Abstract
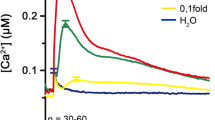
Microbe/pathogen-associated molecular patterns (MAMPs/PAMPs) often induce rises in cytosolic free Ca2+ concentration ([Ca2+]cyt) and protein phosphorylation. Though they are postulated to play pivotal roles in plant innate immunity, their molecular links and the regulatory mechanisms remain largely unknown. To investigate the regulatory mechanisms for MAMP-induced Ca2+ mobilization, we have established a transgenic rice (Oryza sativa) cell line stably expressing apoaequorin, and characterized the interrelationship among MAMP-induced changes in [Ca2+]cyt, production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and protein phosphorylation. Oligosaccharide and sphingolipid MAMPs induced Ca2+ transients mainly due to plasma membrane Ca2+ influx, which were dramatically suppressed by a protein phosphatase inhibitor, calyculin A (CA). Hydrogen peroxide and hypo-osmotic shock triggered similar [Ca2+]cyt elevations, which were not affected by CA. MAMP-induced protein phosphorylation, which is promoted by CA, has been shown to be required for ROS production and MAPK activation, while it negatively regulates MAMPs-induced Ca2+ mobilization and may play a crucial role in temporal regulation of [Ca2+]cyt signature.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ali R, Ma W, Lemtiri-Chlieh F, Tsaltas D, Leng Q, von Bodman S, Berkowitz GA (2007) Death don’t have no mercy and neither does calcium: Arabidopsis CYCLIC NUCLEOTIDE GATED CHANNEL2 and innate immunity. Plant Cell 19:1081–1095
Atlas D, Wiser O, Trus M (2001) The voltage-gated Ca2+ channel is the Ca2+ sensor of fast neurotransmitter release. Cell Mol Neurobiol 21:717–731
Benschop JJ, Mohammed S, O’Flaherty M, Heck AJ, Slijper M, Menke FL (2007) Quantitative phosphoproteomics of early elicitor signaling in Arabidopsis. Mol Cell Proteomics 6:1198–1214
Blume B, Nürnberger T, Nass N, Scheel D (2000) Receptor-mediated increase in cytoplasmic free calcium required for activation of pathogen defense in parsley. Plant Cell 12:1425–1440
Felix G, Regenass M, Spanu P, Boller T (1994) The protein phosphatase inhibitor calyculin A mimics elicitor action in plant cells and induces rapid hyperphosphorylation of specific proteins as revealed by pulse labeling with [33P] phosphate. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:952–956
Findlay I (2004) Physiological modulation of inactivation in L-type Ca2+ channels: one switch. J Physiol 554:275–283
Gerber IB, Laukens K, De Vijlder T, Witters E, Dubery IA (2008) Proteomic profiling of cellular targets of lipopolysaccharide-induced signalling in Nicotiana tabacum BY-2 cells. Biochim Biophys Acta 1784:1750–1762
Hamel LP, Nicole MC, Sritubtim S, Morency MJ, Ellis M, Ehlting J, Beaudoin N, Barbazuk B, Klessig D, Lee J, Martin G, Mundy J, Ohashi Y, Scheel D, Sheen J, Xing T, Zhang S, Seguin A, Ellis BE (2006) Ancient signals: comparative genomics of plant MAPK and MAPKK gene families. Trends Plant Sci 11:192–198
He X, Anderson JC, del Pozo O, Gu YQ, Tang X, Martin GB (2004) Silencing of subfamily I of protein phosphatase 2A catalytic subunits results in activation of plant defense responses and localized cell death. Plant J 38:563–577
Heath MC (2000) Hypersensitive response-related death. Plant Mol Biol 44:321–334
Kadota Y, Goh T, Tomatsu H, Tamauchi R, Higashi K, Muto S, Kuchitsu K (2004) Cryptogein-induced initial events in tobacco BY-2 cells: pharmacological characterization of molecular relationship among cytosolic Ca2+ transients, anion efflux and production of reactive oxygen species. Plant Cell Physiol 45:160–170
Kaku H, Nishizawa Y, Ishii-Minami N, Akimoto-Tomiyama C, Dohmae N, Takio K, Minami E, Shibuya N (2006) Plant cells recognize chitin fragments for defense signaling through a plasma membrane receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:11086–11091
Kikuyama M, Kuchitsu K, Shibuya N (1997) Membrane depolarization induced by N-acetylchitooligosaccharide elicitor in suspension-cultured rice cells. Plan Cell Physiol 38:902–909
Kishi-Kaboshi M, Okada K, Kurimoto L, Murakami S, Umezawa T, Shibuya N, Yamane H, Miyao A, Takatsuji H, Takahashi A, Hirochika H (2010) A rice fungal MAMP-responsive MAPK cascade regulates metabolic flow to antimicrobial metabolite synthesis. Plant J 63:599–612
Knight MR, Campbell AK, Smith SM, Trewavas AJ (1991) Transgenic plant aequorin reports the effects of touch and cold-shock and elicitors on cytoplasmic calcium. Nature 352:524–526
Koga J, Yamauchi T, Shimura M, Ogawa N, Oshima K, Umemura K, Kikuchi M, Ogasawara N (1998) Cerebrosides A and C, sphingolipid elicitors of hypersensitive cell death and phytoalexin accumulation in rice plants. J Biol Chem 273:31985–31991
Kuchitsu K, Kikuyama M, Shibuya N (1993) N-acetylchitooligosaccharides, biotic elicitors for phytoalexin production, induce transient membrane depolarization in suspension-cultured rice cells. Protoplasma 174:79–81
Kuchitsu K, Kosaka H, Shiga T, Shibuya N (1995) EPR evidence for generation of hydroxyl radical triggered by N-acetylchitooligosaccharide elicitor and a protein phosphatase inhibitor in suspension-cultured rice cells. Protoplasma 188:138–142
Kuchitsu K, Yazaki Y, Sakano K, Shibuya N (1997) Transient cytoplasmic pH change and ion fluxes through the plasma membrane in suspension-cultured rice cells triggered by N-acetylchitooligosaccharide elicitor. Plant Cell Physiol 38:1012–1018
Kurusu T, Yagala T, Miyao A, Hirochika H, Kuchitsu K (2005) Identification of a putative voltage-gated Ca2+ channel as a key regulator of elicitor-induced hypersensitive cell death and mitogen-activated protein kinase activation in rice. Plant J 42:798–809
Lecourieux D, Mazars C, Pauly N, Ranjeva R, Pugin A (2002) Analysis and effects of cytosolic free calcium increases in response to elicitors in Nicotiana plumbaginifolia cells. Plant Cell 14:2627–2641
Lecourieux-Ouaked F, Pugin A, Lebrun-Garcia A (2000) Phosphoproteins involved in the signal transduction of cryptogein, an elicitor of defense reactions in tobacco. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 13:821–829
Lieberherr D, Thao NP, Nakashima A, Umemura K, Kawasaki T, Shimamoto K (2005) A sphingolipid elicitor-inducible mitogen-activated protein kinase is regulated by the small GTPase OsRac1 and heterotrimeric G-protein in rice. Plant Physiol 138:1644–1652
Miya A, Albert P, Shinya T, Desaki Y, Ichimura K, Shirasu K, Narusaka Y, Kawakami N, Kaku H, Shibuya N (2007) CERK1, a LysM receptor kinase, is essential for chitin elicitor signaling in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:19613–19618
Navazio L, Moscatiello R, Bellincampi D, Baldan B, Meggio F, Brini M, Bowler C, Mariani P (2002) The role of calcium in oligogalacturonide-activated signalling in soybean cells. Planta 215:596–605
Nishizawa Y, Kawakami A, Hibi T, He DY, Shibuya N, Minami E (1999) Regulation of the chitinase gene expression in suspension-cultured rice cells by N-acetylchitooligosaccharides: differences in the signal transduction pathways leading to the activation of elicitor-responsive genes. Plant Mol Biol 39:907–914
Nühse TS, Peck SC, Hirt H, Boller T (2000) Microbial elicitors induce activation and dual phosphorylation of the Arabidopsis thaliana MAPK6. J Biol Chem 275:7521–7526
Nühse TS, Boller T, Peck SC (2003) A plasma membrane syntaxin is phosphorylated in response to the bacterial elicitor flagellin. J Biol Chem 278:45248–45254
Nühse TS, Stensballe A, Jensen ON, Peck SC (2004) Phosphoproteomics of the Arabidopsis plasma membrane and a new phosphorylation site database. Plant Cell 16:2394–2405
Nürnberger T, Scheel D (2001) Signal transmission in the plant immune response. Trends Plant Sci 6:372–379
Pugin A, Frachisse JM, Tavernier E, Bligny R, Gout E, Douce R, Guern J (1997) Early events induced by the elicitor cryptogein in tobacco cells: involvement of a plasma membrane NADPH oxidase and activation of glycolysis and the pentose phosphate pathway. Plant Cell 9:2077–2091
Ranf S, Wünnenberg P, Lee J, Becker D, Dunkel M, Hedrich R, Scheel D, Dietrich P (2008) Loss of the vacuolar cation channel, AtTPC1, does not impair Ca2+ signals induced by abiotic and biotic stresses. Plant J 53:287–299
Romeis T, Piedras P, Zhang S, Klessig DF, Hirt H, Jones JD (1999) Rapid Avr9- and Cf-9-dependent activation of MAP kinases in tobacco cell cultures and leaves: convergence of resistance gene, elicitor, wound, and salicylate responses. Plant Cell 11:273–287
Su RC, Rudert ML, Hodges TK (1992) Fertile indica and japonica rice plants regenerated from protoplasts isolated from embryogenic haploid suspension cultures. Plant Cell Rep 12:45–49
Takahashi K, Isobe M, Knight MR, Trewavas AJ, Muto S (1997) Hypoosmotic shock induces increases in cytosolic Ca2+ in tobacco suspension-culture cells. Plant Physiol 113:587–594
Tanaka H, Koyano T, Ugaki M, Shiobara F, Onodera H, Ono K, Tagiri A, Nishizawa Y, Shibuya N (2001) Ultra-fast transformation technique for monocotyledons. PCT Application WO 01/06844 A1
Trebak M, Hempel N, Wedel BJ, Smyth JT, Bird GS, Putney JW Jr (2005) Negative regulation of TRPC3 channels by protein kinase C-mediated phosphorylation of serine 712. Mol Pharmacol 67:558–563
Trus M, Wiser O, Goodnough MC, Atlas D (2001) The transmembrane domain of syntaxin 1A negatively regulates voltage-sensitive Ca2+ channels. Neuroscience 104:599–607
Uehara K, Maruyama N, Huang CK, Nakano M (1993) The first application of a chemiluminescence probe, 2-methyl-6-[p-methoxyphenyl]-3,7-dihydroimidazo[1,2-a]pyrazin-3-one (MCLA), for detecting. O2-production, in vitro, from Kupffer cells stimulated by phorbol myristate acetate. FEBS Lett 335:167–170
Yamada A, Shibuya N, Kodama O, Akatsuka T (1993) Induction of phytoalexin formation in suspension-cultured rice cells by N-acetylchitooligosaccharides. Biosci Biotech Biochem 57:405–409
Zhang S, Du H, Klessig DF (1998) Activation of the tobacco SIP kinase by both a cell wall-derived carbohydrate elicitor and purified proteinaceous elicitins from Phytophthora spp. Plant Cell 10:435–450
Zhang XG, Cote GG, Crain RC (2002) Involvement of phosphoinositide turnover in tracheary element differentiation in Zinnia elegans L. cells. Planta 215:312–318
Zipfel C (2009) Early molecular events in PAMP-triggered immunity. Curr Opin Plant Biol 12:414–420
Zipfel C, Robatzek S, Navarro L, Oakeley EJ, Jones JD, Felix G, Boller T (2004) Bacterial disease resistance in Arabidopsis through flagellin perception. Nature 428:764–767
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Prof. Dr. Naoto Shibuya of Meiji University for gift of N-cetylchitooligosaccharides and suggestions, Prof. Dr. Kenzo Nakamura for the pIG121-Hm plasmid, Prof. Dr. Ko Shimamoto for suggestions, and Mr. Jumpei Hamada, Mr. Yohei Iwasaki, and Mr. Hiroshi Nokajima for technical assistance. This work was supported in part by Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research on Innovative Areas (21200067 to T.K.), for Exploratory Research (21658118 to K.K.) and for Young Scientists (B) (21780041 to T.K.), and by a grant from the Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries of Japan (Integrated research project for plants, insects, and animals using genome technology MP-2134 to K.K.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
T. Kurusu, H. Hamada and Y. Sugiyama contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplemental figure S1
RT-PCR analysis of the apoaequorin transformant cell lines. Rice calli (Oryza sativa cultivar Nipponbare) were transformed with apoaequorin gene targetted to the cytoplasm. The gene expression was monitored by RT-PCR analysis. First-strand cDNA was synthesized from total RNA extracted from each cell line and amplified by RT-PCR as described in Materials and methods. Ubiquitin cDNA was used as a control. PCR products were analyzed by agarose gel electrophoresis. (TIFF 814 kb)
Supplemental figure S2
The effect of several inhibitors on the N-acetylchitooligosaccharides-induced [Ca2+]cyt changes. Neomycin (500 μM), U-73122 (1 μM), and LaCl3 (5 mM) were added to the cells 15 min prior to the MAMP treatment (10 μM). Average values and SE of five independent experiments are shown. * P<0.05, ** P<0.01, significant difference as compared with the control according to unpaired Student’s t test. (TIFF 491 kb)
Supplemental figure S3
Ionomycin-induced changes in [Ca2+]cyt in rice (Oryza sativa) cells. Data are representatives of five experiments with similar results. rlu, relative luminescence unit. (TIFF 768 kb)
Supplemental figure S4
The Effect of a CaM antagonist, W7, on N-acetylchitooligosaccharides-induced [Ca2+]cyt changes. W7 (100 μM) were added to the rice (Oryza sativa) cells 15 min prior to the MAMP treatment (10 μM). Data are representatives of three experiments. rlu, relative luminescence unit. (TIFF 868 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kurusu, T., Hamada, H., Sugiyama, Y. et al. Negative feedback regulation of microbe-associated molecular pattern-induced cytosolic Ca2+ transients by protein phosphorylation. J Plant Res 124, 415–424 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10265-010-0388-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10265-010-0388-4