Abstract
Using large twin, family, and adoption studies conducted at the Minnesota Center for Twin and Family Research, we describe our efforts to develop measures of substance use disorder (SUD) related phenotypes for targets in genome wide association analyses. Beginning with a diverse set of relatively narrow facet-level measures, we identified 5 constructs of intermediate complexity: nicotine, alcohol consumption, alcohol dependence, illicit drug, and behavioral disinhibition. The 5 constructs were moderately correlated (mean r = .57) reflecting a general externalizing liability to substance abuse and antisocial behavior. Analyses of the twin and adoption data revealed that this general externalizing liability accounted for much of the genetic risk in each of the intermediate-level constructs, though each also exhibited significant unique genetic and environmental risk. Additional analyses revealed substantial effects for age and sex, significant shared environmental effects, and that the mechanism of these shared environmental effects operates via siblings rather than parents. Our results provide a foundation for genome wide association analyses to detect risk alleles for SUDs as well as novel insights into genetic and environmental risk for SUDs.




Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
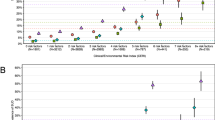
The analysis reported in the text differs slightly from the figure depicting mean behavioral disinhibition scores as a function of age. Specifically, the analysis discussed in the text fits a linear regression model to the full sample and detects overall negative effects for both age and age2. In contrast, for the purpose of better visual presentation, the figure depicts fitting separate linear regression models for offspring (showing a linear increase) and parent (showing a linear decrease) participants.
To ensure the biometric analyses would not be affected by any potential group differences in mean levels of externalizing behaviors, we tested for group differences between offspring from the MTFS and SIBS samples on the lower-order factors and higher-order externalizing factor. Offspring from the MTFS and SIBS exhibited comparable scores with the mean Cohen’s d = −.03 (range −.13 to .09).
References
Achenbach TM, Edelbrock CS (1984) Psychopathology of childhood. Ann Rev Psychol 35:227–256
Agrawal A, Grant JD, Littlefield A, Waldron M, Pergadia ML, Lynskey MT et al (2009) Developing a quantitative measure of alcohol consumption for genomic studies on prospective cohorts. J Stud Alcohol Drugs 70:157–168
Agrawal A, Neale MC, Jacobson KC, Prescott CA, Kendler KS (2005) Illicit drug use and abuse/dependence: modeling of two-stage variables using the CCC approach. Addict Behav 30:1043–1048
American Psychiatric Association (1987) Diagnostic and statistical manual for mental disorders, 3rd edn, Rev. American Psychiatric Association, Washington
Bachman JG, Wadsworth K, O’Malley P, Johnston L, Schulenberg J (1997) Smoking, drinking, and drug use in young adulthood: the impacts of new freedoms and new responsibilities. Erlbaum, Mahwah, NJ
Bacon DR (2001) Evaluation of cluster analytic approaches to initial model specification. Struc Equat Model 8:397–429
Bauer DJ, Hussong AM (2009) Psychometric approaches for developing commensurate measures across independent studies: traditional and new models. Psychol Meth 14:101–125
Bemmels HR, Burt SA, Legrand LN, Iacono WG, McGue M (2008) The heritability of life events: an adolescent twin and adoption study. Twin Res Hum Genet 11:257–265
Bierut LJ, Madden PAF, Breslau N, Johnson EO, Hatsukami D, Pomerleau OF et al (2007) Novel genes identified in a high-density genome wide association study for nicotine dependence. Hum Mol Genet 16:24–35
Bornovalova MA, Hicks BM, Iacono WG, McGue M (2010) Family transmission and heritability of childhood disruptive disorders. Am J Psychiatry 167:1066–1074
Carlson SR, Iacono WG (2006) Heritability of P300 amplitude development from adolescence to adulthood. Psychophysiol 43:470–480
Carlson SR, McLarnon ME, Iacono WG (2007) P300 amplitude, externalizing psychopathology, and earlier versus later onset substance use disorder. J Abnorm Psychol 116:565–577
Chassin L, Flora DB, King KM (2004) Trajectories of alcohol and drug use and dependence from adolescence to adulthood: the effects of familial alcoholism and personality. J Abnorm Psychol 113:483–498
Compton WM, Thomas YF, Stinson FS, Grant BF (2007) Prevalence, correlates, disability, and comorbidity of DSM-IV drug abuse and dependence in the United States. Arch Gen Psychiatry 64:566–576
Dawson DA, Pulay AJ, Grant BF (2010) A comparison of two single-item screeners for hazardous drinking and alcohol use disorder. Alcohol Clin Exper Res 34:364–374
Derringer J, Krueger RF, McGue M, Iacono WG (2008) Genetic and environmental contributions to the diversity of substances used in adolescent twins: a longitudinal study of age and sex effects. Addiction 103:1744–1751
Dick DM (2007) Identification of genes influencing a spectrum of externalizing psychopathology. Curr Direct Psychol Sci 16:331–335
Dick DM, Agrawal A, Wang JC, Hinrichs A et al (2007) Alcohol dependence with comorbid drug dependence: genetic and phenotypic associations suggest a more severe form of the disorder with stronger genetic contribution to risk. Addiction 102:1131–1139
Dick DM, Aliev F, Wang JC, Grucza RA, Schuckit M et al (2008) Using dimensional models of externalizing psychopathology to aid in gene identification. Arch Gen Psychiatry 65:310–318
Dick DM, Latendresse SJ, Lansford JE, Budde JP, Goate A, Dodge KA et al (2009) Role of GABRA2 in trajectories of externalizing behavior across development and evidence of moderation by parental monitoring. Arch Gen Psychiatry 66:649–657
First MB, Gibbon M, Spitzer RL, Williams JBW (1997) Structured clinical interview for DSM-IV axis II personality disorders (SCID-II). American Psychiatric Publishing, Arlington, VA
Fowler Y, Lifford K, Shelton K, Rice F, Thapar A, Neale MC et al (2007) Exploring the relationship between genetic and environmental influences on initiation and progression of substance use. Addiction 101:413–422
Gilmore CS, Malone SM, Iacono WG (2010) Brain electrophysiological endophenotypes for externalizing psychopathology: a multivariate approach. Behav Genet 40:186–200
Goldman D, Oroszi G, Ducci F (2005) The genetics of addictions: uncovering the genes. Nat Rev Genet 6:521–532
Grant JD, Agrawal A, Bucholz KK, Madden PAF, Pergadia ML, Nelson EC et al (2009) Alcohol consumption indices of genetic risk for alcohol dependence. Biol Psychiatry 66:795–800
Harwood R, Fountain D, Livermore G (1998) The economic costs of alcohol and drug abuse in the United States, 1992. National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism and National Institute on Drug Abuse, Bethesda, MD
Hasin DS, Stinson FS, Ogburn E, Grant BF (2007) Prevalence, correlates, disability, and comorbidity of DSM-IV alcohol abuse and dependence in the United States. Arch Gen Psychiatry 64:830–842
Heath AC, Bucholz KK, Madden PA, Dinwiddie SH, Slutske WS, Bierut LJ et al (1997) Genetic and environmental contributions to alcohol dependence risk in a national twin sample: consistency of findings in women and men. Psych Med 27:1381–1396
Heath AC, Martin NG, Lynskey MT, Todorov AA, Madden PAF (2002) Estimating two-stage models for genetic influences of on alcohol, tobacco, or drug use initiation and dependence vulnerability in twin and family data. Twin Res 5:113–124
Hicks BM, Bernat E, Malone SM, Iacono WG, Patrick CJ, Krueger RF, McGue M (2007) Genes mediate the association between P3 amplitude and externalizing disorders. Psychophysiol 44:98–105
Hicks BM, Iacono WG, McGue M (2010) Pre-morbid liability index for substance use disorders: an alternative phenotype for gene association studies. In: Paper presented at the 24th annual meeting of the Society for Research in Psychopathology, Seattle, WA, Oct 2010
Hicks BM, Krueger RF, Iacono WG, McGue M, Patrick CJ (2004) Family transmission and heritability of externalizing disorders: a twin-family study. Arch Gen Psychiatry 61:922–928
Hicks BM, South SC, DiRago AC, Iacono WG, McGue M (2009) Environmental adversity and increasing genetic risk for externalizing disorders. Arch Gen Psychiatry 66:640–648
Higuchi S, Matsushita S, Masaki T, Yokoyama A, Kimura M, Suzuki G et al (2004) Influence of genetic variations of ethanol-metabolizing enzymes on phenotypes of alcohol-related disorders. Ann New York Acad Sci 1025:47–480
Hollingshead AB (1957) Two factor index of social position. Author, New Haven, CT
Iacono WG, Carlson SR, Malone SM, McGue M (2002) P3 event-related potential amplitude and the risk for disinhibitory disorders in adolescent boys. Arch Gen Psychiatry 59:750–757
Iacono WG, Carlson SR, Taylor J, Elkins IJ, McGue M (1999) Behavioral disinhibition and the development of substance use disorders: findings from the Minnesota twin family study. Dev Psychopathol 11:869–900
Iacono WG, Malone SM, McGue M (2008) Behavioral disinhibition and the development of early-onset addiction: common and specific influences. Ann Rev Clin Psychol 4:12.1–12.24
Iacono WG, McGue M (2006) Association between P3 event-related brain potential amplitude and adolescent problem behavior. Psychophysiol 43:465–469
Iacono WG, McGue M, Krueger RF (2006) Minnesota center for twin and family research. Twin Res Hum Genet 9:978–984
Irons DE, McGue M, Iacono WG (2007) Mendelian randomization: a novel test of the gateway hypothesis and models of gene-environment interplay. Dev Psychopathol 19:1181–1195
Jacobson KC, Prescott CA, Kendler KS (2000) Genetic and environmental influences on juvenile antisocial behavior assessed on two occasions. Psychol Med 30:1315–1325
Jessor R, Jessor SL (1977) Problem behavior and psychosocial development: a longitudinal study of youth. Academic Press, New York
Kendler KS, Heath AC, Neale MC, Kessler RC, Eaves LJ (1992) A population-based twin study of alcoholism in women. JAMA 268:1877–1882
Kendler KS, Prescott CA, Myers J, Neale MC (2003) The structure of genetic and environmental risk factors for common psychiatric and substance use disorders in men and women. Arch Gen Psychiatry 60:929–937
Kendler KS, Schmitt BS, Aggen SH, Presott CA (2008) Genetic and environmental influences on alcohol, caffeine, cannabis, and nicotine use from early adolescence to middle adulthood. Arch Gen Psychiatry 65:674–682
Kessler RC, McGonagle KA, Zhao S, Nelson CB, Hughes M, Eshleman S et al (1994) Lifetime and 12-month prevalence of DSM-III-R psychiatric disorders in the United States: results from the national comorbidity survey. Arch Gen Psychiatry 51:8–19
Keyes MA, Malone SM, Elkins IJ, Legrand LN, McGue M, Iacono WG (2009) The enrichment study of the Minnesota twin family study: increasing the yield of twin families at high risk for externalizing psychopathology. Twin Res Hum Genet 12:489–501
Krueger RF, Hicks BM, Patrick CJ, Carlson SR, Iacono WG, McGue M (2002) Etiologic connections among substance dependence, antisocial behavior and personality: modeling the externalizing spectrum. J Abnorm Psychol 111:411–424
Krueger RF, Markon KE (2006) Reinterpreting comorbidity: a model-based approach to understanding and classifying psychopathology. Ann Rev Clin Psychol 2:111–133
Krueger RF, Markon KE, Patrick CJ, Benning SD, Kramer M (2007) Linking antisocial behavior, substance use, and personality: an integrative quantitative model of the adult externalizing spectrum. J Abnorm Psychol 116:645–666
Krueger RF, Nichol PE, Hicks BM, Markon KE, Patrick CJ, Iacono WG, McGue M (2004) Using latent trait modeling to conceptualize an alcohol problems continuum. Psychol Assess 16:107–119
Lyons MJ, True WR, Eisen SA, Goldberg J, Meyer JM, Faraone SV et al (1995) Differential heritability of adult and juvenile antisocial traits. Arch Gen Psychiatry 52:906–915
Malone SM, McGue MK, Iacono WG (2002) Drinks of the father: father’s maximum number of drinks consumed predicts externalizing disorders, substance use, and substance use disorders in preadolescent and adolescent offspring. Alcohol Clinc Exp Res 26:1823–1832
Markon KE (2010) Modeling psychopathology structure: a symptom-level analysis of axis I and II disorders. Psychol Med 40:273–288
Markon KE, Krueger RF (2005) Categorical and continuous models of liability to externalizing disorders: a direct comparison in NESARC. Arch Gen Psychiatry 62:1352–1359
Markon KE, Krueger RF, Watson D (2005) Delineating the structure of normal and abnormal personality: an integrative hierarchical approach. J Per Soc Psychol 88:139–157
McGue M, Elkins I, Iacono WG (2000) Genetic and environmental influences on adolescent substance use and abuse. Am J Med Genet 96:671–677
McGue M, Iacono WG (2005) The association of early adolescent problem behavior with adult psychopathology. Am J Psychiatry 162:1118–1124
McGue M, Iacono WG, Krueger RF (2006) The association of early adolescent problem behavior and adult psychopathology: a multivariate behavioral genetic perspective. Behav Genet 36:591–602
McGue M, Iacono WG, Legrand LN, Malone S, Elkins I (2001) Origins and consequences of age at first drink. I. Associations with substance use disorders, disinhibitory behavior and psychopathology, and P3 amplitude. Alcohol Clin Exper Res 25:1156–1165
McGue M, Keyes M, Sharma A, Elkins I, Legrand L, Johnson W, Iacono WG (2007) The environments of adopted and non-adopted youth: evidence on range restriction from the Sibling interaction and behavior study (SIBS). Behav Genet 37:449–462
Moffitt TE (1993) Adolescence-limited and life-course-persistent antisocial behavior: a developmental taxonomy. Psychol Rev 100:674–701
Muthen LK, Muthen BO (2007) Mplus user’s guide, 5th edn. Muthen & Muthen, Los Angles
Nathan PE, Gorman JM (1998) A guide to treatments that work. Oxford University Press, New York
Neale MC, Boker SM, Xie G, Maes HH (2004) Mx: statistical modeling, 6th edn, rev. Department of Psychiatry, Virginia Commonwealth University, Richmond
Patrick CJ, Bernat EM, Malone SM, Iacono WG, Krueger RF, McGue M (2006) P300 amplitude as an indicator of externalizing in adolescent males. Psychophysiol 43:84–92
Prescott CA, Kendler KS (1999) Genetic and environmental contributions to alcohol abuse and dependence in a population-based sample of male twins. Am J Psychiatry 156:34–40
R Development Core Team (2008) R: a language and environment for statistical computing. Vienna, Austria (ISBN 3-900051-07-0)
Revelle W (1979) Hierarchical cluster analysis and the internal structure of tests. Multivar Behav Res 14:57–74
Revelle W (2009) Psych: procedures for personality and psychological research. R package version (1.0-88)
Rhee SH, Hewitt JK, Young SE, Corley RP, Crowley TJ, Stallings MC (2003) Genetic and environmental influences on substance initiation, use, and problem use in adolescents. Arch Gen Psychiatry 60:1256–1264
Roberts BW, Walton KE, Viechtbauer W (2006) Patterns of mean-level change in personality traits across the life course: a meta-analysis of longitudinal studies. Psychol Bull 132:1–25
Robins LM, Babor T, Cottler LB (1987) Composite international diagnostic interview: expanded substance abuse module. Authors, St. Louis
Sameroff AJ, Seifer R, Baldwin A, Baldwin C (1993) Stability of intelligence from pre-school to adolescence: the influence of social and family risk factors. Child Dev 64:80–97
Schmid JJ, Leiman JM (1957) The development of hierarchical factor solutions. Psychometrika 22:83–90
Stallings MC, Corley RP, Dennehey B, Hewitt JK, Krauter KS, Lessem JM et al (2005) A genome-wide search for quantitative trait loci that influence antisocial drug dependence in adolescence. Arch Gen Psychiatry 62:1042–1051
Taylor J, McGue M, Iacono WG, Lykken DT (2000) A behavioral genetic analysis of the relationship between the socialization scale and self-reported delinquency. J Pers 68:29–50
Tellegen A, Waller NG (2008) Exploring personality through test construction: development of the multidimensional personality questionnaire. In Boyle GJ, Matthews G, Saklofske DH (eds), The Sage handbook of personality theory and assessment: personality measurement and testing, vol II. Sage, London, pp. 261–292
World Health Organization (WHO) (2004) Global status report on alcohol 2004. Author, Geneva
World Health Organization (WHO) (2008) WHO report on the global tobacco epidemic, 2008: the MPOWER package. Author, Geneva
Yoon HH, Iacono WG, Malone SM, McGue M (2006) Using the brain P300 response to identify novel phenotypes reflecting genetic vulnerability for adolescent substance misuse. Addict Behav 31:1067–1087
Young SE, Stallings MC, Corley RP, Krauter KS, Hewitt JK (2000) Genetic and environmental influences on behavioral disinhibition. Am J Med Genet (Neuropsych Genet) 96:684–695
Zinbarg RE, Revelle W, Yovel I, Li W (2005) Cronbach’s α, Revelle’s β, and McDonald’s ω: their relations with each other and two alternative conceptualizations of reliability. Psychometrika 70:123–133
Zinbarg RE, Yovel I, Revelle W, McDonald R (2006) Estimating generalizability to a latent variable common to all of a scale’s indicators: a comparison of estimators for ω. Appl Psychol Measur 30:121–144
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by USPS grants U01 DA024417, R01 DA005147, R01 DA013240, R01 AA009367, R01 AA011886, and R01 MH066140. Brian M. Hicks was supported by K01 DA025868. Stephen M. Malone was supported by K01 AA015621.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Edited by Michael Lyons.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hicks, B.M., Schalet, B.D., Malone, S.M. et al. Psychometric and Genetic Architecture of Substance Use Disorder and Behavioral Disinhibition Measures for Gene Association Studies. Behav Genet 41, 459–475 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10519-010-9417-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10519-010-9417-2