Abstract
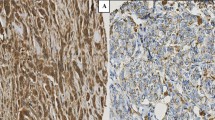
Invasive tumor cells and their microenvironments are enriched with a broad spectrum of different proteases. Legumain, a novel asparaginyl endopeptidase, has been observed to be highly expressed in several types of solid tumors. However, there is no data available identifying the relationship of legumain expression and clinicopathologic or biological variables in invasive breast cancer. For the first time, the prevalence of legumain expression in invasive breast cancer (n = 432) and non-neoplastic breast tissues (n = 128) was investigated by immunohistochemistry. Three staining patterns were observed in the cytoplasm: diffuse positivity, tiny dots and vesicles. Whereas vesicular positivity in the majority of tumor cells was significantly correlated to an adverse outcome, cytoplasmic and dot-like staining showed no prognostic effect. Vesicular positivity was observed in 24% of carcinomas, but only in one case of non-neoplastic breast tissue (<1%; proliferative mastopathy). This staining pattern was found to be independent of other factors analysed as grading, nodal status or HER2 expression. Besides being of prognostic value, legumain might prove to be an important predictive factor in breast cancer, since its unique cleavage specificity is already used in prodrug activation strategies.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barrett AJ, Rawlings ND, O’Brien EA (2001) The MEROPS database as a protease information system. J Struct Biol 134(2–3):95–102
Dando PM, Fortunato M, Smith L et al (1999) Pig kidney legumain: an asparaginyl endopeptidase with restricted specificity. Biochem J 339(Pt 3):743–749
Chen JM, Fortunato M, Stevens RA et al (2001) Activation of progelatinase A by mammalian legumain, a recently discovered cysteine proteinase. Biol Chem 382(5):777–783
Liu C, Sun C, Huang H et al (2003) Overexpression of legumain in tumors is significant for invasion/metastasis and a candidate enzymatic target for prodrug therapy. Cancer Res 63(11):2957–2964
Murthy RV, Arbman G, Gao J et al (2005) Legumain expression in relation to clinicopathologic and biological variables in colorectal cancer. Clin Cancer Res 11(6):2293–2299
Kroger N, Milde-Langosch K, Riethdorf S et al (2006) Prognostic and predictive effects of immunohistochemical factors in high-risk primary breast cancer patients. Clin Cancer Res 12(1):159–168
Crisi GM, Marconi SA, Makari-Judson G et al (2005) Expression of c-kit in adenoid cystic carcinoma of the breast. Am J Clin Pathol 124(5):733–739
Sarandeses CS, Covelo G, Diaz-Jullien C et al (2003) Prothymosin alpha is processed to thymosin alpha 1 and thymosin alpha 11 by a lysosomal asparaginyl endopeptidase. J Biol Chem 278(15):13286–13293
Traub F, Jost M, Hess R et al (2006) Peptidomic analysis of breast cancer reveals a putative surrogate marker for estrogen-receptor negative carcinomas. Lab Invest 86(3):246–253
Traub F, Mengel M, Lück HJ et al (2006) Prognostic impact of Skp2 and p27 in human breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat (in press)
Mengel M, Kreipe HH, von Wasielewski R (2003) Rapid and large-scale transition of new tumor biomarkers to clinical biopsy material by innovative tissue microarray systems. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 11:261–268
Bast RC Jr, Ravdin P, Hayes DF et al (2001) 2000 Update of recommendations for the use of tumor markers in breast and colorectal cancer: clinical practice guidelines of the American Society of Clinical Oncology. J Clin Oncol 19(6):1865–1878
Chen JM, Dando PM, Rawlings ND et al (1997) Cloning, isolation, and characterization of mammalian legumain, an asparaginyl endopeptidase. J Biol Chem 272(12):8090–8098
Zornig M, Hueber A, Baum W et al (2001) Apoptosis regulators and their role in tumorigenesis. Biochim Biophys Acta 1551(2):F1–F37
Chen JM, Dando PM, Stevens R et al (1998) Cloning, isolation, and characterization of mouse legumain, a lysosomal endopeptidase. Biochem J 335:111–117
Yonezawa S, Takahashi T, Wang XJ et al (1988) Strucures at the proteolytic processing region of cathepsin D. J Biol Chem 263:16504–16511
Wu W, Luo Y, Sun C et al (2006) Targeting cell-impermeable prodrug activation to tumor microenvironment eradicates multiple drug-resistant neoplasms. Cancer Res 66(2):970–980
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank Ms. Henriette Bruchhardt for her excellent technical assistance with the immunohistochemistry. This study is supported by Deutsche Krebshilfe Grant 70-3121-Kr1.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Jessica Gawenda and Frank Traub contributed equally to this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gawenda, J., Traub, F., Lück, H.J. et al. Legumain expression as a prognostic factor in breast cancer patients. Breast Cancer Res Treat 102, 1–6 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-006-9311-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-006-9311-z