Abstract
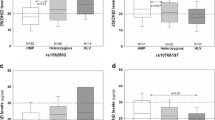
Recently, the ER22/23EK, N363S and BclI polymorphisms in the glucocorticoid receptor (GR) gene have been linked to altered cortisol sensitivity and to cortisol-associated disorders. The aim of this study was to investigate the effect of these genetic variants in the GR gene on cardiovascular disease and mortality in elderly persons aged 85 years and over. In the population-based Leiden 85-plus Study, 552 participants were genotyped for the ER22/23EK, N363S and BclI polymorphisms, and the effects of the polymorphisms on metabolic profile, body composition, and on the prevalence of cardiovascular pathologies at baseline, were assessed. Allcause and cardiovascular disease mortality risks␣dependent on the SNPs were calculated after a 4.2-year follow-up. The analyses of metabolic profile revealed that carriers of the ER22/23EK polymorphism have higher HbA1C levels (P<0.001) and carriers of the N363S SNP have higher LDL cholesterol (P<0.001) and triglyceride concentrations (P=0.03), compared to the non-carriers. The only significant association between genotype and body composition analyses was for height and the ER22/23EK polymorphism. Men carrying the ER22/23EK polymorphism were taller (P=0.02) compared to non-carriers. No associations with cardiovascular pathologies, allcause and cardiovascular mortality were observed for any of the polymorphisms. We conclude that, in spite the effect of the ER22/23EK and N363S SNPs on metabolism, these polymorphisms together with the BclI SNP, do not affect the risks of cardiovascular disease and survival at old age.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bootsma-van der Wiel A, van Exel E, De Craen AJ, Gussekloo J, Lagaay AM, Knook DL, Westendorp RG (2002) A high response is not essential to prevent selection bias: results␣from the Leiden 85-plus study. J Clin Epidemiol 55:1119–1125
Chrousos GP (1995) The hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis and immune-mediated inflammation. N Engl J Med 332:1351–1363
Chrousos GP (1998) Stressors, stress, and neuroendocrine integration of the adaptive response: the 1997 Hans Selye Memorial Lecture. Ann NY Acad Sci 851:311–335
de Kloet ER, Vreugdenhil E, Oitzl MS, Joels M (1998) Brain corticosteroid receptor balance in health and disease. Endocr Rev 19:269–301
de Lange P, Koper JW, Huizenga NA, Brinkmann AO, de Jong FH, Karl M, Chrousos GP, Lamberts SW (1997) Differential hormone-dependent transcriptional activation and -repression by naturally occurring human glucocorticoid receptor variants. Mol Endocrinol 11:1156–1164
Di Blasio AM, van Rossum EF, Maestrini S, Berselli ME, Tagliaferri M, Podesta F, Koper JW, Liuzzi A, Lamberts SW (2003) The relation between two polymorphisms in the glucocorticoid receptor gene and body mass index, blood pressure and cholesterol in obese patients. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 59:68–74
Dobson MG, Redfern CP, Unwin N, Weaver JU (2001) The N363S polymorphism of the glucocorticoid receptor: potential contribution to central obesity in men and lack of association with other risk factors for coronary heart disease and diabetes mellitus. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 86:2270–2274
Echwald SM, Sorensen TI, Andersen T, Pedersen O (2001) The Asn363Ser variant of the glucocorticoid receptor gene is not associated with obesity or weight gain in Danish men. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 25:1563–1565
Friedewald WT, Levy RI, Fredrickson DS (1972) Estimation of the concentration of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol in plasma, without use of the preparative ultracentrifuge. Clin Chem 18:499–502
Heijmans BT, Gussekloo J, Kluft C, Droog S, Lagaay AM, Knook DL, Westendorp RG, Slagboom EP (1999) Mortality risk in men is associated with a common mutation in the methylene-tetrahydrofolate reductase gene (MTHFR). Eur J Hum Genet 7:197–204
Huizenga NA, Koper JW, de Lange P, Pols HA, Stolk RP, Burger H, Grobbee DE, Brinkmann AO, de Jong FH, Lamberts SW (1998a) A polymorphism in the glucocorticoid receptor gene may be associated with and increased sensitivity to glucocorticoids in vivo. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 83:144–151
Huizenga NA, Koper JW, de Lange P, Pols HA, Stolk RP, Grobbee DE, de Jong FH, Lamberts SW (1998b) Interperson variability but intraperson stability of baseline plasma cortisol concentrations, and its relation to feedback sensitivity of the hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenal axis␣to a low dose of dexamethasone in elderly individuals. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 83:47–54
Ioannidis JP, Ntzani EE, Trikalinos TA, Contopoulos-Ioannidis DG (2001) Replication validity of genetic association studies. Nat Genet 29:306–309
Koper JW, Stolk RP, de Lange P, Huizenga NA, Molijn GJ, Pols HA, Grobbee DE, Karl M, de Jong FH, Brinkmann AO, Lamberts SW (1997) Lack of association between five polymorphisms in the human glucocorticoid receptor␣gene and glucocorticoid resistance. Hum Genet 99:663–668
Lin RC, Wang WY, Morris BJ (1999) High penetrance, overweight, and glucocorticoid receptor variant: case–control study. BMJ 319:1337–1338
Lin RC, Wang XL, Morris BJ (2003) Association of coronary artery disease with glucocorticoid receptor N363S variant. Hypertension 41:404–407
Macfarlane PW, Latif S (1996) Automated serial ECG comparison based on the Minnesota code. J Electrocardiol 29(Suppl):29–34
McEwen BS (1998) Protective and damaging effects of stress mediators. N Engl J Med 338:171–179
Munck A, Guyre PM, Holbrook NJ (1984) Physiological functions of glucocorticoids in stress and their relation to pharmacological actions. Endocr Rev 5:25–44
Panarelli M, Holloway CD, Fraser R, Connell JM, Ingram MC, Anderson NH, Kenyon CJ (1998) Glucocorticoid receptor polymorphism, skin vasoconstriction, and other metabolic intermediate phenotypes in normal human subjects. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 83:1846–1852
Rosmond R, Bouchard C, Bjorntorp P (2001) Tsp509I polymorphism in exon 2 of the glucocorticoid receptor gene in relation to obesity and cortisol secretion: cohort study. BMJ 322:652–653
Russcher H, van Rossum EF, de Jong FH, Brinkmann AO, Lamberts SW, Koper JW (2005) Increased expression of the glucocorticoid receptor-A translational isoform as a result of the ER22/23EK polymorphism. Mol Endocrinol 19:1687–1696
van Exel E, Gussekloo J, Houx P, de Craen AJM, Macfarlane PW, Bootsma-van der Wiel A, Blauw GJ, Westendorp RGJ (2002) Atherosclerosis and cognitive impairment are linked in the elderly. The Leiden 85-plus Study. Atherosclerosis 165:353–359
van Rossum EF, Feelders RA, Van Den Beld AW, Uitterlinden AG, Janssen JA, Ester W, Brinkmann AO, Grobbee DE, de Jong FH, Pols HA, Koper JW, Lamberts SW (2004a) Association of the ER22/23EK polymorphism in the glucocorticoid receptor gene with survival and C-reactive protein levels in elderly men. Am J Med 117:158–162
van Rossum EF, Koper JW, Huizenga NA, Uitterlinden AG, Janssen JA, Brinkmann AO, Grobbee DE, de Jong FH, van Duyn CM, Pols HA, Lamberts SW (2002) A polymorphism in the glucocorticoid receptor gene, which decreases sensitivity to glucocorticoids in vivo, is associated␣with low insulin and cholesterol levels. Diabetes 51:3128–3134
van Rossum EF, Koper JW, Van Den Beld AW, Uitterlinden AG, Arp P, Ester W, Janssen JA, Brinkmann AO, de Jong FH, Grobbee DE, Pols HA, Lamberts SW (2003) Identification of the BclI polymorphism in the glucocorticoid receptor gene: association with sensitivity to glucocorticoids in vivo and body mass index. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 59:585–592
van Rossum EF, Voorhoeve PG, te Velde SJ, Koper JW, Delemarre-van de Waal HA, Kemper HC, Lamberts SW (2004b) The ER22/23EK polymorphism in the glucocorticoid receptor gene is associated with a beneficial body composition and muscle strength in young adults. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 89:4004–4009
Weverling-Rijnsburger AW, Blauw GJ, Lagaay AM, Knook DL, Meinders AE, Westendorp RG (1997) Total cholesterol and risk of mortality in the oldest old. Lancet 350:1119–1123
Weverling-Rijnsburger AW, Jonkers IJ, van Exel E, Gussekloo J, Westendorp RG (2003) High-density vs low-density lipoprotein cholesterol as the risk factor for coronary artery disease and stroke in old age. Arch Intern Med 163:1549–1554
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by an IOP grant (Innovative Orientated Research) from the Dutch Ministry of Economic Affairs (grant number IGE010114), and by the Centre for Medical Systems Biology (CMSB), which is a center of excellence approved by the Netherlands Genomics Initiative/Netherlands Organisation for Scientific Research (NWO). The study was also supported by a Marie Curie Fellowship of the European Community programme EUROGENDIS “The Genetic Basis of Disease” for Maris Kuningas, under contract number QLGA-GH-00-60005-59. We thank Anton J. M. de Craen for the help in data analyses.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kuningas, M., Mooijaart, S.P., Slagboom, P.E. et al. Genetic variants in the glucocorticoid receptor gene (NR3C1) and cardiovascular disease risk. The Leiden 85-plus Study. Biogerontology 7, 231–238 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10522-006-9021-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10522-006-9021-2