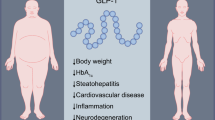
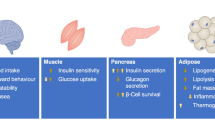
Abstract
Obesity is perhaps an evolutionary consequence of a species reared with intermittent caloric reward. Humans are hardwired to enjoy food, and our bodies voraciously extract and store energy from food as if each meal was the last. As an amalgam of behavioral and metabolic disturbance, obesity is an attractive target for deep brain stimulation (DBS) since neuromodulation may be able to influence both eating behavior and metabolism. The current pandemic proportions of obesity combined with the failures and morbidity of modern treatments remain the impetus behind the application of DBS to this complex disease. We review the rationale and scientific foundations for obesity DBS and explain how this preclinical evidence has helped sculpt the design of the first human pilot study.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anand BK, Brobeck JR (1951) Localization of a “feeding center” in the hypothalamus of the rat. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 77:323–324
Andersson B (1951) The effect and localization of electrical stimulation of certain parts of the brain stem in sheep and goats. Acta Physiol Scand 23:8–23
Benoit SC, Clegg DJ, Seeley RJ et al (2004) Insulin and leptin as adiposity signals. Recent Prog Horm Res 59:267–285
Bernardis LL, Bellinger LL (1993) The lateral hypothalamic area revisited: neuroanatomy, body weight regulation, neuroendocrinology, and metabolism. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 17:141–193
Bray GA, Nielsen SJ, Popkin BM (2004) Consumption of high-fructose corn syrup in beverages may play a role in the epidemic of obesity. Am J Clin Nutr 79:537–543
Champault A, Duwat O, Polliand C et al (2006) Quality of life after laparoscopic gastric banding: prospective study (152 cases) with a follow-up of 2 years. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech 16:131–136
Cho M, Pinto D, Carrodeguas L et al (2006) Frequency and management of internal hernias after laparoscopic antecolic antegastric Roux-en-Y gastric bypass without division of the small bowel mesentery of closure of mesenteric defects: review of 1400 consecutive cases. Surg Obes Relat Dis 2:87–91
Christou NV, Look D, Maclean LD (2006) Weight gain after short- and long-limb gastric bypass in patients followed for longer than 10 years. Ann Surg 244:734–740
Covalin A, Feshali A, Judy J (2005) Deep brain stimulation for obesity control: analyzing stimulation parameters to modulate energy expenditure. Proceedings of the 2nd International IEEE EMBS, Conference on Neural Engineering. Arlington, VA: IEEE EMBS, pp. v–viii.
Cox JE, Powley TL (1981) Intragastric pair feeding fails to prevent VMH obesity or hyperinsulinemia. Am J Physiol 240:E566–E572
Dalcanale L, Oliveira CP, Faintuch J et al (2010) Long-term nutritional outcome after gastric bypass. Obes Surg 20:181–187
Davis JR (1979) Weight loss, slower growth, and lower fasting heat production rates following LH lesions in female rats. Physiol Behav 23:121–127
Davis L (1934) The relation of the hypophysis, hypothalamus, and the autonomic nervous system to carbohydrate metabolism. Ann Surg 100:654–666
De Prisco C, Levine SN (2005) Metabolic bone disease after gastric bypass surgery for obesity. Am J Med Sci 329:57–61
D’Haeninck A, De Leyn P, Swinnen F (2009) Internal herniation after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass: case reports and a review of the literature. Acta Chir Belg 109:385–391
Duffey BG, Pedro RB, Makhlouf A et al (2008) Roux-en-Y gastric bypass is associated with early increased risk factors for development of calcium oxalate nephrolithiasis. J Am Coll Surg 206:1145–1153
Figlewicz DP, MacDonald NA, Sipols AJ (2006) Modulation of food reward by adiposity signals. Physiol Behav 91:473–478
Frohlich A (1901) Ein fall von tumor der hypophysis cerebri ohne akromegalie. Wiener Klinische Rundschau 15(833–836):906–908
Gasteyger C, Suter M, Gaillard RC et al (2008) Nutritional deficiencies after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass for morbid obesity often cannot be prevented by standard multivitamin supplementation. Am J Clin Nutr 87:1128–1133
Goldner WS, O’Dorisio TM, Dillon JS et al (2002) Severe metabolic bone disease as a long-term complications of obesity surgery. Obes Surg 12:685–692
Goldney RD (1978) Craniopharyngioma simulating anorexia nervosa. J Nerv Ment Dis 166:135–138
Gottig S, Daskalakis M, Weiner S et al (2009) Analysis of safety and efficacy of intragastric balloon in extremely obese patients. Obes Surg 19:677–683
Halpern CH, Wolf JA, Bale TL et al (2008) Deep brain stimulation in the treatment of obesity: a review. J Neurosurg 109:625–634
Hamani C, McAndrews MP, Cohn M et al (2008) Memory enhancement induced by hypothalamic/fornix deep brain stimulation. Ann Neurol 63:119–123
Harrell LE, Decastro JM, Balagura S (1975) A critical evaluation of body weight loss following lateral hypothalamic lesions. Physiol Behav 15:133–136
Hefco V, Artenie V (1977) The hypothalamus and protein metabolism in rats. Physiologie 14:39–42
Heron GB, Johnston DA (1976) Hypothalamic tumor presenting as anorexia nervosa. Am J Psychiatry 133:580–582
Hetherington AW, Ranson SW (1940) Hypothalamic lesions and adiposity in the rat. Anat Rec 78:149–172
Iannelli A, Facchiano E, Gugenheim J (2006) Internal hernia after laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass for morbid obesity. Obes Surg 16:1265–1271
Issa H, Al-Saif O, Al-Momen S et al (2010) Bleeding duodenal ulcer after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery: the value of laparoscopic gastroduodenoscopy. Ann Saudi Med 30:67–69
John S, Hoegerl C (2009) Nutritional deficiencies after gastric bypass surgery. J Am Osteopath Assoc 109:601–604
Kamalian N, Keesey RE, ZuRhein GM (1975) Lateral hypothalamic demyelination and cachexia in a case of “malignant” multiple sclerosis. Neurol 25:25
Keesey RE, Corbett SW, Hirvonen MD et al (1984) Heat production and body weight changes following lateral hypothalamic lesions. Physiol Behav 32:309–317
Keesey RE, Powley TL (1973) Self-stimulation and body weight in rats with lateral hypothalamic lesions. Am J Physiol 224:970–978
Kolb B, Dodic R, Whishaw IQ (1979) Effects of serial lateral hypothalamic destruction on feeding behavior, body weight, and neocortical and hippocampal EEG activity. Exp Neurol 66:263–276
Lacan C, De Salles AAF, Gorgulho AA et al (2008) Modulation of food intake following deep brain stimulation of the ventromedial hypothalamus in the vervet monkey: laboratory investigation. J Neurosurg 108:336–342
Lauta AD (1974) Characteristics of the change in lipid metabolism in lesion of the hypothalamus. Fiziol Zh 20:517–522
Leone M, Franzini A, Felisati G et al (2005) Deep brain stimulation and cluster headache. Neurol Sci 26(2 Suppl):s138–s139
Lopez M, Lage R, Saha AK (2008) Hypothalamic fatty acid metabolism mediates the orexigenic action of ghrelin. Cell Metab 7:389–399
Matrana MR, Davis WE (2009) Vitamin deficiency after gastric bypass surgery: a review. South Med J 102:1025–1031
McLaughlin T, Peck M, Holst J et al (2010) Reversible hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia after gastric bypass: a consequence of altered nutrient deficiency. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 95:1851–1855
Morton GJ (2007) Hypothalamic leptin regulation of energy homeostasis and glucose metabolism. J Physiol 583:437–443
Munzberg H (2010) Leptin-signaling pathways and leptin resistance. Forum Nutr 63:123–132
Myers MG, Cowley MA, Munzberg H (2008) Mechanisms of leptin action and leptin resistance. Annu Rev Physiol 70:537–555
Ogden CL, Carroll MD, Curtin LR et al (2006) Prevalence of overweight and obesity in the United States, 1999–2004. JAMA 295:1549–1555
Ohkawara K, Tanaka S, Ishikawa-Takata K et al (2008) Twenty-four hour analysis of elevated energy expenditure after physical activity in a metabolic chamber: models of daily total energy expenditure. Am J Clin Nutr 87:1268–1276
Padoin AV, Galvao NM, Moretto M et al (2009) Obese patients with type 2 diabetes submitted to banded gastric bypass: greater incidence of dumping syndrome. Obes Surg 19:1481–1484
Pandey S, Bhattacharya S (2010) Impact of obesity on gynecology. Womens Health 6:107–117
Parent A (1996) Carpenter’s human neuroanatomy, 9th edn. Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore
Park AM, Storm DW, Fulmer BR et al (2009) A prospective study of risk factors for nephrolithiasis after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery. J Urol 182:2334–2339
Penicaud L, Larue-Achagiotis C, Magnen JL (1983) Endocrine basis for weight gain after fasting or VMH lesion in rats. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 245:246–252
Pinsker MO, Bartsch T, Falk D et al (2008) Failure of deep brain stimulation of the posterior inferior hypothalamus in chronic cluster headache—report of two cases and review of the literature. Zentralbl Neurochir 69:76–79
Quaade F, Vaernet K, Larsson S (1974) Stereotaxic stimulation and electrocoagulation of the lateral hypothalamus in obese humans. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 30:111–117
Reisin E, Wilson JR, Frohlich ED (1987) Hypertension and obesity in rats with ventromedial-hypothalamic lesions and low salt intake. J Hyperten 5:173–178
Sangiao-Alvarellos S, Varela L, Vazquez MJ et al (2010) Influence of ghrelin and GH deficiency on AMPK and hypothalamic lipid metabolism. J Neuroendocrinol 22:543–556
Sani S, Jobe K, Smith A et al (2007) Deep brain stimulation for treatment of obesity in rats. J Neurosurg 107:809–813
Scarpace PJ, Zhang Y (2009) Leptin resistance: a predisposing factor for diet-induced obesity. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 296:493–500
Schallert T, Whishaw IQ, Flannigan KP (1977) Gastric pathology and feeding deficits induced by hypothalamic damage in rats: effects of lesion type, size, and placement. J Comp Physiol Psychol 91:598–610
Schaltenbrand G, Wahren W (1977) Atlas for stereotaxy of the human brain. Thieme, Stuttgart
Schoenen J, Di Clemente L, Vandenheede M et al (2005) Hypothalamic stimulation in chronic cluster headache: a pilot study of efficacy and mode of action. Brain 128:940–947
Schulkin J, Ruger J (1980) Relation between lateral hypothalamic damage and impairment of sodium appetite: evidence of subcortical mass action. Behav Neur Biol 30:90–96
Sears D, Fillmore G, Bui M et al (2008) Evaluation of gastric bypass patients 1 year after surgery: changes in quality of life and obesity-related complications. Obes Surg 18:1522–1525
Shahidzadeh R, Sridhar S (2008) Profound copper deficiency in a patient with gastric bypass. Am J Gastroenterol 103:2660–2662
Shapiro A, Mu W, Roncal C et al (2008) Fructose-induced leptin resistance exacerbates weight gain in response to subsequent high-fat feeding. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 295:1370–1375
Singh GK, Siahpush M, Kogan MD (2010) Rising social inequalities in US childhood obesity, 2003–2007. Ann Epidemiol 20:40–52
Sobocki J, Krolczyk G, Herman RM et al (2005) Influence of vagal nerve stimulation on food intake and body weight—results of experimental studies. J Physiol Pharmacol 56(6 Suppl):27–33
Spiegel EA, Wycis HT, Freed H et al (1953) Thalamotomy and hypothalamotomy for the treatment of psychosis. Res Assoc Nerv Ment Dis 31:379–391
Spires WV, Morris DM (1987) Bleeding duodenal ulcer after gastric bypass procedure for obesity. South Med J 80:1325–1326
Stevenson JAF (1949) Effects of hypothalamic lesions on water and energy metabolism in the rat. Recent Prog Horm Res 4:363–394
Tack J, Arts J, Caenepeel P et al (2009) Pathophysiology, diagnosis, and management of postoperative dumping syndrome. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 6:583–590
Thornton SN, Larue-Achagiotis N, Campfield A (1991) Body weight gain after VMH lesions in adult female rats guanethidine-sympathectomied at birth. Appetite 17:47–53
Torres N, Chabardes S, Benabid AL (2011) Rationale for hypothalamus-deep brain stimulation in food intake disorders and obesity. Adv Tech Stand Neurosurg 36:17–30
van Hout GC, Jakimowicz JJ, Fortuin FA et al (2007) Weight loss and eating behavior following vertical banded gastroplasty. Obes Surg 17:1226–1234
Von Der Porten K, Davis JR (1979) Weight loss following LH lesions independent of changes in motor activity and metabolic rate. Physiol Behav 23:813–819
Weller RA, Weller EB (1982) Anorexia nervosa in a patient with an infiltrating tumor of the hypothalamus. Am J Psychiatry 139:824–825
Zerey M, Sigmon LB, Kuwada TS et al (2008) Bleeding duodenal ulcer after roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery. J Am Osteopath Assoc 108:25–27
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Kurt W. Finnis Ph.D. of Medtronic for his help with Figure 1.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Comments
Hans-Joachim Freund, Hannover, Germany
In my opinion, this proposal is well founded on the knowledge of hypothalamic mechanisms involved in energy administration and considers all the safety aspects and possible risks of the neurosurgical approach. Certainly, other parts of the hypothalamus participate in the regulation of food intake, energy metabolism and reward. None of these nuclei have only one function as we define it from behaviour, but animal experiments and human pathology indicate: this is a sensitive trial.
Johannes Sarnthein, Zurich, Switzerland
After deep brain stimulation (DBS) has proven its effectiveness for patients with movement disorders, several researchers began to search for other patient groups that might benefit equally from the technique. However, DBS is an invasive therapy and, since it targets the brain, DBS is associated with the risk of serious morbidity and mortality. Therefore, safety and efficacy of DBS in the respective patient group have to be addressed with special attention. In the case of obese patients, also ethical questions are often raised.
In their publication, Tomycz et al. describe their rationale for conducting a first human pilot study in patients suffering from severe obesity. The main goal of the study is to monitor the safety of the three patients implanted with DBS stimulators. Metabolic chamber measurements are proposed to overcome the inherent difficulties in testing the efficacy of DBS for obesity.
Given the high prevalence of obesity and its serious implications, there is a general interest in potential treatments. I therefore welcome the description of the rationale for the ongoing study at this time, and I am looking forward to learn about the results of this pioneering study in the near future.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tomycz, N.D., Whiting, D.M. & Oh, M.Y. Deep brain stimulation for obesity—from theoretical foundations to designing the first human pilot study. Neurosurg Rev 35, 37–43 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10143-011-0359-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10143-011-0359-9