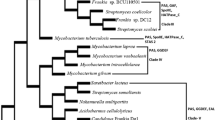
Abstract
The Actinobacteria constitute one of the main phyla of Bacteria. Presently, no morphological and very few molecular characteristics are known which can distinguish species of this highly diverse group. In this work, we have analyzed the genomes of four actinobacteria (viz. Mycobacterium leprae TN, Leifsonia xyli subsp. xyli str. CTCB07, Bifidobacterium longum NCC2705 and Thermobifida fusca YX) to search for proteins that are unique to Actinobacteria. Our analyses have identified 233 actinobacteria-specific proteins, homologues of which are generally not present in any other bacteria. These proteins can be grouped as follows: (i) 29 proteins uniquely present in most sequenced actinobacterial genomes; (ii) 6 proteins present in almost all actinobacteria except Bifidobacterium longum and another 37 proteins absent in B. longum and few other species; (iii) 11 proteins which are mainly present in Corynebacterium, Mycobacterium and Nocardia (CMN) subgroup as well as Streptomyces, T. fusca and Frankia sp., but they are not found in Bifidobacterium and Micrococcineae; (iv) 8 proteins that are specific for T. fusca and Streptomyces species, plus 2 proteins also present in the Frankia species; (v) 13 proteins that are specific for the Corynebacterineae or the CMN group; (vi) 14 proteins only found in Mycobacterium and Nocardia; (vii) 24 proteins unique to different Mycobacterium species; (viii) 8 proteins specific to the Micrococcineae; (ix) 85 proteins which are distributed sporadically in actinobacterial species. Additionally, many examples of lateral gene transfer from Actinobacteria to Magnetospirillum magnetotacticum have also been identified. The identified proteins provide novel molecular means for defining and circumscribing the Actinobacteria phylum and a number of subgroups within it. The distribution of these proteins also provides useful information regarding interrelationships among the actinobacterial subgroups. Most of these proteins are of unknown function and studies aimed at understanding their cellular functions should reveal common biochemical and physiological characteristics unique to either all actinobacteria or particular subgroups of them. The identified proteins also provide potential targets for development of drugs that are specific for actinobacteria.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altschul S.F., Madden T.L., Schaffer A.A., Zhang J.H., Zhang Z., Miller W., Lipman D.J. 1997. Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res. 25:3389–3402
Balows A., Trüper H.G., Dworkin M., Harder W., Schleifer K.H. 1992. The Prokaryotes. Springer-Verlag, New York
Bazylinski D.A., Frankel R.B. 2004. Magnetosome formation in prokaryotes. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2:217–230
Belanger A.E., Besra G.S., Ford M.E., Mikusova K., Belisle J.T., Brennan P.J., Inamine J.M. 1996. The embAB genes of Mycobacterium avium encode an arabinosyl transferase involved in cell wall arabinan biosynthesis that is the target for the antimycobacterial drug ethambutol. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 93:11919–11924
Benson D.R., Silvester W.B., (1993). Biology of Frankia Strains, Actinomycete Symbionts of Actinorhizal Plants. Microbiol Rev. 57:293–319
Bentley S.D., Brosch R., Gordon S.V., Hopwood D.A., Cole S.T., (2004). Genomics of Actinobacteria, the high G+C Gram-positive bacteria. In: Fraser C.M., Read T.D., Nelson K.E., (eds) Microbial Genomes. Humana Press, Totowa, NJ, pp. 333–359
Bentley S.D., Chater K.F., Cerdeno-Tarraga A.M., Challis G.L., Thomson N.R., James K.D., Harris D.E., Quail M.A., Kieser H., Harper D., Bateman A., Brown S., Chandra G., Chen C.W., Collins M., Cronin A., Fraser A., Goble A., Hidalgo J., Hornsby T., Howarth S., Huang C.H., Kieser T., Larke L., Murphy L., Oliver K., O’Neil S., Rabbinowitsch E., Rajandream M.A., Rutherford K., Rutter S., Seeger K., Saunders D., Sharp S., Squares R., Squares S., Taylor K., Warren T., Wietzorrek A., Woodward J., Barrell B.G., Parkhill J., Hopwood D.A., (2002). Complete genome sequence of the model actinomycete Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). Nature 417:141–147
Bentley S.D., Maiwald M., Murphy L.D., Pallen M.J., Yeats C.A., Dover L.G., Norbertczak H.T., Besra G.S., Quail M.A., Harris D.E., von Herbay A., Goble A., Rutter S., Squares R., Squares S., Barrell B.G., Parkhill J., Relman D.A., (2003). Sequencing and analysis of the genome of the Whipple’s disease bacterium Tropheryma whipplei. Lancet 361:637–644
Bentley S.D., Parkhill J., (2004). Comparative genomic structure of prokaryotes. Annu. Rev. Genet. 38:771–792
Berg S., Starbuck J., Torrelles J.B., Vissa V.D., Crick D.C., Chatterjee D., Brennan P.J., (2005). Roles of conserved proline and glycosyltransferase motifs of embC in biosynthesis of lipoarabinomannan. J. Biol. Chem. 280:5651–5663
Boone D.R. 2001. Bergey’s Manual of systematic bacteriology, Springer
Brennan P.J. (2003). Structure, function, and biogenesis of the cell wall of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Tuberculosis 83:91–97
Brennan P.J., Nikaido H., (1995). The envelope of mycobacteria. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 64:29–63
Bruggemann H., Henne A., Hoster F., Liesegang H., Wiezer A., Strittmatter A., Hujer S., Durre P., Gottschalk G., (2004). The complete genome sequence of Propionibacterium acnes, a commensal of human skin. Science 305:671–673
Cerdeno-Tarraga A.M., Efstratiou A., Dover L.G., Holden M.T.G., Pallen M., Bentley S.D., Besra G.S., Churcher C., James K.D., De Zoysa A., Chillingworth T., Cronin A., Dowd L., Feltwell T., Hamlin N., Holroyd S., Jagels K., Moule S., Quail M.A., Rabbinowitsch E., Rutherford K.M., Thomson N.R., Unwin L., Whitehead S., Barrell B.G., Parkhill J., (2003). The complete genome sequence and analysis of Corynebacterium diphtheriae NCTC13129. Nucleic Acids Res. 31:6516–6523
Coenye T., Gevers D., de Peer Y.V., Vandamme P., Swings J., (2005). Towards a prokaryotic genomic taxonomy. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 29:147–167
Cole S.T. (2002). Comparative and functional genomics of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex. Microbiology 148:2919–2928
Cole S.T., Brosch R., Parkhill J., Garnier T., Churcher C., Harris D., Gordon S.V., Eiglmeier K., Gas S., Barry C.E., Tekaia F., Badcock K., Basham D., Brown D., Chillingworth T., Conner R., Davies R., Devlin K., Feltwell T., Gentles S., Hamlin N., Holroyd S., Hornsby T., Jagels K., Krogh A., McLean J., Moule S., Murphy L., Oliver K., Osborne J., Quail M.A., Rajandream M.A., Rogers J., Rutter S., Seeger K., Skelton J., Squares R., Squares S., Sulston J.E., Taylor K., Whitehead S., Barrell B.G., (1998). Deciphering the biology of Mycobacterium tuberculosis from the complete genome sequence (vol 393, pg 537, 1998). Nature 396:190–198
Cole S.T., Eiglmeier K., Parkhill J., James K.D., Thomson N.R., Wheeler P.R., Honore N., Garnier T., Churcher C., Harris D., Mungall K., Basham D., Brown D., Chillingworth T., Connor R., Davies R.M., Devlin K., Duthoy S., Feltwell T., Fraser A., Hamlin N., Holroyd S., Hornsby T., Jagels K., Lacroix C., Maclean J., Moule S., Murphy L., Oliver K., Quail M.A., Rajandream M.A., Rutherford K.M., Rutter S., Seeger K., Simon S., Simmonds M., Skelton J., Squares R., Squares S., Stevens K., Taylor K., Whitehead S., Woodward J.R., Barrell B.G., (2001). Massive gene decay in the leprosy bacillus. Nature 409:1007–1011
Collier L., Balows A., Sussman M., (1998). Topley &Wilson’s Microbiology and Microbial Infections, Vol. 2, Systematic Bacteriology. Arnold, London
Daffe M., Draper P., (1998). The envelope layers of mycobacteria with reference to their pathogenicity. Adv. Microb. Physiol. 39:131–203
Daubin V., Ochman H., (2004). Bacterial genomes as new gene homes: the genealogy of ORFans in E. coli. Genome Res. 14:1036–1042
Domenech P., Barry C.E., Cole S.T., (2001). Mycobacterium tuberculosis in the post-genomic age. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 4:28–34
Embley T.M., Stackebrandt E., (1994). The molecular phylogeny and systematics of the actinomycetes. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 48:257–289
Fleischmann R.D., Alland D., Eisen J.A., Carpenter L., White O., Peterson J., Deboy R., Dodson R., Gwinn M., Haft D., Hickey E., Kolonay J.F., Nelson W.C., Umayam L.A., Ermolaeva M., Salzberg S.L., Delcher A., Utterback T., Weidman J., Khouri H., Gill J., Mikula A., Bishai W., Jacobs W.R., Venter J.C., Fraser C.M., (2002). Whole-genome comparison of Mycobacterium tuberculosis clinical and laboratory strains. J. Bacteriol. 184:5479–5490
Fraser C.M., Read T.D., Nelson K.E. (eds). (2004). Microbial Genomes. Humana Press, Totowa, NJ
Gao B., Gupta R.S., (2005). Conserved indels in protein sequences that are characteristic of the phylum Actinobacteria. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 151:2647–2657
Garnier T., Eiglmeier K., Camus J.C., Medina N., Mansoor H., Pryor M., Duthoy S., Grondin S., Lacroix C., Monsempe C., Simon S., Harris B., Atkin R., Doggett J., Mayes R., Keating L., Wheeler P.R., Parkhill J., Barrell B.G., Cole S.T., Gordon S.V., Hewinson R.G., (2003). The complete genome sequence of Mycobacterium bovis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 100:7877–7882
Garrity G.M., Holt J.G., (2001). The road map to the manual. In: Boone D.R., Castenholz R.W. (eds) Bergey’s Manual of Systematic Bacteriology. Springer-Verlag, Berlin, pp. 119–166
Gogarten J.P., Townsend J.P., (2005). Horizontal gene transfer, genome innovation and evolution. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 3:679–687
Goodfellow M., Williams S.T., (1983). Ecology of Actinomycetes. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 37:189–216
Gordon S.V., Eiglmeier K., Garnier T., Brosch R., Parkhill J., Barrell B., Cole S.T., Hewinson R.G., (2001). Genomics of Mycobacterium bovis. Tuberculosis 81:157–163
Griffiths E., Gupta R.S., (2004). Signature sequences in diverse proteins provide evidence for the late divergence of the order Aquificales. Intl Microbiol. 7:41–52
Griffiths E., Petrich A., Gupta R.S., (2005). Conserved indels in essential proteins that are distinctive characteristics of Chlamydiales and provide novel means for their identification. Microbiology 151:2647–2657
Griffiths E., Ventresca M.S., Gupta R.S. 2006. BLAST screening of chlamydial genomes to identify signature proteins that are unique for the Chlamydiales, Chlamydiaceae, Chlamydophila and Chlamydia groups of species. BMC Genomics 7:14
Gupta R.S. (1998). Protein phylogenies and signature sequences: a reappraisal of evolutionary relationships among archaebacteria, eubacteria, and eukaryotes. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 62:1435–1491
Gupta R.S. (2000). The phylogeny of Proteobacteria: relationships to other eubacterial phyla and eukaryotes. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 24:367–402
Gupta R.S. (2004). The Phylogeny and Signature Sequences characteristics of Fibrobacters, Chlorobi and Bacteroidetes. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 30:123–143
Gupta R.S. (2005). Protein signatures distinctive of Alpha proteobacteria and its subgroups and a model for Alpha proteobacterial evolution. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 31:135
Ikeda H., Ishikawa J., Hanamoto A., Shinose M., Kikuchi H., Shiba T., Sakaki Y., Hattori M., Omura S., (2003). Complete genome sequence and comparative analysis of the industrial microorganism Streptomyces avermitilis. Nat. Biotechnol. 21:526–531
Ishikawa J., Yamashita A., Mikami Y., Hoshino Y., Kurita H., Hotta K., Shiba T., Hattori M., (2004). The complete genomic sequence of Nocardia farcinica IFM 10152. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 101:14925–14930
Kainth P., Gupta R.S., (2005). Signature proteins that are distinctive of alpha proteobacteria. BMC Genomics 6:94
Kalinowski J., Bathe B., Bartels D., Bischoff N., Bott M., Burkovski A., Dusch N., Eggeling L., Eikmanns B.J., Gaigalat L., Goesmann A., Hartmann M., Huthmacher K., Kramer R., Linke B., McHardy A.C., Meyer F., Mockel B., Pfefferle W., Puhler A., Rey D.A., Ruckert C., Rupp O., Sahm H., Wendisch V.F., Wiegrabe I., Tauch A., (2003). The complete Corynebacterium glutamicum ATCC 13032 genome sequence and its impact on the production of L-aspartate-derived amino acids and vitamins. J. Biotechnol. 104:5–25
Karlin S., Altschul S.F., (1990). Methods for assessing the statistical significance of molecular sequence features by using general scoring schemes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 87:2264–2268
Karlin S., Campbell A.M., Mrázek J. (1998). Comparative DNA analysis across diverse genomes. Annu. Rev. Genet. 32:185–225
Lechevalier H.A., Lechevalier M.P., (1967). Biology of Actinomycetes. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 21:71–100
Lerat E., Daubin V., Moran N.A., (2003). From gene trees to organismal phylogeny in prokaryotes: the case of the gamma-proteobacteria. PLoS. Biol. 1:E19
Ludwig W., Klenk H.-P., (2001). Overview: A phylogenetic backbone and taxonomic framework for prokaryotic systamatics. In: Boone D.R., Castenholz R.W., (eds) Bergey’s Manual of Systematic Bacteriology. Springer-Verlag, Berlin, pp. 49–65
Mazumder R., Natale D.A., Murthy S., Thiagarajan R., Wu C.H., (2005). Computational identification of strain-, species- and genus-specific proteins. BMC Bioinform. 6:279
McAlpine J.B., Bachmann B.O., Piraee M., Tremblay S., Alarco A.M., Zazopoulos E., Farnet C.M., (2005). Microbial Genomics as a guide to drug discovery and structural elucidation: ECO-02301, a novel antifungal agent, as an example. J. Nat. Prod. 68:493–496
Monteiro-Vitorello C.B., Camargo L.E.A., Van Sluys M.A., Kitajima J.P., Truffi D., do Amaral A.M., Harakava R., de Oliveira J.C.F., Wood D., de Oliveira M.C., Miyaki C., Takita M.A., da Silva A.C.R., Furlan L.R., Carraro D.M., Camarotte G., Almeida N.F., Carrer H., Coutinho L.L., El Dorry H.A., Ferro M.I.T., Gagliardi P.R., Giglioti E., Goldman M.H.S., Goldman G.H., Kimura E.T., Ferro E.S., Kuramae E.E., Lemos E.G.M., Lemos M.V.F., Mauro S.M.Z., Machado M.A., Marino C.L., Menck C.F., Nunes L.R., Oliveira R.C., Pereira G.G., Siqueira W., de Souza A.A., Tsai S.M., Zanca A.S., Simpson A.J.G., Brumbley S.M., Setubal J.C., (2004). The genome sequence of the gram-positive sugarcane pathogen Leifsonia xyli subsp xyli. Mol. Plant Microb. Interact. 17:827–836
Moran N.A., Wernegreen J.J., (2000). Lifestyle evolution in symbiotic bacteria: insights from genomics. Trends Ecol. Evol. 15:321–326
Morse R., O’Hanlon K., Collins M.D., (2002). Phylogenetic, amino acid content and indel analyses of the beta subunit of DNA-dependent RNA polymerase of gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 52:1477–1484
Nishio Y., Nakamura Y., Kawarabayasi Y., Usuda Y., Kimura E., Sugimoto S., Matsui K., Yamagishi A., Kikuchi H., Ikeo K., Gojobori T., (2003). Comparative complete genome sequence analysis of the amino acid replacements responsible for the thermostability of Corynebacterium efficiens. Genome Res. 13:1572–1579
Pedulla M.L., Ford M.E., Houtz J.M., Karthikeyan T., Wadsworth C., Lewis J.A., Jacobs-Sera D., Falbo J., Gross J., Pannunzio N.R., Brucker W., Kumar V., Kandasamy J., Keenan L., Bardarov S., Kriakov J., Lawrence J.G., Jacobs W.R., Hendrix R.W., Hatfull G.F., (2003). Origins of highly mosaic mycobacteriophage genomes. Cell 113:171–182
Puech V., Chami M., Lemassu A., Laneelle M.A., Schiffler B., Gounon P., Bayan N., Benz R., Daffe M., (2001). Structure of the cell envelope of corynebacteria: importance of the non-covalently bound lipids in the formation of the cell wall permeability barrier and fracture plane. Microbiology 147:1365–1382
Raoult D., Ogata H., Audic S., Robert C., Suhre K., Drancourt M., Claverie J.M., (2003). Tropheryma whipplei twist: a human pathogenic Actinobacteria with a reduced genome. Genome Res. 13:1800–1809
Ravel J., DiRuggiero J., Robb F.T., Hill R.T., (2000). Cloning and sequence analysis of the mercury resistance operon of Streptomyces sp. strain CHR28 reveals a novel putative second regulatory gene. J. Bacteriol. 182:2345–2349
Roller C., Ludwig W., Schleifer K.H. (1992). Gram-positive bacteria with a high DNA G+C content are characterized by a common insertion within their 23S rRNA genes. J. Gen. Microbiol. 138:167–175
Rother D., Mattes R., Altenbuchner J., (1999). Purification and characterization of MerR, the regulator of the broad-spectrum mercury resistance genes in Streptomyces lividans 1326. Mol. Gen. Genet. 262:154–162
Schell M.A., Karmirantzou M., Snel B., Vilanova D., Berger B., Pessi G., Zwahlen M.C., Desiere F., Bork P., Delley M., Pridmore R.D., Arigoni F., (2002). The genome sequence of Bifidobacterium longum reflects its adaptation to the human gastrointestinal tract. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 99:14422–14427
Schorey J.S., Li Q.L., Mccourt D.W., Bongmastek M., Clarkcurtiss J.E., Ratliff T.L., Brown E.J., (1995). A mycobacterium-leprae gene encoding a fibronectin-binding protein is used for efficient invasion of epithelial-cells and schwann-cells. Infect. Immun. 63:2652–2657
Soliveri J.A., Gomez J., Bishai W.R., Chater K.F., (2000). Multiple paralogous genes related to the Streptomyces coelicolor developmental regulatory gene whiB are present in Streptomyces and other actinomycetes. Microbiol.-Uk 146:333–343
Stackebrandt E., Rainey F.A., WardRainey N.L., (1997). Proposal for a new hierarchic classification system, Actinobacteria classis nov. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 47:479–491
Stackebrandt E., Schumann P., (2000). Introduction to the taxonomy of actinobacteria. In: Dworkin M., et al. (eds) The Prokaryotes: An Evolving Electronic Resource for the Microbiological Community. Springer-Verlag, New York, http://www.141.150.157.117:8080/prokPUB/chaprender/jsp/showchap.jsp?chapnum=291
Sutcliffe I.C. (1998). Cell envelope composition and organisation in the genus Rhodococcus. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 74: 49–58
Sutcliffe I.C., Harrington D.J., (2004). Lipoproteins of Mycobacterium tuberculosis: an abundant and functionally diverse class of cell envelope components. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 28:645–659
Sutcliffe I.C., Russell R.R., (1995). Lipoproteins of gram-positive bacteria. J. Bacteriol. 177:1123–1128
Tauch A., Kaiser O., Hain T., Goesmann A., Weisshaar B., Albersmeier A., Bekel T., Bischoff N., Brune I., Chakraborty T., Kalinowski J., Meyer F., Rupp O., Schneiker S., Viehoever P., Puhler A., (2005). Complete genome sequence and analysis of the multiresistant nosocomial pathogen Corynebacterium jeikeium K411, a lipid-requiring bacterium of the human skin flora. J. Bacteriol. 187:4671–4682
Ueda K., Ohno M., Yamamoto K., Nara H., Mori Y., Shimada M., Hayashi M., Oida H., Terashima Y., Nagata M., Beppu T., (2001). Distribution and diversity of symbiotic thermophiles, Symbiobacterium thermophilum and related bacteria, in natural environments. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 67:3779–3784
Ueda K., Yamashita A., Ishikawa J., Shimada M., Watsuji T., Morimura K., Ikeda H., Hattori M., Beppu T., (2004). Genome sequence of Symbiobacterium thermophilum, an uncultivable bacterium that depends on microbial commensalism. Nucleic Acids Res. 32:4937–4944
Yang Z. (2005). The power of phylogenetic comparison in revealing protein function. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 102:3179–3180
Zazopoulos E., Huang K.X., Staffa A., Liu W., Bachmann B.O., Nonaka K., Ahlert J., Thorson J.S., Shen B., Farnet C.M., (2003). A genomics-guided approach for discovering and expressing cryptic metabolic pathways. Nat. Biotechnol. 21:187–190
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by research grants from the National Science and Engineering Research Council of Canada and the Canadian Institute of Health Research. We thank the editor and two anonymous reviewers for various helpful suggestions toward improvement of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, B., Paramanathan, R. & Gupta, R. Signature proteins that are distinctive characteristics of Actinobacteria and their subgroups. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 90, 69–91 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-006-9061-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-006-9061-2