Abstract
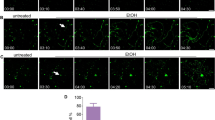
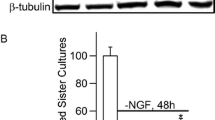
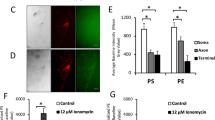
Axonal injury to retinal ganglion cells, a defined central neuron, induces a burst of intracellular superoxide anion that precedes externalization of membrane phosphatidylserine and subsequent apoptotic cell death. Dismutation of superoxide prevents the signal and delays loss of these cells, consistent with superoxide being necessary for transduction of the axotomy signal. However, phosphatidylserine externalization is a relatively late step in apoptosis, and it is possible that the superoxide burst is not an early axotomy signal but rather a result of cytochrome c release from the mitochondrial inner membrane with consequent accumulation of reduced intermediates. Other possibilities are that both superoxide generation and cytochrome c release are induced in parallel by axotomy, or that cytochrome c release potentiates the effect of the superoxide burst. To distinguish these various possibilities, serum-deprived neuronal retinal cells were assayed in vitro for superoxide elevation and release of cytochrome c from mitochondria, and the distribution of these two markers across a large number of cells used to model the temporal ordering of events. Based on this model of factor-dependent cell death, superoxide precedes, and possibly potentiates, cytochrome c release, and thus the former is likely an early signal for certain types of neuronal apoptosis in the central nervous system.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Charles I, Khalyfa A, Kumar DM et al (2005) Serum deprivation induces apoptotic cell death of transformed rat retinal ganglion cells via mitochondrial signaling pathways. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 46:1330–1338
Rello S, Stockert JC, Moreno V et al (2005) Morphological criteria to distinguish cell death induced by apoptotic and necrotic treatments. Apoptosis 10:201–208
Hogg N, Browning J, Howard T, Winterford C, Fitzpatrick D, Gobe G (1999) Apoptosis in vascular endothelial cells caused by serum deprivation, oxidative stress and transforming growth factor-beta. Endothelium 7:35–49
Lee M, Hyun DH, Halliwell B, Jenner P (2001) Effect of overexpression of wild-type and mutant Cu/Zn-superoxide dismutases on oxidative stress and cell death induced by hydrogen peroxide, 4-hydroxynonenal or serum deprivation: potentiation of injury by ALS-related mutant superoxide dismutases and protection by Bcl-2. J Neurochem 78:209–220
Berkelaar M, Clarke DB, Wang YC, Bray GM, Aguayo AJ (1994) Axotomy results in delayed death and apoptosis of retinal ganglion cells in adult rats. J Neurosci 14:4368–4374
Johnson JE, Barde YA, Schwab M, Thoenen H (1986) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor supports the survival of cultured rat retinal ganglion cells. J Neurosci 6:3031–3038
Quigley HA, McKinnon SJ, Zack DJ et al (2000) Retrograde axonal transport of BDNF in retinal ganglion cells is blocked by acute IOP elevation in rats. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 41:3460–3466
Franklin Hughes W, La Velle A (1975) The effects of early tectal lesions on development in the retinal gonglion cell layer of chick embryos. J Comp Neurol 163:265–283
Lieven CJ, Schlieve CR, Hoegger MJ, Levin LA (2006) Retinal ganglion cell axotomy induces an increase in intracellular superoxide anion. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 47:1477–1485
Kanamori A, Catrinescu MM, Kanamori N, Mears KA, Beaubien R, Levin LA (2010) Superoxide is an associated signal for apoptosis in axonal injury. Brain 133:2612–2625
Fujimura M, Morita-Fujimura Y, Kawase M et al (1999) Manganese superoxide dismutase mediates the early release of mitochondrial cytochrome c and subsequent DNA fragmentation after permanent focal cerebral ischemia in mice. J Neurosci 19:3414–3422
Niizuma K, Yoshioka H, Chen H et al (2010) Mitochondrial and apoptotic neuronal death signaling pathways in cerebral ischemia. Biochim Biophys Acta 1802:92–99
Krishnamoorthy RR, Agarwal P, Prasanna G et al (2001) Characterization of a transformed rat retinal ganglion cell line. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 86:1–12
Van Bergen NJ, Wood JP, Chidlow G et al (2009) Recharacterization of the RGC-5 retinal ganglion cell line. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 50:4267–4272
Frassetto LJ, Schlieve CR, Lieven CJ et al (2006) Kinase-dependent differentiation of a retinal ganglion cell precursor. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 47:427–438
Gorman A, McGowan A, Cotter TG (1997) Role of peroxide and superoxide anion during tumour cell apoptosis. FEBS Lett 404:27–33
Schlieve CR, Lieven CJ, Levin LA (2006) Biochemical activity of reactive oxygen species scavengers do not predict retinal ganglion cell survival. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 47:3878–3886
Luetjens CM, Bui NT, Sengpiel B et al (2000) Delayed mitochondrial dysfunction in excitotoxic neuron death: cytochrome c release and a secondary increase in superoxide production. J Neurosci 20:5715–5723
Kanamori A, Catrinescu MM, Mahammed A, Gross Z, Levin LA (2010) Neuroprotection against superoxide anion radical by metallocorroles in cellular and murine models of optic neuropathy. J Neurochem 114:488–498
Shen HM, Yang CF, Ding WX, Liu J, Ong CN (2001) Superoxide radical-initiated apoptotic signalling pathway in selenite-treated HepG(2) cells: mitochondria serve as the main target. Free Radic Biol Med 30:9–21
Hearps AC, Burrows J, Connor CE, Woods GM, Lowenthal RM, Ragg SJ (2002) Mitochondrial cytochrome c release precedes transmembrane depolarisation and caspase-3 activation during ceramide-induced apoptosis of Jurkat T cells. Apoptosis 7:387–394
Goldstein JC, Waterhouse NJ, Juin P, Evan GI, Green DR (2000) The coordinate release of cytochrome c during apoptosis is rapid, complete and kinetically invariant. Nat Cell Biol 2:156–162
Cai J, Jones DP (1998) Superoxide in apoptosis. Mitochondrial generation triggered by cytochrome c loss. J Biol Chem 273:11401–11404
Denecker G, Dooms H, Van Loo G et al (2000) Phosphatidyl serine exposure during apoptosis precedes release of cytochrome c and decrease in mitochondrial transmembrane potential. FEBS Lett 465:47–52
Matsura T, Serinkan BF, Jiang J, Kagan VE (2002) Phosphatidylserine peroxidation/externalization during staurosporine-induced apoptosis in HL-60 cells. FEBS Lett 524:25–30
Chauhan D, Li G, Sattler M et al (2003) Superoxide-dependent and-independent mitochondrial signaling during apoptosis in multiple myeloma cells. Oncogene 22:6296–6300
Lieven CJ, Millet LE, Hoegger MJ, Levin LA (2007) Induction of axon and dendrite formation during early RGC-5 cell differentiation. Exp Eye Res 85:678–683
Chen K, Zhang Q, Wang J et al (2009) Taurine protects transformed rat retinal ganglion cells from hypoxia-induced apoptosis by preventing mitochondrial dysfunction. Brain Res 1279:131–138
Acknowledgment
Grant Support: NIH R21 EY017970 and P30EY016665, Retina Research Foundation, and an unrestricted departmental grant from Research to Prevent Blindness, Inc. LAL is a Canada Research Chair of Ophthalmology and Visual Sciences.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lieven, C.J., Thurber, K.A., Levin, E.J. et al. Ordering of neuronal apoptosis signaling: a superoxide burst precedes mitochondrial cytochrome c release in a growth factor deprivation model. Apoptosis 17, 591–599 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-012-0714-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-012-0714-5