Chem 275:35122–35128
Zang XX, Maizels RM (2001) Serine proteinase inhibitors from nematodes and the arms race between host and pathogen. Trends Biochem Sci 26:191–197
Zhang Q, Law R, Buckle AM, Cabrita L, McGowan S, Irving JA, Faux NG, Lesk AM, Bottomley SP, Whisstock JC (2007) Serpins in prokaryotes. In: Silverman GA, Lomas DA (eds) Molecular and cellular aspects of the serpinopathies and disorders in serpin activity. World Scientific, New Jersey, pp 131–162
Zhou Q, Snipas S, Orth K, Muzio M, Dixit VM, Salvesen GS (1997) Target protease specificity of the viral serpin CrmA. Analysis of five caspases. J Biol Chem 272:7797–7800
Zhou AW, Carrell RW, Huntington JA (2001) The serpin inhibitory mechanism is critically dependent on the length of the reactive center loop. J Biol Chem 276:27541–27547
Zhou A, Wei Z, Read RJ, Carrell RW (2006) Structural mechanism for the carriage and release of thyroxine in the blood. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:13321–13326
Zhu YF, Wang Y, Gorman MJ, Jiang HB, Kanost MR (2003) Manduca sexta serpin-3 regulates prophenoloxidase activation in response to infection by inhibiting prophenoloxidase-activating proteinases. J Biol Chem 278:46556–46564
Zimmermann P, Hirsch-Hoffmann M, Hennig L, Gruissem W (2004) Genevestigator. Arabidopsis microarray database and analysis toolbox. Plant Physiol 136:2621–2632
Zou Z, Jiang H (2005) Manduca sexta serpin-6 regulates immune serine proteinases PAP-3 and HP8. cDNA cloning, protein expression, inhibition kinetics, and function elucidation. J Biol Chem 280:14341–14348
Acknowledgments
We thank Moreland Gibbs and David Briscoe (Macquarie University) for advice on the phylogenetic analysis; Roberts’ past and current research students Karlie Neilson, Tom Joss and Joon-Woo Ahn for helpful discussions; Robert Fluhr (Weizmann Institute) for insights into the possible roles of plant serpins; and Macquarie University for funding support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Roberts, T.H., Hejgaard, J. Serpins in plants and green algae. Funct Integr Genomics 8, 1–27 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-007-0059-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-007-0059-2