Abstract
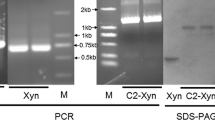
An artificial, bifunctional, thermostable cellulase–xylanase enzyme from Thermotoga maritima by gene fusion. The fusion protein exhibited both cellulase and xylanase activity when xynA was fused downstream of cel5C but no activities were shown when xynA was fused upstream of cel5C. The enzyme was optimally active at pH 5.0 and 80°C over 30 min. E. coli expressed the fusion enzyme, with an apparent molecular mass of approximately 152 kDa by carboxymethyl cellulose- and xylan-SDS-PAGE.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
An JM, Kim YK, Lim WJ, Hong SY, An CL, Shin EC, Cho KM, Choi BR, Kang JM, Lee SM, Kim H, Yun HD (2005) Evaluation of a novel bifunctional xylanase-cellulase constructed by gene fusion. Enzyme Microb Technol 36:989–995
Bergquist PL, Gibbs MD, Morris DD, Thompson DR, Uhl AM, Daniel RM (2001) Hyperthermophilic xylanases. Methods Enzymol 330:301–319
Bok JD, Yernool DA, Eveleigh DE (1998) Purification, characterization, and molecular analysis of thermostable cellulases CelA and CelB from Thermotoga neapolitana. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:4774–4781
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Bronnenmeier K, Kern A, Liebl W, Staudenbauer WL (1995) Purification of Thermotoga maritima enzymes for the degradation of cellulosic materials. Appl Environ Microbiol 61:1399–1407
Chhabra SR, Kelly RM (2002) Biochemical characterization of Thermotoga maritima endoglucanase Cel74 with and without a carbohydrate binding module (CBM). FEBS Lett 531:375–380
Chhabra SR, Shockley KR, Conners SB, Scott KL, Wolfinger RD, Kelly RM (2003) Carbohydrate-induced differential gene expression patterns in the hyperthermophilic bacterium Thermotoga maritima. J Biol Chem 278:7540–7552
Chhabra SR, Shockley KR, Ward DE, Kelly RM (2002) Regulation of endo-acting glycosyl hydrolases in the hyperthermophilic bacterium Thermotoga maritima grown on glucan-and mannan-based polysaccharides. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:545–554
Doi N, Yanagawa H (1999) Insertional gene fusion technology. FEBS Lett 457:1–4
Gilbert M, Bayer R, Cunningham AM, DeFrees S, Gao Y, Watson DC, Young NM, Wakarchuk WW (1998) The synthesis of sialylated oligosaccharides using a CMP-Neu5Ac synthetase/sialyltransferase fusion. Nat Biotechnol 16:769–772
Goyal K, Selvakumar P, Hayashi K (2001) Characterization of a thermostable β-glucosidase (BglB) from Thermotoga maritima showing transglycosylation activity. J Mol Cata B: Enzymatic 15:45–53
Jiang Z, Zhu Y, Li L, Yu X, Kusakabe I, Kitaoka M, Hayashi K (2004) Transglycosylation reaction of xylanase B from the hyperthermophilic Thermotoga maritima with the ability of synthesis of tertiary alkyl β-D-xylobiosides and xylosides. J Biotechnol 114:125–134
Lu Q (2005) Seamless cloning and gene fusion. Trends Biotechnol 23:199–207
Nixon AE, Ostermeier M, Benkovic SJ (1998) Hybrid enzymes: manipulating enzyme design. Trends Biotechnol 16:258–264
Park SR, Lim WJ, Kim MK, Hong SY, Shin EC, Kim EJ, Lee JR, Woo JG, Kim H, Yun HD (2004) Analysis of cel and pel genes from Pectobacterium chrysanthemi PY35 for relatedness to pathogenecity. J Microbiol Biotechnol 14:1047–1051
Sambrook J, Russell DW (2001) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, 3rd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, NY
Wassenberg D, Liebl W, Jaenicke R (2000) Maltose-binding protein from the hyperthermophilic bacterium Thermotoga maritima: stability and binding properties. J Mol Biol 295:279–288
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the 21C Frontier Microbial Genomics and Application Center Program, Ministry of Science & Technology. This work was supported by the Brain Korea21 project in 2006.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hong, S.Y., Lee, J.S., Cho, K.M. et al. Assembling a novel bifunctional cellulase–xylanase from Thermotoga maritima by end-to-end fusion. Biotechnol Lett 28, 1857–1862 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-006-9166-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-006-9166-8