Abstract
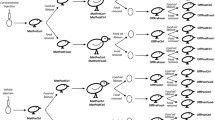
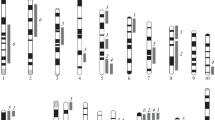
A genome-wide scan was carried out on a segregating F2 population of rats derived from reciprocal intercrosses between two inbred strains of rats, Fisher 344 (F344) and Wistar Kyoto (WKY) that differ significantly in their behavioral coping responses to stress measured by the defensive burying (DB) test. The DB test measures differences in coping strategies by assaying an animal’s behavioral response to an immediate threat. We have previously identified three X-linked loci contributing to the phenotypic variance in behavioral coping. Here we report on six significant autosomal quantitative trait loci (QTL) related to different behaviors in the DB test:one for the number of shocks received, three for number of prod approaches, one for latency to bury, and one pleiotropic locus affecting both approach and latency. These QTL contributing to different aspects of coping behaviors show that the effect of genotype on phenotype is highly dependent on lineage. The WKY lineage was particularly influential, with five out of the six QTL affecting coping behavior only in rats of the WKY lineage, and one locus affecting only those in the F344 lineage. Thus, epigenetic factors, primarily of WKY origin, may significantly modulate the genetic contribution to variance in behavioral responses to stress in the DB test.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
N. Ahmadiyeh G. A. Churchill K. Shimomura L. C. Solberg J. S. Takahashi et al. (2003) ArticleTitleX-linked and lineage-dependent inheritance of coping responses to stress Mamm. Genome 14 748–757 Occurrence Handle14722724
N. Ahmadiyeh J. Slone-Wilcoxon J. Takahashi E. Redei (2004) ArticleTitlePostnatal maternal environment significantly alters adult coping behaviors Biol. Psychiat. 55 1069–1074 Occurrence Handle15158425
K. W. Broman H. Wu S. Sen G. A. Churchill (2003) ArticleTitleR/qtl:QTL mapping in experimental crosses Bioinformatics 19 889–890 Occurrence Handle12724300 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXjsVKmtb0%3D
C. Caldji B. Tannenbaum S. Sharma D. Francis P. M. Plotsky et al. (1998) ArticleTitleMaternal care during infancy regulates the development of neural systems mediating the expression of fearfulness in the rat Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95 5335–5340 Occurrence Handle9560276 Occurrence Handle1998PNAS...95.5335C Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1cXivV2jtLY%3D
F. Champagne M. J. Meaney (2001) ArticleTitleLike motherlike daughter:Evidence for non-genomic transmission of parental behavior and stress responsivity Prog. Brain Res. 133 287–302 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0079-6123(01)33022-4 Occurrence Handle11589138 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXns1yqs70%3D
G. A. Churchill R. W. Doerge (1994) ArticleTitleEmpirical threshold values for quantitative trait mapping Genetics 138 963–971 Occurrence Handle7851788 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:ByqC2MvntFw%3D
A. Darvasi (2003) ArticleTitleGenomics:Gene expression meets genetics Nature 422 269–270 Occurrence Handle12646905 Occurrence Handle2003Natur.422..269D Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXitFKmtb4%3D
S. F. Boer ParticleDe J. M. Koolhaas (2003) ArticleTitleDefensive burying in rodents:Ethology, neurobiology and psychopharmacology Eur. J. Pharmacol. 463 145–161 Occurrence Handle12600707
J. Flint (2003) ArticleTitleAnalysis of quantitative trait loci that influence animal behavior J. Neurobiol. 54 46–77 Occurrence Handle12486698 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXps1Gjuw%3D%3D
D. Francis J. Diorio D. Liu M. J. Meaney (1999a) ArticleTitleNongenomic transmission across generations of maternal behavior and stress responses in the rat Science 286 1155–1158 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXnt1Krsrs%3D
D. D. Francis C. Caldji F. Champagne P. M. Plotsky M. J. Meaney (1999b) ArticleTitleThe role of corticotropin-releasing factor–norepinephrine systems in mediating the effects of early experience on the development of behavioral and endocrine responses to stress Biol. Psychiat. 46 1153–1166 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK1MXotVOktr8%3D
D. D. Francis K. Szegda G. Campbell W. D. Martin T. R. Insel (2003) ArticleTitleEpigenetic sources of behavioral differences in mice Nat. Neurosci. 6 445–446 Occurrence Handle12665797 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXjtFKnsLw%3D
H. Herman M. Lu M. Anggraini A. Sikora Y. Chang B. J. Yoon P. D. Soloway (2003) ArticleTitleTrans allele methylation and paramutation-like effects in mice Nat. Genet. 34 199–202 Occurrence Handle12740578 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXktFSlt7o%3D
H. A. Hofmann (2003) ArticleTitleFunctional genomics of neural and behavioral plasticity J. Neurobiol. 54 272–282 Occurrence Handle12486709 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXps1Ggtg%3D%3D
J. M. Koolhaas S. M. Korte S. F. Boer ParticleDe B. J. Der Vegt C. G. Van Reenen et al. (1999) ArticleTitleCoping styles in animals:Current status in behavior and stress-physiology Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 23 925–935 Occurrence Handle10580307 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3c%2Fks1amsA%3D%3D
S. M. Korte G. A. H. Bouws J. M. Koolhaas B. Bohus (1992) ArticleTitleNeuroendocrine and behavioral responses during conditioned active and passive behavior in the defensive burying/probe avoidance paradigm:Effects of ipsapirone Physiol. Behavior. 52 355–361 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK38XlsVegtLk%3D
A. Lahmame A. Armario (1996) ArticleTitleDifferential responsiveness of inbred strains of rats to antidepressants in the forced swimming test:Are Wistar Kyoto rats an animal model of subsensitivity to antidepressants? Psychopharmacology 123 191–198 Occurrence Handle8741943 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK28XjtFSgt7s%3D
E. S. Lander D. Botstein (1989) ArticleTitleMapping Mendelian factors underlying quanititative traits using RFLP linkage maps Genetics 121 185–199 Occurrence Handle2563713 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:BiaC3sjpsVw%3D
E. S. Lander N. J. Schork (1994) ArticleTitleGenetic dissection of complex traits Science 265 2037–2048 Occurrence Handle8091226 Occurrence Handle1994Sci...265.2037L Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:ByuA2sfgtVQ%3D
D. Liu J. Diorio B. Tannenbaum C. Caldji D. Francis et al. (1997) ArticleTitleMaternal carehippocampal glucocorticoid receptors, and hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal responses to stress Science 277 1659–1662 Occurrence Handle9287218 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK2sXmtVSgsL0%3D
C. Lopez-Rubalcava I. Lucki (2000) ArticleTitleStrain differences in the behavioral effects of antidepressant drugs in the rat forced swimming test Neuropsychopharmacology 22 191–199 Occurrence Handle10649831 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXhtVeitA%3D%3D
M. J. Meaney (2001) ArticleTitleMaternal caregene expression, and the transmission of individual differences in stress reactivity across generations Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 24 1161–1192 Occurrence Handle11520931 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXls1Shsbs%3D
M. P. Moisan B. Llamas M. N. Cook P. Mormede (2003) ArticleTitleFurther dissection of a genomic locus associated with behavioral activity in the Wistar-Kyoto hyperactive ratan animal model of hyperkinesis Mol. Psychiat. 8 348–352 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3sXitlyqsL0%3D
W. P. Pare (1989) ArticleTitle“Behavioral Despair” predicts ulceration in WKY rats Physiol. Behav. 46 483–487 Occurrence Handle2623074 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:By%2BC28%2FosFA%3D
W. P. Pare (1994) ArticleTitleOpen fieldlearned helplessness, conditioned defensive burying, and forced-swim tests in WKY rats Physiol. Behav. 55 433–439 Occurrence Handle8190758 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:ByuB2cfhvVQ%3D
W. P. Pare E. Redei (1993) ArticleTitleDepressive behavior and stress ulcer in Wistar Kyoto rats J. Physiol. Paris 87 229–238 Occurrence Handle8136789 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:ByuC1cvjtFE%3D
K. C. Price J. Shibley hyde C. L. Coe (1999) ArticleTitleMatrilinear transmission of birth weight in the rhesus monkey (Macaca mulatta) across several gnerations Obstet. Gynecol. 94 128–134 Occurrence Handle10389733 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DyaK1Mzhs1Gqtw%3D%3D
A. Ramos M. P. Moisan F. Chaouloff C. Mormede P. Mormede (1999) ArticleTitleIdentification of female-specific QTLs affecting an emotionality-related behavior in rats Mol. Psychiat.. 4 453–462 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXlvVWltbk%3D
E. E. Redei N. Ahmadiyeh A. Baum D. Sasso J. et␣al. Slone (2001) Novel animal models of affective disorders G. J. Tucker W. McKinney W. B. Saunders (Eds) Seminars in Clinical Neuropsychiatry Saunders Company Philadelphia
P. C. Reifsnyder G. Churchill E. H. Leiter (2000) ArticleTitleMaternal environment and genotype interact to establish diabesity in mice Genome Res. 10 1568–1578 Occurrence Handle11042154 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXns1Siu7Y%3D
S. Sen G. A. Churchill (2001) ArticleTitleA statistical framework for quantitative trait mapping Genetics 159 371–387 Occurrence Handle11560912 Occurrence Handle1:STN:280:DC%2BD3MrhtlShsA%3D%3D
K. Shimomura S. S. Low-Zeddies D. P. King T. D. Steeves A. Whiteley et al. (2001) ArticleTitleGenome-wide epistatic interaction analysis reveals complex genetic determinants of circadian behavior in mice Genome Res. 11 959–980 Occurrence Handle11381025 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXkt12rur0%3D
F. Sluyter S. M. Korte B. Bohus G. A. Oortmerssen ParticleVan (1996) ArticleTitleBehavioral stress response of genetically selected aggressive and nonagressive wild house mice in the shock-probe/defensive burying test Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 54 113–116 Occurrence Handle8728547 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaK28XisVOis7k%3D
L Solberg A Baum N Ahmadiyeh K Shimomura et al. (2004) ArticleTitleSex- and lineage-specific inheritance of depression-like behaviour in the rat Mamm. Genome 15 IssueID8 648–662 Occurrence Handle15457344
D. Treit (1985) ArticleTitleAnimal models for the study of anti-anxiety agents:A review Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 9 203–22 Occurrence Handle2861589 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL2sXmtFWgs70%3D
D. Treit (1991) Defensive burying:A pharmacolgocial animal␣model for specific fears? P. Soubrie D. Widlocker (Eds) Anxiety, Depression, and Mania:Animal Models of Psyrchiatric Disorders Basel:Karger New York 1– 19
D. Treit J. P. Pinel H. C. Fibiger (1981) ArticleTitleConditioned␣defensive burying:A new paradigm for the study of␣anxiolytic agents Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 15 619–626 Occurrence Handle6117086 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaL3MXmtFGjur8%3D
M. G. Turri S. R. Datta J. Fries ParticleDe N. D. Henderson J. Flint (2001a) ArticleTitleQTL analysis identifies multiple behavioral dimensions in ethological tests of anxiety in laboratory mice Curr. Biol. 11 725–734 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXjvFSiurw%3D
M. G. Turri N. D. Henderson J. C. Fries ParticleDe J. Flint (2001b) ArticleTitleQuantitative trait locus mapping in laboratory mice derived from a replicated selection experiment for open-field activity Genetics 158 1217–1226 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3MXmtVKqtrw%3D
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ahmadiyeh, N., Churchill, G.A., Solberg, L.C. et al. Lineage is an Epigenetic Modifier of QTL Influencing Behavioral Coping with Stress. Behav Genet 35, 189–198 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10519-004-1018-5
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10519-004-1018-5