Abstract
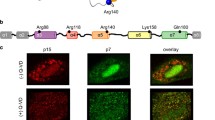
Bid, a member of the pro-apoptotic Bcl-2 protein family, is activated through caspase-8-mediated cleavage into a truncated form (p15 tBid) during TNF-α(tumor necrosis factor α)-induced apoptosis. Activated tBid can induce Bax oligomerization and translocation to mitochondria, triggering the release of cytochrome c, caspase-3 activation and cell apoptosis. However, it is debatable that whether Bid and tBid can interact directly with Bax in living cells. In this study, we used confocal fluorescence microscope, combined with both FRET (fluorescence resonance energy transfer) and acceptor photobleaching techniques, to study the dynamic interaction between Bid and Bax during TNF-α-induced apoptosis in single living cell. In ASTC-a-1 cells, full length Bid induced Bax translocation to mitochondria by directly interacting with Bax transiently in response to TNF-α treatment before cell shrinkage. Next, we demonstrated that, in both ASTC-a-1 and HeLa cells, Bid was not cleaved before cell shrinkage even under the condition that caspase-8 had been activated, but in MCF-7 cells Bid was cleaved. In addition, in ASTC-a-1 cells, caspase-3 activation was a biphasic process and Bid was cleaved after the second activation of caspase-3. In summary, these findings indicate that, FL-Bid (full length-Bid) directly regulated the activation of Bax during TNF-α-induced apoptosis in ASTC-a-1 cells and that the cleavage of Bid occurred in advanced apoptosis.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tracey KJ, Cerami A (1993) Tumor necrosis factor, other cytokines and disease. Annu Rev Cell Biol 9:317–343
Stanger BZ, Leder P, Lee TH, Kim E, Seed B (1995) RIP: a novel protein containing a death domain that interacts with Fas/APO-l (CD95) in yeast and causes cell death. Cell 81:513–523
Medema JP, Scaffidi C, Kischkel FC et al (1997) FLICE is activated by association with CD95 death-inducing signaling complex (DISC). EMBO J 16:2794–2804
Li H, Zhou H, Xu C-j Yuan J (1998) Cleavage of Bid by caspase 8 mediates the mitochondrial damage in the Fas pathway of apoptosis. Cell 94:491–501
Luo X, Budihardjo I, Zou H, Slaughter C, Wang X (1998) Bid, a Bcl2 interacting protein, mediates cytochrome c release from mitochondria in response to activation of cell surface death receptors. Cell 94:481–490
Gross A, Yin X-M, Wang K et al (1999) Caspase cleaved BID targets mitochondria and is required for cytochrome c release, while BCL-XL prevents this release but not tumor necrosis factor-R1/Fas Death. J Biol Chem 274:1156–1163
Roucou X, Rostovtseva T, Montessuit S, Martinou J-C, Antonsson B (2002) Bid induces cytochrome c-impermeable Bax channels in liposomes. Biochem J 363:547–552
Zheng TS, Hunot S, Kuida K, Flavell RA (1999) Caspase knockouts: matters of life and death. Cell Death Differ 6:1043–1053
Yin X-M (2006) Bid, a BH3-only multi-functional molecule, is at the cross road of life and death. Gene 369:7–19
Eskes R, Desagher S, Antonsson B, Martinou J-C (2000) Bid induces the oligomerization and insertion of Bax into the outer mitochondrial membrane. Mol Cell Biol 20:929–935
Wei MC, Lindsten T, Mootha VK et al (2000) tBID, a membrane-targeted death ligand, oligomerizes BAK to release cytochrome c. Genes Dev 14:2060–2071
Desagher S, Osen-Sand A, Nichols A et al (1999) Bid-induced conformational change of Bax is responsible for mitochondrial Cytochrome c release during apoptosis. J Cell Biol 144:891–901
Kim T-H, Zhao Y, Barber MJ, Kuharsky DK, Yin X-M (2000) Bid-induced cytochrome c release is mediated by a pathway independent of mitochondrial permeability transition pore and Bax. J Biol Chem 275:39474–39481
Shimizu S, Tsujimoto Y (2000) Proapoptotic BH3-only Bcl-2 family members induce cytochrome c release, but not mitochondrial membrane potential loss, and do not directly modulate voltage-dependent anion channel activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 97:577–582
Grinberg M, Sarig R, Zaltsman Y et al (2002) tBID homooligomerizes in the mitochondrial membrane to induce apoptosis. J Biol Chem 277:12237–12245
Walensky LD, Pitter K, Morash J et al (2006) A stapled BID BH3 helix directly binds and activates BAX. Molecular Cell 24:199–210
Terrones O, Antonsson B, Yamaguchi H et al (2004) Lipidic pore formation by the concerted action of proapoptotic BAX and tBID. J Biol Chem 279:30081–30091
Nechushtan A, Smith CL, Lamensdorf I, Yoon S-H, Youle RJ (2001) Bax and Bak coalesce into novel mitochondria-associated clusters during apoptosis. J Cell Biol 153:1265–1276
Ward MW, Rehm M, Duessmann H, Kacmar S, Concannon CG, Prehn JHM (2006) Real time single cell analysis of Bid cleavage and Bid translocation during caspase-dependent and neuronal caspase-independent apoptosis. J Biol Chem 281:5837–5844
Miyawaki A (2003) Visualization of the spatial and temporal dynamics of intracellular signaling. Dev Cell 4:295–305
Zhang J, Campbell RE, Ting AY, Tsien RY (2002) Creating new fluorescent probes for cell biology. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 3:906–918
Wu Y-X, Xing D, Chen WR (2006) Single cell FRET imaging for determination of pathway of tumor cell apoptosis induced by photofrin-PDT. Cell Cycle 5:729–734
Onuki R, Nagasaki A, Kawasaki H, Baba T, Uyeda TQP, Taira K (2002) Confirmation by FRET in individual living cells of the absence of significant amyloid β-mediated caspase 8 activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 99:14716–14721
Valentijn AJ, Metcalfe AD, Kott J, Streuli CH, Gilmore AP (2003) Spatial and temporal changes in Bax subcellular localization during anoikis. J Cell Biol 162:599–612
Tsuruta F, Gotoh NMY (2002) The phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase (PI3K)-Akt pathway suppresses Bax translocation to mitochondria. J Biol Chem 277:14040–14047
Gao X-J, Chen T-S, Xing D, Wang F, Pei Y-H, Wei X-B (2006) Single cell analysis of pkc activation during proliferation and apoptosis induced by laser irradiation. J Cell Physiol 206:441–448
Adams JM (2003) Ways of dying: multiple pathways to apoptosis. Genes Dev 17:2481–2495
Jänicke RU, Sprengart ML, Wati MR, Porter AG (1998) Caspase-3 is required for DNA fragmentation and morphological changes associated with apoptosis. J Biol Chem 273:9357–9360
Luo KQ, Yu VC, Pu Y, Chang DC (2003) Measuring dynamics of caspase-8 activation in a single living HeLa cell during TNFα-induced apoptosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 304:217–222
Grinberg M, Schwarz M, Zaltsman Y et al (2005) Mitochondrial carrier homolog 2 is a target of tBID in cells signaled to die by tumor necrosis factor alpha. Mol Cell Biol 25:4579–4590
Green DR (2000) Apoptotic pathways: paper wraps stone blunts scissors. Cell 102:1–4
Wolter KG, Hsu Yi-Te, Smith CL, Nechushtan A, Xi Xu-Guang, Youle RJ (1997) Movement of Bax from the cytosol to mitochondria during apoptosis. J Cell Biol 139:1281–1292
Stoka V, Turk B, Schendel SL et al (2001) Lysosomal protease pathways to apoptosis. Cleavage of Bid, not pro-caspases, is the most likely route. J Biol Chem 276:3149–3157
Desagher S, Osen-Sand A, Montessuit S et al (2001) Phosphorylation of bid by casein kinases I and II regulates its cleavage by caspase-8. Mol Cell 8:601–611
Tafani M, Karpinich NO, Hurster KA et al (2002) Cytochrome c release upon fas receptor activation depends on translocation of full-length Bid and the induction of the mitochondrial permeability transition. J Biol Chem 277:10073–10082
Krysko DV, Roels F, Leybaert L, Herde K (2001) Mitochondrial transmembrane potential changes support the concept of mitochondrial heterogeneity during apoptosis. J Histochem Cytochem 49:1277–1284
Wei QQ, Alam MM, Wang MH, Yu F, Dong Z (2004) Bid activation in kidney cells following ATP depletion,in vitro and ischemia in vivo. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 286:F803–F809
Slee EA, Keogh SA, Martin SJ (2000) Cleavage of BID during cytotoxic drug and UV radiation-induced apoptosis occurs downstream of the point of Bcl-2 action and is catalysed by caspase-3: a potential feedback loop for amplification of apoptosis-associated mitochondrial cytochrome c release. Cell Death Differ 7:556–565
Acknowledgements
This research is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (60378043; 30470494), and the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province (015012; 04010394; 2004B10401011). We thank Dr. R. Onuki (National Institute of Advanced Industrial Science and Technology, Tsukuba, Japan) for providing FRET-Bid and Bid-CFP plasmids. We thank Professor Andrew P. Gilmore (Wellcome Trust Centre for Cell Matrix Research, School of Biological Sciences, University of Manchester, UK) for providing the YFP-Bax plasmid. We also thank Professor Yukiko Gotoh (the Japan Science and Technology Corporation, Japan) for providing DsRed-Mit.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pei, Y., Xing, D., Gao, X. et al. Real-time monitoring full length bid interacting with Bax during TNF-α-induced apoptosis. Apoptosis 12, 1681–1690 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-007-0091-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-007-0091-7