Abstract
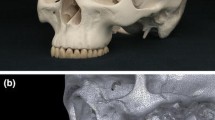
The purpose of this study is to assess the accuracy and reproducibility of cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) measurements of a human dry skull by comparing them to direct digital caliper measurements. Heated gutta-percha was used to mark 13 specific distances on a human skull, and the distances were directly measured using a digital caliper and on CBCT images obtained with Iluma (3M Imtec, OK, USA) and 3D Accuitomo 170 (3D Accuitomo; J Morita Mfg. Corp., Kyoto, Japan) CBCT imaging systems. Iluma images were obtained at 120 kVp and 3.8 mA and reconstructed using voxel sizes of 0.2 and 0.3 mm3. Accuitomo images were obtained at 60 kVp and 2 mA and a voxel size of 0.250 mm3. In addition, 3-D reconstructions were produced from images obtained from both systems. All measurements were made independently by three trained observers and were repeated after an interval of 1 week. Agreement between observers and image type was assessed by calculating Pearson correlation coefficients, with a level of significance set at p < 0.05. Pearson correlation coefficients between readings ranged from 0.995 to 1 for all image types. Correlations among observers were also very high, ranging from 0.992 to 1 for the first reading and from 0.992 to 1 for the second reading for the different image types. All CBCT image measurements were identical and highly correlated with digital caliper measurements. Accuracy of measurements of various distances on a human skull obtained from different CBCT units and image types is comparable to that of digital caliper measurements.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kau CH, Bozic M, English J, Lee R, Bussa H, Ellis RK: Cone-beam computed tomography of the maxillofacial region—an update. Int J Med Robot 5(4):366–380, 2009
Mischkowski RA, Pulsfort R, Ritter L, Neugebauer J, Brochhagen HG, Keeve E, Zöller JE: Geometric accuracy of a newly developed cone-beam device for maxillofacial imaging. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 104(4):551–559, 2007
Al-Rawi B, Hassan B, Vandenberge B, Jacobs R: Accuracy assessment of three-dimensional surface reconstructions of teeth from cone beam computed tomography scans. J Oral Rehabil 37(5):352–358, 2010
Scarfe WC, Farman AG: What is cone-beam CT and how does it work? Dent Clin North Am 52(4):707–730, 2008
White SC: Cone-beam imaging in dentistry. Health Phys 95(5):628–637, 2008
Patel S: New dimensions in endodontic imaging: Part 2. Cone beam computed tomography. Int Endod J 42(6):463–475, 2009
Watanabe H, Honda E, Kurabayashi T: Modulation transfer function evaluation of cone beam computed tomography for dental use with the oversampling method. Dentomaxillofac Radiol 39(1):28–32, 2010
Scarfe WC, Farman AG, Sukovic P: Clinical applications of cone-beam computed tomography in dental practice. J Can Dent Assoc 72(1):75–80, 2006
Ludlow JB, Ludlow LED, Brooks SL, Howerton WB: Dosimetry of 3 CBCT devices for oral and maxillofacial radiology: CB Mercuray, NewTom 3G and i-CAT. Dentomaxillofac Radiol 35(4):219–226, 2006
Hirsch E, Wolf U, Heinicke F, Silva MA: Dosimetry of the cone beam computed tomography Veraviewepocs 3D compared with the 3D Accuitomo in different field of views. Dentomaxillofac Radiol 37(5):268–273, 2008
Ritter L, Mischkowski RA, Neugebauer J, Dreiseidler T, Scheer M, Keeve E, Zöller JE: The influence of body mass index, age, implants, and dental restorations on image quality of cone beam computed tomography. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 108(3):e108–e116, 2009
Draenert FG, Coppenrath E, Herzog P, Müller S, Mueller-Lisse UG: Beam hardening artefacts occur in dental implant scans with the NewTom cone beam CT but not with the dental 4-row multidetector CT. Dentomaxillofac Radiol 36(4):198–203, 2007
Hsieh J, Molthen RC, Dawson CA, Johnson RH: An iterative approach to the beam hardening correction in cone beam CT. Med Phys 27(1):23–29, 2000
Carrafiello G, Dizonno M, Colli V, et al: Comparative study of jaws with multislice computed tomography and cone-beam computed tomography. Radiol Med 115(4):600–611, 2010
Scarfe WC, Farman AG: Cone beam computed tomography. In: White SC, Pharoah MJ Eds. Oral Radiology. Principles and Interpretation, 6th edition. Elsevier, St. Louis, 2009, pp 225–243
Stratemann SA, Huang JC, Maki K, Miller AJ, Hatcher DC: Comparison of cone beam computed tomography imaging with physical measures. Dentomaxillofac Radiol 37(2):80–93, 2008
Damstra J, Fourie Z, Huddleston Slater JJ, Ren Y: Accuracy of linear measurements from cone-beam computed tomography-derived surface models of different voxel sizes. Am J Orthod Dentofac Orthop 137(1):16.e1–16.e6, 2010
Lascala CA, Panella J, Marques MM: Analysis of the accuracy of linear measurements obtained by cone beam computed tomography (CBCT-NewTom). Dentomaxillofac Radiol 33(5):291–294, 2004
Moshiri M, Scarfe WC, Hilgers ML, Scheetz JP, Silveira AM, Farman AG: Accuracy of linear measurements from imaging plate and lateral cephalometric images derived from cone-beam computed tomography. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop 132(4):550–560, 2007
van Vlijmen OJC, Maal TJJ, Berge SJ, Bronkhorst EM, Katsaros C, Kuijpers-Jagtman AM: A comparison between two-dimensional and three-dimensional cephalometry on frontal radiographs and on cone beam computed tomography scans of human skulls. Eur J Oral Sci 117(3):300–305, 2009
Chien PC, Parks ET, Eraso F, Hartsfield Jr, JK, Roberts WE, Ofner S: Comparison of reliability in anatomical landmark identification using two-dimensional digital cephalometrics and three-dimensional cone beam computed tomography in vivo. Dentomaxillofac Radiol 38(5):262–273, 2009
Hilgers ML, Scarfe WC, Scheetz JP, Farman AG: Accuracy of linear temporomandibular joint measurements with cone beam computed tomography and digital cephalometric radiography. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop 128(6):803–811, 2005
Ludlow JB, Laster WS, See M, Bailey LJ, Hershey HG: Accuracy of measurements of mandibular anatomy in cone beam computed tomography images. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 103(4):534–542, 2007
Berco M, Rigali PH, Miner M, DeLuca S, Anderson NK, Will LA: Accuracy and reliability of linear cephalometric measurements from cone-beam computed tomography scans of a dry human skull. Am J Orthod Dentofacial Orthop 136(1):171–179, 2009
Hassan B, van der Stelt P, Sanderink G: Accuracy of three-dimensional measurements obtained from cone beam computed tomography surface-rendered images for cephalometric analysis: influence of patient scanning position. Eur J Orthod 31(2):129–134, 2009
Loubele M, Van Assche N, Carpentier K, Maes F, Jacobs R, Van Steenberghe D, Suetens P: Comparative localized linear accuracy of small-field cone-beam CT and multislice CT for alveolar bone measurements. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 105(4):512–518, 2008
Suomalainen A, Vehmas T, Kortesniemi M, Robinson S, Peltola J: Accuracy of linear measurements using dental cone beam and conventional multislice computed tomography. Dentomaxillofac Radiol 37(1):10–17, 2008
Kobayashi K, Shimoda S, Nakagawa Y, Yamamoto A: Accuracy in measurement of distance using limited cone-beam computerized tomography. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants 19(2):228–231, 2004
Periago DR, Scarfe WC, Moshiri M, Scheetz JP, Silveira AM, Farman AG: Linear accuracy and reliability of cone-beam CT derived 3-dimensional images constructed using an orthodontic volumetric rendering program. Angle Orthod 78(3):387–395, 2008
Brown AA, Scarfe WC, Scheetz JP, Silveira AM, Farman AG: Linear accuracy of cone-beam CT derived 3D images. Angle Orthod 79(1):150–157, 2009
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kamburoğlu, K., Kolsuz, E., Kurt, H. et al. Accuracy of CBCT Measurements of a Human Skull. J Digit Imaging 24, 787–793 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10278-010-9339-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10278-010-9339-9