Abstract
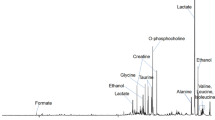
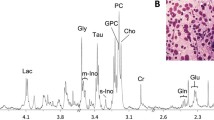
The purpose of the study was to evaluate the use of metabolic phenotype, described by high-resolution magic angle spinning magnetic resonance spectroscopy (HR MAS MRS), as a tool for prediction of histological grade, hormone status, and axillary lymphatic spread in breast cancer patients. Biopsies from breast cancer (n = 91) and adjacent non-involved tissue (n = 48) were excised from patients (n = 77) during surgery. HR MAS MR spectra of intact samples were acquired. Multivariate models relating spectral data to histological grade, lymphatic spread, and hormone status were designed. The multivariate methods applied were variable reduction by principal component analysis (PCA) or partial least-squares regression-uninformative variable elimination (PLS-UVE), and modelling by PLS, probabilistic neural network (PNN), or cascade correlation neural network. In the end, model verification by prediction of blind samples (n = 12) was performed. Validation of PNN training resulted in sensitivity and specificity ranging from 83 to 100% for all predictions. Verification of models by blind sample testing showed that hormone status was well predicted by both PNN and PLS (11 of 12 correct), lymphatic spread was best predicted by PLS (8 of 12), whereas PLS-UVE PNN was the best approach for predicting grade (9 of 12 correct). MR-determined metabolic phenotype may have a future role as a supplement for clinical decision-making-concerning adjuvant treatment and the adaptation to more individualised treatment protocols.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cancer in Norway 2001 (2004) Cancer Registry of Norway. Institute of Population-based Cancer Research, Oslo, Norway
Cancer in Norway 2003 (2005) Cancer Registry of Norway. Institute of Population-based Cancer Research, Oslo, Norway
Botha JL, Bray F, Sankila R, Parkin DM (2003) Breast cancer incidence and mortality trends in 16 European countries. Eur J Cancer 39:1718–1729
Negendank W (1992) Studies of human tumors by MRS: a review. NMR Biomed 5:303–324
Bakken IJ, Axelson D, Kvistad KA, Gribbestad IS (2001) Classification of in vivo 1H MR spectra from breast tissue using artificial neural networks. Anticancer Res 21:1481–1486
Bolan PJ, Meisamy S, Baker E, Lin J, Emory T, Nelson M, Everson L, Yee D, Garwood M (2003) In vivo quantification of choline compounds in the breast with 1H MR spectroscopy. Magn Reson Med 50:1134–1143
Jagannathan NR, Kumar M, Seenu V, Coshic O, Dwivedi SN, Julka P, Srivastava A, Rath G (2001) Evaluation of total choline from in vivo volume localized proton MR spectroscopy and its response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in locally advanced breast cancer. Br J Cancer 84:1016–1022
Kim JK, Park S, Lee H, Lee Y, Sung N, Chung D, Kim O (2003) In vivo 1H-MRS evaluation of malignant and benign breast diseases. Breast 12:179–182
Kvistad KA, Bakken I, Gribbestad I, Ehrnhom B, Lundgren S, Fjøsne H, Haraldseth O (2001) Characterization of neoplastic and normal human breast tissues with in vivo (1)H MR spectroscopy. J Magn Reson Imaging 10:159–164
Stanwell P, Gluch L, Clark D, Tomanek B, Baker L, Giuffre B, Lean C, Malycha P, Mountford C (2005) Specificity of choline metabolites for in vivo diagnosis of breast cancer using 1H MRS at 1.5 T. Eur Radiol 15:1037–1043
Gribbestad IS, Singstad TE, Nilsen G, Fjosne HE, Engan T, Haugen OA, Rinck PA (1998) In vivo H-1 MRS of normal breast and breast tumors using a dedicated double breast coil. J Magn Reson Imaging 8:1191–1197
Sitter B, Sonnewald U, Spraul M, Fjosne HE, Gribbestad IS (2002) High-resolution magic angle spinning MRS of breast cancer tissue. NMR Biomed 15:327–337
Griffin JL, Shockcor JP (2004) Metabolic profiles of cancer cells. Nat Rev Cancer 4:551–561
Bathen TF, Engan T, Krane J, Axelson D (2000) Analysis and classification of proton NMR spectra of lipoprotein fractions from healthy volunteers and patients with cancer or CHD. Anticancer Res 20:2393–2408
Sitter B, Bathen T, Hagen B, Arentz C, Skjeldestad F, Gribbestad I (2004) Cervical cancer tissue characterized by high-resolution magic angle spinning MR spectroscopy. Magma 16:174–181
Sitter B, Autti T, Tyynela J, Sonnewald U, Bathen T, Puranen J, Santavuori P, Haltia M, Paetau A, Polvokoski T, Gribbestad I, Häkkinen A (2004) High-resolution magic angle spinning and 1H magnetic resonance spectroscopy reveal significantly altered neuronal metabolite profiles in CLN1 but not in CLN3. J Neurosci Res 77:762–769
Tessem M, Bathen TF, Cejkova J, Midelfart A (2005) Effect of UV-A and UV-B irradiation on the metabolic profile of aqueous humor in rabbits analyzed by 1H NMR spectroscopy. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 46:776–781
Bloom HJG, Richardson W (1957) Histological grading and prognosis in breast cancer: a study of 1409 cases of which 359 have been followed for 15 years. Br J Cancer 11:359–377
Elston CW, Ellios I (1991) Pathological prognostic factors in breast cancer. I. The value of histological grade in breast cancer: experience from a large study with long-term follow-up. Histopathology 19:403–410
Forshed J, Schuppe-Koistinen I, Jacobsson S (2003) Peak alignment of NMR signals by means of a genetic algorithm. Anal Chim Acta 487:189–199
Lee GC, Woodruff D (2004) Beam search for peak alignment of NMR signals. Anal Chim Acta 513:413–416
Kennard RW, Stone L (1969) Computer aided design of experiments. Technometrics 11:137–148
de Nord OE (1994) The influence of data preprocessing on the robustness and parsimony of multivariate calibration models. Chem Intell Lab Syst 23:65–70
Livingstone DJ, Manallack D (1993) Statistics using neural networks: chance effects. J Med Chem 36:1295–1297
Seasholtz MB, Kowalski B (1993) The parsimony principle applied to multivariate calibration. Anal Chim Acta 277:165–177
Martens H, Naes T (1991) Assessment, validation and choice of calibration method. In: Multivariate calibration. Wiley, Chichester, pp 237–266
Centner V, Massart D, de Nord O, de Jong S, Vandegniste B, Sterna C (1996) Elimination of uninformative variables for multivariate calibration. Anal Chem 68:3851–3858
Specht DF (1990) Probabilistic neural networks. Neural Networks 3:109–118
Lucasius CB, Kateman G (1993) Understanding and using genetic algorithms. Part 1. Concepts, properties and context. Chem Intell Lab Syst 19:1–33
Zweig MH, Campbell G (1993) Receiver-operating characteristic (ROC) plots: a fundamental evaluation tool in clinical medicine. Clin Chem 39:561–577
Fahlman SE, Lebiere C (1990) The cascade-correlation learning architecture. In: Touretzky DS (eds) Advances in neural information processing systems 2. Kaufmann, Los Altos, CA, pp 524–532
Hoehfeld M, Fahlman S (1992) Learning with limited numerical precision using the cascade correlation learning algorithm. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 3:602–611
Gribbestad IS, Sitter B, Lundgren S, Krane J, Axelson D (1999) Metabolite composition in breast tumors examined by proton nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Anticancer Res 19:1737–1746
Mountford CE, Somorjai RL, Malycha P, Gluch L, Lean C, Russell P, Barraclough B, Gillett D, Himmelreich U, Dolenko B, Nikulin AE, Smith ICP (2001) Diagnosis and prognosis of breast cancer by magnetic resonance spectroscopy of fine-needle aspirates analysed using a statistical classification strategy. Br J Surg 88:1234–1240
Noguchi M (2002) Therapeutic relevance of breast cancer micrometastases in sentinel lymph nodes. Br J Surg 89:1505–1515
Lean C, Doran S, Somorjai RL, Malycha P, Clark D, Himmelreich U, Bourne R, Dolenko B, Nikulin AE, Mountford C (2004) Determination of grade and receptor status from the primary breast lesion by magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Technol Cancer Res Treat 3:551–556
Baumann K, Albert H, von Koff M (2002) A systematic evaluation of the benefits and hazards of variable selection in latent variable regression. Part I. Search algorithm, theory and simulations. J Chemom 16:339–350
Yarden Y, Baselga J, Miles D (2004) Molecular approach to breast cancer treatment. Semin Oncol 31:6–13
Acknowledgment
This work was sponsored by the Norwegian Women’s Public Health Association, Trondheim, Norway.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bathen, T.F., Jensen, L.R., Sitter, B. et al. MR-determined metabolic phenotype of breast cancer in prediction of lymphatic spread, grade, and hormone status. Breast Cancer Res Treat 104, 181–189 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-006-9400-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-006-9400-z